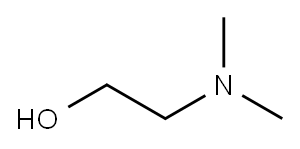
2-Dimethylaminoethanol
- CAS No.
- 108-01-0
- Chemical Name:
- 2-Dimethylaminoethanol
- Synonyms
- DMAE;DIMETHYLETHANOLAMINE;N,N-DIMETHYLETHANOLAMINE;DIMETHYLAMINOETHANOL;2-(N,N-DIMETHYLAMINO)ETHANOL;DEANOL;N,N-DIMETHYLAMINOETHANOL;(CH3)2NCH2CH2OH;DMEOA;amietolm21
- CBNumber:
- CB6256870
- Molecular Formula:
- C4H11NO
- Molecular Weight:
- 89.14
- MOL File:
- 108-01-0.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
- Modify Date:
- 2024/3/14 15:18:27
| Melting point | −70 °C(lit.) |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 134-136 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 0.886 g/mL at 20 °C(lit.) |
| vapor density | 3.03 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 100 mm Hg ( 55 °C) |
| refractive index |
n |
| Flash point | 105 °F |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | alcohol: miscible(lit.) |
| form | Liquid |
| pka | pK1:9.26(+1) (25°C) |
| color | Clear colorless to pale yellow |
| Odor | Amine like |
| PH Range | 10.5 - 11.0 at 100 g/l at 20 °C |
| PH | 10.5-11 (100g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
| explosive limit | 1.4-12.2%(V) |
| Water Solubility | miscible |
| FreezingPoint | -59.0℃ |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| Merck | 14,2843 |
| BRN | 1209235 |
| Stability | Stable. Flammable. Incompatible with oxidizing agents, copper, copper alloys, zinc, acids, galvanised iron. Hygroscopic. |
| InChIKey | UEEJHVSXFDXPFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| LogP | -0.55 at 23℃ |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 108-01-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Ethanol, 2-(dimethylamino)-(108-01-0) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Dimethylaminoethanol (108-01-0) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |    GHS02,GHS05,GHS06 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H226-H302+H312-H314-H331-H335 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P210-P280-P301+P312+P330-P303+P361+P353-P304+P340+P311-P305+P351+P338+P310 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | C | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 10-20/21/22-34 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 25-26-36/37/39-45 | |||||||||
| RIDADR | UN 2051 8/PG 2 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 1 | |||||||||
| RTECS | KK6125000 | |||||||||
| Autoignition Temperature | 245 °C | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 8 | |||||||||
| PackingGroup | II | |||||||||
| HS Code | 29221980 | |||||||||
| Toxicity | LD50 orally in Rabbit: 2130 mg/kg LD50 dermal Rabbit 1220 mg/kg | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
2-Dimethylaminoethanol price More Price(20)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 8.03237 | 2-(Dimethylamino)-ethanol for synthesis | 108-01-0 | 1L | ₹4110.01 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 8.03237 | 2-(Dimethylamino)-ethanol for synthesis | 108-01-0 | 100ML | ₹4480 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 8.03237 | 2-(Dimethylamino)-ethanol for synthesis | 108-01-0 | 25KG | ₹30380.01 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 471453 | 2-Dimethylaminoethanol ≥99.5% | 108-01-0 | 100ML | ₹1948.5 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 471453 | 2-Dimethylaminoethanol ≥99.5% | 108-01-0 | 500ML | ₹4243.4 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
2-Dimethylaminoethanol Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Chemical Properties
colorless or slightly yellow liquid with ammonia odor. It is miscible with water, ethanol, benzene, ether and acetone.
Uses
2-Dimethylaminoethanol (deanol, DMAE) may be employed as a ligand in the copper-catalyzed amination of aryl bromides and iodides.
Production Methods
Synthesis of dimethylaminoethanol can be accomplished from equimolar amounts of ethylene oxide and dimethylamine (HSDB 1988).
Definition
ChEBI: N,N-dimethylethanolamine is a tertiary amine that is ethanolamine having two N-methyl substituents. It has a role as a curing agent and a radical scavenger. It is a tertiary amine and a member of ethanolamines.
Preparation
The synthesis of 2-Dimethylaminoethanol by the ethylene oxide method is obtained by the ammonification of dimethylamine with ethylene oxide, which is distilled, refined and dehydrated.
General Description
A clear colorless liquid with a fishlike odor. Flash point 105°F. Less dense than water. Vapors heavier than air. Toxic oxides of nitrogen produced during combustion. Used to make other chemicals.
