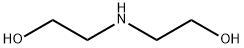
Diethanolamine
- CAS No.
- 111-42-2
- Chemical Name:
- Diethanolamine
- Synonyms
- DEA;Aliphatic amine;Diolamine;Diethanolamin;dela;Iminodiethanol;2,2'-Azanediyldiethanol;2-(2-hydroxyethylamino)ethanol;2,2-IMINODIETHANOL;2,2'-DIHYDROXYDIETHYLAMINE
- CBNumber:
- CB5852839
- Molecular Formula:
- C4H11NO2
- Molecular Weight:
- 105.14
- MOL File:
- 111-42-2.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
- Modify Date:
- 2024/7/25 20:04:51
| Melting point | 28 °C (lit.) |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 217 °C/150 mmHg (lit.) |
| Density | 1.097 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| vapor density | 3.6 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | <0.98 atm ( 100 °C) |
| refractive index |
n |
| Flash point | 280 °F |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | H2O: 1 M at 20 °C, clear, colorless |
| form | Viscous Liquid or Low Melting Solid |
| color | APHA: ≤15 |
| Specific Gravity | 1.09 |
| PH | 11.0-12.0 (25℃, 1M in H2O) |
| pka | 8.88(at 25℃) |
| Odor | Mild ammoniacal; faint, fishy; characteristic. |
| explosive limit | 2.1-10.6%(V) |
| Water Solubility | MISCIBLE |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| λmax |
λ: 260 nm Amax: 0.04 λ: 280 nm Amax: 0.02 |
| Merck | 14,3107 |
| BRN | 605315 |
| Exposure limits | TLV-TWA 3 ppm (~13 mg/m3) (ACGIH). |
| Dielectric constant | 2.8(25℃) |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with carbon dioxide, strong acids, strong oxidizing agents. Deliquescent. |
| InChIKey | ZBCBWPMODOFKDW-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| LogP | -2.46 at 25℃ |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 111-42-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| IARC | 2B (Vol. 77, 101) 2013 |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Diethanolamine(111-42-2) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Diethanolamine (111-42-2) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |    GHS05,GHS07,GHS08 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H302-H315-H318-H361fd-H373 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P202-P280-P301+P312-P302+P352-P305+P351+P338-P308+P313 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | Xn | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 22-38-41-48/22 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 26-36/37/39-46 | |||||||||
| RIDADR | 3267 | |||||||||
| OEB | A | |||||||||
| OEL | TWA: 3 ppm (15 mg/m3) | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 1 | |||||||||
| RTECS | KL2975000 | |||||||||
| F | 3 | |||||||||
| Autoignition Temperature | 689 °F | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| PackingGroup | II | |||||||||
| HS Code | 29221200 | |||||||||
| Toxicity | LD50 orally in rats: 12.76 g/kg (Smyth) | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Diethanolamine price More Price(29)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | D8885 | Diethanolamine reagent grade, ≥98.0% | 111-42-2 | 100G | ₹3106.78 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | D8885 | Diethanolamine reagent grade, ≥98.0% | 111-42-2 | 25G | ₹3182.55 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | D8885 | Diethanolamine reagent grade, ≥98.0% | 111-42-2 | 500G | ₹4167.63 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | PHR1220 | Diethanolamine Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material | 111-42-2 | 3.2ML | ₹8042.98 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | D8885 | Diethanolamine reagent grade, ≥98.0% | 111-42-2 | 1KG | ₹7122.85 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
Diethanolamine Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Diethanolamine is an organic base which has been used as an emulsifying and dispersing agent.It can also be used as a basic buffer, with optimal pH about pH 9, if titrated with HCl or other acid. Other uses include: to "scrub" gases, as a chemical intermediate, as humectant or softening agent.
Chemical Properties
The USP32–NF27 describes diethanolamine as a mixture of ethanolamines consisting largely of diethanolamine. At about room temperature it is a white, deliquescent solid. Above room temperature diethanolamine is a clear, viscous liquid with a mildly ammoniacal odor.

Diethanolamine is used as surface-active agent in metal-cutting fluids and oils, as a corrosion inhibitor, as a dispersant in agricultural chemical formulations, and as an intermediate in the production of other compounds such as fatty acid condensates of diethanolamine which are extensively used in soaps and cosmetics as emulsifiers, thickeners, wetting agents and detergents (Beyer et al., 1983). In the cosmetic formulations, the concentration of diethanolamine may range from 1 to 25% (National Toxicology Program, 1999a).
Uses
Diethanolamine similar to triethanolamine (T775580) is used as a surfactant. It also has the potential to be a corrosion inhibitor by means of chemisorption.
Preparation
Diethanolamine is prepared commercially by the ammonolysis of ethylene oxide. The reaction yields a mixture of monoethanolamine, diethanolamine, and triethanolamine which is separated to obtain the pure products.
