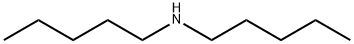
Diamylamine
- CAS No.
- 2050-92-2
- Chemical Name:
- Diamylamine
- Synonyms
- DIAMYLAMINE;Dipentylamin;Dipentanamine;DIPENTYLAMINE;amine,dipentyl;DI-N-AMYLAMINE;Di-2-amylamine;Twopentyl aMine;N,N-Diamylamine;Diamylamine >
- CBNumber:
- CB8306575
- Molecular Formula:
- C10H23N
- Molecular Weight:
- 157.3
- MOL File:
- 2050-92-2.mol
- Modify Date:
- 2023/11/28 16:31:44
| Melting point | -44°C |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 202-203 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 0.767 g/mL at 25 °C |
| vapor density | 5.42 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 0.3 mm Hg ( 20 °C) |
| refractive index |
n |
| Flash point | 157 °F |
| form | clear liquid |
| pka | 11.25±0.19(Predicted) |
| color | Colorless to Light yellow to Light orange |
| Specific Gravity | 0.775 (25/4℃) |
| Water Solubility | Slightly soluble (0.1-1 g/100 mL) |
| BRN | 906746 |
| Dielectric constant | 2.5 |
| Stability | Stable, but air-sensitive. Flammable. Incompatible with oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 2050-92-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | 1-Pentanamine, N-pentyl-(2050-92-2) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Diamylamine (2050-92-2) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |     GHS09,GHS02,GHS05,GHS06 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H226-H301+H311-H301+H311+H331-H314-H400 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P261-P273-P280-P301+P310-P305+P351+P338-P310-P210-P233-P240-P241+P242+P243-P260-P264-P270-P301+P330+P331+P310-P303+P361+P353+P310+P363-P304+P340+P310-P305+P351+P338+P310-P370+P378-P403+P235-P405-P501 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | T,N,C | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 23/24/25-34-37/38-24-22-50/53 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 26-27-36/37/39-45-61-60 | |||||||||
| RIDADR | UN 2841 3/PG 3 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 3 | |||||||||
| RTECS | RZ9100000 | |||||||||
| HS Code | 2921.19.6190 | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 3.2 | |||||||||
| PackingGroup | III | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Diamylamine price More Price(3)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TCI Chemicals (India) | D0286 | Diamylamine (mixture) min. 97.0 %(total of isomer) | 2050-92-2 | 25ML | ₹2200 | 2022-05-26 | Buy |
| TCI Chemicals (India) | D0286 | Diamylamine (mixture) min. 97.0 %(total of isomer) | 2050-92-2 | 500ML | ₹5100 | 2022-05-26 | Buy |
| TCI Chemicals (India) | D0129 | Diamylamine min. 98.0 % | 2050-92-2 | 25ML | ₹5300 | 2022-05-26 | Buy |
Diamylamine Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Chemical Properties
Diamylamine is a relatively strong base and forms salts with acids. Its vapors can form explosive mixtures with air.
Uses
Di-n-amylamine is manufactured from amyl chloride and ammonia. It is used in organic syntheses and as a solvent, rubber accelerator, flotation reagent, and corrosion inhibitor.
Production Methods
Diamylamine is manufactured by the same processes as n-amylamine by reaction of amyl chloride with ammonia and then separated from the amylenes and amyl alcohol by steam distillation (Hawley 1977). It also can be synthesized by amination of alkyl halides at high temperature and pressure (Schweizer et al 1978). The commercial product may be a mixture of amyl isomers (HSDB 1989).
General Description
A clear colorless liquid with an ammonia-like odor. Very slightly soluble in water. Density 6.40 lb / gal (less than water) Vapors heavier than air. Flash point 152°F. Difficult to ignite. Moderately toxic. Contact with liquid may cause a chemical burn. Vapors may irritate respiratory tract. Used in the manufacture of rubber, resins, and dyes.
