Boron nitride

- CAS No.
- 10043-11-5
- Chemical Name:
- Boron nitride
- Synonyms
- Boron nitrite;Hexagonal boron nitride;BNNT;Nitriloboron;boron mononi;Cubic Boron nitride;BORON NITRIDE NANOTUBE;Boron nitride,hexagonal;Boron nitride nanopowder, APS 5-20nm;BN C
- CBNumber:
- CB9266197
- Molecular Formula:
- BN
- Molecular Weight:
- 24.82
- MOL File:
- 10043-11-5.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
- Modify Date:
- 2024/7/3 16:00:59
| Melting point | 2700℃ |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | sublimes sl below 3000℃ [MER06] |
| Density | 0.9-1.1 g/mL at 25 °C |
| storage temp. | no restrictions. |
| solubility | insoluble in H2O, acid solutions |
| form | Powder |
| Specific Gravity | 3.48 |
| color | White |
| PH | 5-8 (100g/l, H2O, 20℃)(slurry) |
| Resistivity | 10*19 (ρ/μΩ.cm) |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water (slightly soluble) at 20°C, and water (soluble) at 95°C. |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| Crystal Structure | Hexagonal |
| Merck | 14,1346 |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with oxidizing agents, water. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 10043-11-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Boron nitride(10043-11-5) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Boron nitride (BN) (10043-11-5) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |    GHS02,GHS05,GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H226-H315-H318-H335 |
| Precautionary statements | P210-P233-P240-P280-P303+P361+P353-P305+P351+P338 |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
| Risk Statements | 36/37 |
| Safety Statements | 26-36 |
| RIDADR | UN1950 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | ED7800000 |
| TSCA | Yes |
| HS Code | 2850 00 20 |
| HazardClass | 2.1 |
| Toxicity | LD50 orally in Rabbit: > 2000 mg/kg LD50 dermal Rat > 2000 mg/kg |
Boron nitride price More Price(66)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | SAB1305023 | ANTI-BNC1 (N-TERM) antibody produced in rabbit IgG fraction of antiserum, buffered aqueous solution | 10043-11-5 | 400μL | ₹47796.6 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 921521 | Monolayer hexagonal Boron Nitride (hBN) on copper foil size 6?in. (6?in.) × 150?mm (150?mm) | 10043-11-5 | 1EACH | ₹68392.35 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 920967 | Monolayer hexagonal Boron Nitride (hBN) on copper foil size 3?in. (3?in.) × 76?mm (76?mm) | 10043-11-5 | 1EACH | ₹37400.38 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 920940 | Monolayer hexagonal Boron Nitride (hBN) on Si/SiO2 wafer diam. 150?mm (6?in.) | 10043-11-5 | 1EACH | ₹85485.03 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 920932 | Monolayer hexagonal Boron Nitride (hBN) on Si/SiO2 wafer diam. 100?mm (4?in.) | 10043-11-5 | 1EACH | ₹88689.23 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
Boron nitride Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Boron nitride is a material in which the extra electron of nitrogen (with respect to carbon) enables it to form structures that are isoelectronic with carbon allotropes.
Boron nitride is an inorganic compound with a flat, hexagonal crystal similar to graphite, but with the carbon atoms replaced by boron and nitrogen atoms. The alternate boron and nitrogen atoms are linked to form interlocking hexagonal rings with three boron atoms and three nitrogen atoms, and the layers are held together by van der Waals forces. There is no boron-nitrogen bonding between the layers.The bond length is 1.466Å and the interlayer spacing is 3.331 Å. A spherical form (with a hexagonal crystal structure) is also available.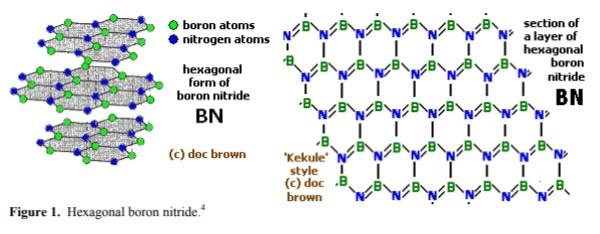
Boron nitride can also be in cubic form in which alternately linked boron and nitrogen atoms form a tetrahedral bond network, similar to carbon atoms in diamond.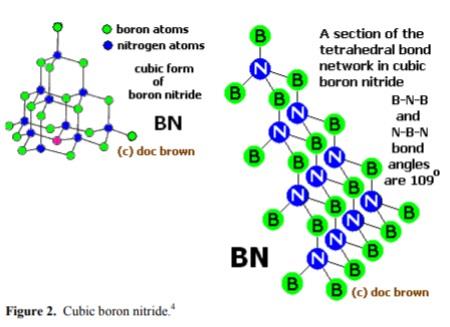
Chemical Properties
white powder(s), 1μm or less 99.5% pure; hexagonal, most common form: a=0.2504 nm, c=0.6661nm; fcc: a=0.3615nm; hardness: hexagonal like graphite,?cub approaches that of diamond; band gap ~7.5 eV at 300K; dielectric 7.1; used in furnace insulation and in crucibles for melting aluminum, boron, iron, and silicon, also as sputtering target for dielectrics, diffusion masks, passivation layers [KIR81] [HAW93] [MER06] [CER91]
Physical properties
Insulator (Eg=7.5 eV). Crucibles for melting molten metals such as Na, B, Fe, Ni, Al, Si, Cu, Mg, Zn, In, Bi, Rb, Cd, Ge, and Sn. Corroded by molten metals U, Pt, V, Ce, Be, Mo, Mn, Cr, V, and Al. Attacked by molten salts PbO2, Sb2O3, AsO3, Bi2O3, KOH, and K2CO3. Used in furnace insulation-diffusion masks and passivation layers.