Production Methods
Diethanolamine is produced with monoethanolamine and triethanolamine by ammonolysis of ethylene oxide; diethanolamine is then separated by distillation (Mullins 1978). In 1984, 166.2 million pounds of diethanolamine were produced in the United States (USTIC 1985).
Definition
ChEBI: A member of the class of ethanolamines that is ethanolamine having a N-hydroxyethyl substituent.
General Description
Oily colorless liquid or solid white crystals. Slight rotten fish or ammonia odor. Denser than water.
Air & Water Reactions
Water soluble.
Reactivity Profile
2,2'-Iminodiethanol is an aminoalcohol. Amines are chemical bases. They neutralize acids to form salts plus water. These acid-base reactions are exothermic. The amount of heat that is evolved per mole of amine in a neutralization is largely independent of the strength of the amine as a base. Amines may be incompatible with isocyanates, halogenated organics, peroxides, phenols (acidic), epoxides, anhydrides, and acid halides. Flammable gaseous hydrogen is generated by amines in combination with strong reducing agents, such as hydrides. 2,2'-Iminodiethanol is hygroscopic. 2,2'-Iminodiethanol may be sensitive to exposure to air and light. 2,2'-Iminodiethanol can react with oxidizing materials, acids, CO2, copper alloys, aluminum, zinc, galvanized iron and copper.
Health Hazard
The irritant action of diethanolamine on theeyes can be severe. Direct contact of thepure liquid can impair vision. Irritation onthe skin may be mild to moderate. Theacute oral toxicity of this compound waslow in test animals. The toxic symptomsinclude somnolence, excitement, and musclecontraction.
LD50 value, oral (mice): 3300 mg/kg
The vapor pressure of diethanolamine isnegligibly low (<0.01 torr at 20°C (68°F)).At ordinary temperature, this compoundshould not cause any inhalation hazard. Themists, fumes, or vapors at high temperatures,however, can produce eye, skin, and respiratory tract irritation.
In contrast to monoethanolamine, dieth anolamine administered to mice at 1125 mg/kg/day caused no change in maternal mortality, litter size, or percentage survival of thepups (Environmental Health Research andTesting 1987).
Fire Hazard
Special Hazards of Combustion Products: Irritating vapors are generated when heated.
Chemical Reactivity
Reactivity with Water : No reaction; Reactivity with Common Materials: No reaction; Stability During Transport: Stable; Neutralizing Agents for Acids and Caustics: Flush with water; Polymerization: Not pertinent; Inhibitor of Polymerization: Not pertinent.
Pharmaceutical Applications
Diethanolamine is primarily used in pharmaceutical formulations as a buffering agent, such as in the preparation of emulsions with fatty acids. In cosmetics and pharmaceuticals it is used as a pH adjuster and dispersant.
Diethanolamine has also been used to form the soluble salts of active compounds, such as iodinated organic acids that are used as contrast media. As a stabilizing agent, diethanolamine prevents the discoloration of aqueous formulations containing hexamethylenetetramine-1,3-dichloropropene salts.
Diethanolamine is also used in cosmetics.
Contact allergens
Diethanolamine is contained in many products, as a metalworking fuid. Traces may exist in other etha- nolamine-containing fuids.
Safety Profile
Poison by intraperitoneal route. Moderately toxic by ingestion and subcutaneous routes. Mildly toxic by skin contact. A severe eye and mild skin irritant. Experimental reproductive effects. Combustible when exposed to heat or flame; can react with oxidizing materials. To fight fire, use alcohol foam, water, Co2, dry chemical. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes such as NOx. See also AMINES.
Potential Exposure
Diethanolamine is present in machining and grinding fluids and has been detected in workplace air in the metal manufacturing industry. It was present in bulk cutting fluids at levels ranging from 4 to 5% (Kenyon et al., 1993). Diethanolamine has also been reported to be present in wetting fluids used in road paving. A level of 0.05 mg/m3 was detected in a stationary sample at a slurry machine discharging a bitumen emulsion containing 0.2% of the amine. All personal exposures were below the detection limit (0.02 mg/m3) (Levin et al., 1994). In a German study (1992–94), diethanolamine was measured in samples of metalworking fluids in a range of 0–44% (n = 69). The number of samples with diethanolamine present steadily declined from 90% to 60% over the study period (Pfeiffer et al., 1996).
Carcinogenicity
When DEA was administered cutaneously
to pregnant rats and rabbits during organogenesis,
developmental toxicity (skeletal variations)
was observed only in the rat and only at
doses causing significant maternal toxicity.
The 2003 ACGIH threshold limit valuetime-
weighted average (TLV-TWA) is 3ppm
(13mg/m3).