Air & Water Reactions
Flammable. Sensitive to air and heat. Slightly soluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Diamylamine neutralizes acids to form salts plus water. May be incompatible with isocyanates, halogenated organics, peroxides, phenols (acidic), epoxides, anhydrides, and acid halides. Flammable gaseous hydrogen is generated in combination with strong reducing agents, such as hydrides.
Health Hazard
Diamylamine is a strong eye, skin, and respiratory irritant owing to its basicity (HSDB 1989). Vapor exposure results in irritation of the nose and throat with distressed breathing and coughing. Prolonged exposure may lead to pulmonary edema. Direct skin contact can cause secondary burns.
Fire Hazard
HIGHLY FLAMMABLE: Will be easily ignited by heat, sparks or flames. Vapors may form explosive mixtures with air. Vapors may travel to source of ignition and flash back. Most vapors are heavier than air. They will spread along ground and collect in low or confined areas (sewers, basements, tanks). Vapor explosion and poison hazard indoors, outdoors or in sewers. Runoff to sewer may create fire or explosion hazard. Containers may explode when heated. Many liquids are lighter than water.
Industrial uses
Diamylamine is less widely used than n-amylamine with only 20 tons being manufactured in the U.S. in 1976. Its most widespread use is as a corrosion inhibitor and rubber accelerator (Hawley 1977). It is also useful as a solvent for oils, resins, and some cellulose esters. Introduction of the amyl group imparts oil solubility to otherwise oil-insoluble substances. Diamylamine also is used in flotation reagents, dyestuffs and as a cockroach repellent (HSDB 1989).
Safety Profile
Poison by inhalation, ingestion, and skin contact. A severe skin irritant. See also AMINES. Flammable liquid when exposed to heat or flame; can react with oxidizing materials. To fight fire, use alcohol foam, foam, CO2, dry chemical. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx.
Metabolism
In contrast to n-amylamine, little information is available on diamylamine metabolism,
particularly with respect to its suitability as a substrate for the amine
oxidases. Generally, the rate of oxidation of secondary amines by monoamine
oxidase is slower than that of primary amines (Beard and Noe 1981). In agreement,
Yamada et al (1965) demonstrated that crystalline amine oxidase prepared
from Aspergillus niger oxidized diamylamine very slowly with respect to n-amylamine.
As with other secondary aliphatic amines, the propensity of diamylamine to
form nitrosamines is of interest. It has been shown that treatment of diamylamine
with nitrous acid in dilute aqueous solution gave optimum nitrosamine formation
between pH 1 and 3, corresponding to stomach conditions (Sander et al 1968).
When rats were fed a diet supplemented with sodium nitrite and secondary amines
of low basicity, synthesis of nitrosamines in the stomach was observed. Malignant
tumors arising through formation of nitrosamines in the stomach was demonstrated
only when nitrite was present in the stomach concomitantly with secondary
amines which readily formed carcinogenic nitrosamines.
Diamylamine Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
Preparation Products
| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLEARSYNTH LABS LTD. | +91-22-45045900 | Hyderabad, India | 6351 | 58 | Inquiry |
| TCI Chemicals (India) Pvt. Ltd. | 1800 425 7889 | New Delhi, India | 6778 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Career Henan Chemica Co | +86-0371-86658258 +8613203830695 | China | 30253 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Hefei TNJ Chemical Industry Co.,Ltd. | 0551-65418671 | China | 34571 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Hebei Guanlang Biotechnology Co., Ltd. | +86-19930503259 +86-19930503259 | China | 18435 | 58 | Inquiry |
| PT CHEM GROUP LIMITED | +86-85511178 +86-85511178 | China | 35451 | 58 | Inquiry |
| SUZHOU SENFEIDA CHEMICAL CO.,LTD | +86-0512-83500002 +8615195660023 | China | 23053 | 58 | Inquiry |
| LEAPCHEM CO., LTD. | +86-852-30606658 | China | 43348 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Aladdin Scientific | +1-+1(833)-552-7181 | United States | 52927 | 58 | Inquiry |
| ABCR GmbH & CO. KG | 49 721 95061 0 | Germany | 6846 | 75 | Inquiry |
2050-92-2(Diamylamine)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