Air & Water Reactions
Flammable. Partially soluble in water and less dense than water.
Reactivity Profile
DIMETHYLAMINOETHANOL is an aminoalcohol. Amines are chemical bases. They neutralize acids to form salts plus water. These acid-base reactions are exothermic. The amount of heat that is evolved per mole of amine in a neutralization is largely independent of the strength of the amine as a base. Amines may be incompatible with isocyanates, halogenated organics, peroxides, phenols (acidic), epoxides, anhydrides, and acid halides. Flammable gaseous hydrogen is generated by amines in combination with strong reducing agents, such as hydrides. N,N-Dimethylethanolamine may react vigorously with oxidizing materials.
Health Hazard
Dimethylaminoethanol is classified as a mild skin irritant and a severe eye irritant (HSDB 1988). Doses as high as 1200 mg daily produce no serious side effects and a single dose of 2500 mg taken in a suicide attempt had no adverse effects (Gosselin et al 1976). Inhalation of the vapor or mist can cause irritation to the upper respiratory tract. Asthmatic symptoms have been reported. Extremely irritating; may cause permanent eye injury. Corrosive; will cause severe skin damage with burns and blistering. Ingestion may cause damage to the mucous membranes and gastrointestinal tract. No reports were found in the literature regarding carcinogenic or mutagenic potential.
Industrial uses
Dimethylaminoethanol is used as a chemical intermediate for antihistamines and local anesthetics; as a catalyst for curing epoxy resins and polyurethanes; and as a pH control agent for boiler water treatment. However, dimethylaminoethanol in the salt form, (i.e. dimethylaminoethanol acetamidobenzoate) is primarily utilized therapeutically as an antidepressant (HSDB 1988).
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by ingestion, inhalation, skin contact, intraperitoneal, and subcutaneous routes. A skin and severe eye irritant. Used medically as a central nervous system stimulant. Flammable liquid when exposed to heat or flame; can react vigorously with oxidzing materials. Ignites spontaneously in contact with cellulose nitrate of high surface area. To fight fire, use alcohol foam, foam, CO2, dry chemical. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx
Metabolism
When administered orally, dimethylaminoethanol acetamidobenzoate (the therapeutic
salt formulation) has been shown to cross the blood-brain barrier (HSDB 1988). Two other studies have examined the pharmacokinetics of dimethylaminoethanol
in rats (Dormand et al 1975) and healthy adults (Bismut et al 1986).
It has been postulated that dimethylaminoethanol undergoes endogenous methylation
(LaDu et al 1971). After intravenous treatment of mice with [14C]-labeled
dimethylaminoethanol in the brain, dimethylaminoethanol yielded phosphoryldimethylaminoethanol
and phosphatidyldimethylaminoethanol. Acid-soluble and
lipid cholines derived from dimethylaminoethanol also were found in brain
(Miyazaki et al 1976). While examining the pharmacokinetics of the maleate acid
of [14C]-dimethylaminoethanol in rats, Dormand et al (1975) observed that dimethylaminoethanol
was metabolized in the phospholipid cycle and produced
metabolites such as phosphoryldimethylaminoethanolamine, and glycerophosphatidylcholine.
In kainic-acid lesioned rats, dimethylaminoethanol was converted to
a substance which cross-reacted in the radioenzymatic assay for acetylcholine
(London et al 1978). Ansell and Spanner (1979) demonstrated that [14C]-dimethylaminoethanol
rapidly disappeared from brain; after 0.5, 1, and 7 h, only 30, 27,
and 16% of the administered radioactivity, respectively, remained in the brain
after intracerebral injection. They also showed that brain levels of phosphodimethylaminoethanol
increased to a maximum at 1-2 h and decreased afterwards,
whereas concentrations of phosphatidylethanolamine increased continuously
throughout the 7 h observation period. This study further found that after i.p.
injections of labeled dimethylaminoethanol, the brain content of phosphatidylethanolamine
increased through the 7 h period and the levels were 10-40 fold higher
than those of phosphodimethylaminoethanol.
Purification Methods
Dry the amine with anhydrous K2CO3 or KOH, and fractionally distil it. [Beilstein 4 IV 1424.]
2-Dimethylaminoethanol Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
Preparation Products
1of4
chevron_rightRelated articles
- The performance of N. N-dimethyl ethanolamine
- N. N-dimethyl ethanolamine is an organic compound with chemical formula C4H11NO. It is mainly used as resin raw material and a....
- May 5,2022
108-01-0(2-Dimethylaminoethanol)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