Metabolism
Treatment of Wistar or Sherman rats with diethanolamine caused increases in the
formation of hepatic phospholipids (Artom et al 1949). In addition, dietary
administration led to incorporation of ethanolamine into hepatic phospholipids
(Artom et al 1949), and repeated oral administration of diethanolamine in drinking
water (one to three wk) at a dose of 320 mg/kg/d was found to reduce the level of
incorporation of ethanolamine and choline into hepatic and renal phospholipids in
Sprague-Dawley rats (Barbee and H?rtung 1979b).
Dermal absorption of diethanolamine is suggested to occur in rats since Nnitrosodiethanolamine
was excreted in the urine of male Sprague-Dawley rats
which had been administered diethanolamine by dermal application and given
nitrite in their drinking water (Preussman et al 1981).
storage
Diethanolamine is hygroscopic and light- and oxygen-sensitive; it should be stored in an airtight container, protected from light, in a cool, dry place.
Shipping
UN2491 Ethanol amine or Ethanolamine solutions, Hazard class: 8; Labels: 8-Corrosive material.
Purification Methods
Fractionally distil the amine twice, then fractionally crystallise it from its melt. Its solubility in H2O is 10% at 20o. [Perrin & Dempsey Buffers for pH and Metal Ion Control Chapman & Hall, London 1974, Beilstein 4 H 283, 4 II 729, 4 III 689, 4 IV 1514.]
Incompatibilities
Diethanolamine is a secondary amine that contains two hydroxy groups. It is capable of undergoing reactions typical of secondary amines and alcohols. The amine group usually exhibits the greater activity whenever it is possible for a reaction to take place at either the amine or a hydroxy group.
Diethanolamine will react with acids, acid anhydrides, acid chlorides, and esters to form amide derivatives, and with propylene carbonate or other cyclic carbonates to give the corresponding carbonates. As a secondary amine, diethanolamine reacts with aldehydes and ketones to yield aldimines and ketimines. Diethanolamine also reacts with copper to form complex salts. Discoloration and precipitation will take place in the presence of salts of heavy metals.
Waste Disposal
Controlled incineration; incinerator equipped with a scrubber or thermal unit to reduce nitrogen oxides emissions
Regulatory Status
Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (IV infusions, ophthalmic solutions, and topical preparations). Included in medicines licensed in the UK. Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients.
Diethanolamine Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
Preparation Products
1of8
chevron_right| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SRI HAIMAVATHI ORGANICS | +91-040-40030163 +91-9493978643 | Hyderabad, India | 21 | 58 | Inquiry |
| AMINES AND PLASTICIZERS LTD. | +91-22-24935282 +91-9167680626 | Mumbai, India | 26 | 58 | Inquiry |
| PAARICHEM RESOURCES LLP | +91-8104961021 +91-8104961021 | Maharashtra, India | 82 | 58 | Inquiry |
| JSK Chemicals | +919879767970 | Gujarat, India | 3756 | 58 | Inquiry |
| BASF India Limited | +91-2262785600 +91-2262785600 | Maharashtra, India | 209 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Kawaken Sterling Surfactants Pvt Ltd (Sterling Group) | +91-2240320200 +91-9082327304 | Karnataka, India | 25 | 58 | Inquiry |
| RYZE CHEMIE | +91-9702966440 +91-9702966440 | Maharashtra, India | 335 | 58 | Inquiry |
| S P Chem India | 08048954283 | Ahmedabad, India | 21 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Manav Bio -Chem Impex Pvt Ltd | 91-22-25916910 | Maharashtra, India | 204 | 58 | Inquiry |
| H.R.Dyechem | 91-22-65285662 | Maharashtra, India | 56 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Supplier | Advantage |
|---|---|
| SRI HAIMAVATHI ORGANICS | 58 |
| AMINES AND PLASTICIZERS LTD. | 58 |
| PAARICHEM RESOURCES LLP | 58 |
| JSK Chemicals | 58 |
| BASF India Limited | 58 |
| Kawaken Sterling Surfactants Pvt Ltd (Sterling Group) | 58 |
| RYZE CHEMIE | 58 |
| S P Chem India | 58 |
| Manav Bio -Chem Impex Pvt Ltd | 58 |
| H.R.Dyechem | 58 |
Related articles
- Health Hazard of Diethanolamine
- Diethanolamine contains a secondary amine and two alcohol groups. It is a viscous liquid with a freezing point of 28 oC. It is....
- Jan 7,2022
111-42-2(Diethanolamine)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_rightDIETHANOLAMINE Amine diethanol Diethanolamine [Matrix for FABMS and liquid SIMS] Iminodiethyl alcohol 2,2'-Iminodiethanol, Diethanolamine, 2,2'-Dihydroxydiethylamine Diethanolamine 80% Aqueous Diethanolamine 85% Aqueous Diethanolamine 88% Aqueous Diethanolamine (3 mL) DiethanolaMine, 99% 1KG 2,2'-Dihydroxydiethylamine 2,2'-Iminodiethanol DIETHANOLAMINE FOR SYNTHESIS 2-(2-hydroxyethylamino)-ethanol