Uses
Boron nitride is a material in which the extra electron of nitrogen (with respect to carbon) enables it to form structures that are isoelectronic with carbon allotropes. Also used in manufacture of alloys; in semiconductors, nuclear reactors, lubricants.
Hexagonal boron nitride can be used as an electrical insulator; as thermocouple protection sheaths, crucibles and linings for reaction vessels; and as a coating for refractory molds used in glass forming and in superplastic forming of titanium. It can also be incorporated in ceramics, alloys, resins, plastics, and rubber to give them self-lubricating properties. Hexagonal boron nitride is used the formulation of coatings and paints for high temperature applications. It is also used as a substrate for semi-conductors, lens coatings, and transparent windows.
https://www.cir-safety.org
Production Methods
In tonnage production, acetaldehyde may be manufactured by:
1. The direct oxidation of ethylene, requiring a catalytic solution of copper chloride plus small quantities of palladium chloride Cl2Pd.
2. The oxidation of ethyl alcohol C2H6O with sodium dichromate Cr2Na2O7, and
3. The dry distillation of calcium acetate C4H6CaO4 with calcium formate C2H2CaO4.
Definition
boron nitride: A solid, BN, insolublein cold water and slowly decomposedby hot water; r.d. 2.25 (hexagonal);sublimes above 3000°C. Boronnitride is manufactured by heatingboron oxide to 800°C on an acid-solublecarrier, such as calcium phosphate,in the presence of nitrogen orammonia. It is isoelectronic with carbonand, like carbon, it has a veryhard cubic form (borazon) and asofter hexagonal form; unlikegraphite this is a nonconductor. It isused in the electrical industrieswhere its high thermal conductivityand high resistance are of especialvalue.
Application
Boron nitride finds applications in shaping tools in industries due to its ability to withstand temperatures greater than 2,000°C. Cutting tools and abrasive components, designed specifically for use with low-carbon ferrous metals, have been developed using cubic boron nitride. These tools perform similarly to polycrystalline diamond (PCD) tools but can be utilized on iron and low-carbon alloys without the risk of a reaction occurring.
Preparation
Boron nitride is prepared by heating boric oxide with ammonia:
B2O3 + 2NH3 → 2BN + 3H2O
Alternatively, the compound can be prepared by heating boric oxide or boric acid with ammonium chloride or an alkali metal cyanide. Purified product can be obtained by high temperature reaction of boron halide with ammonia:
BCl3 + NH3 → BN + 3HCl
Boron nitride can also be made from the elements by heating boron and nitrogen at red heat.
General Description
Boron nitride in cubic form, known as Borazon, is a manufactured abrasive that was discovered by General Electric Co. Laboratories in 1957. Unlike manufactured diamond, Borazon does not have a natural counterpart. It is produced under temperatures and pressures similar to those required for diamond manufacture. Additionally, cubic boron nitride exhibits greater thermal stability compared to diamond. It remains stable at temperatures exceeding 1,371°C, while diamond reverts to graphite at temperatures above 816°C. Borazon has a Knoop hardness (K100) of 7800, which is higher than ordinary abrasives but lower than diamond.
Industrial uses
Boron nitride (BN) has many potential commercial applications. It is a white, fluffy powder with a greasy feel. It is used for heat-resistant parts by molding and pressing the powder without a binder to a specific gravity of 2.1 to 2.25.
BN may be prepared in a variety of ways, for example, by the reaction of boron oxide with ammonia, alkali cyanides, and ammonium chloride, or of boron halides and ammonia. The usually high chemical and thermal stability, combined with the high electrical resistance of BN, suggests numerous uses for this compound in the field of high-temperature technology. BN can be hot-pressed into molds and worked into desired shapes.
BN powders can be used as mold-release agents, high-temperature lubricants, and additives in oils, rubbers, and epoxies to improve thermal conductance of dielectric compounds. Powders also are used in metal- and ceramicmatrix composites (MMC and CMC) to improve thermal shock and to modify wetting characteristics.
The platy habit of the particles and the fact that boron nitride is not wet by glass favors use of the powder as a mold wash, e.g., in the fabrication of high-tension insulators. It is also useful as thermal insulation in induction heating. A cubic form of boron nitride (Borazon) similar to diamond in hardness and structure has been synthesized by the high-temperature, high-pressure process for making synthetic diamonds. Any uses it may find as a substitute for diamonds will depend on its greatly superior oxidation resistance.
Industrial uses
The major industrial applications of hexagonal boron nitride rely on its high thermal conductivity, excellent dielectric properties, self-lubrication, chemical inertness, nontoxicity, and ease of machining. These are, for instance, mold wash for releasing molds, high-temperature lubricants, insulating filler material in composite materials, as an additive in silicone oils and synthetic resins, as filler for tubular heaters, and in neutron absorbers. On the other hand, the industrial applications of cubic boron nitride rely on its high hardness and are mainly as abrasives.
Forms and nomenclature
Boron nitride exists as three different poly-morphs:
Alpha-boron nitride (α-BN), a soft and ductile polymorph (ρ = 2280 kg.m–3 and m.p. = 2700°C) with a hexagonal crystal lattice similar to that of graphite, also called hexagonal boron nitride
(HBN) or white graphite;
Beta-boron nitride (β-BN), the hardest manmade material and densest polymorph (ρ = 3480 kg.m–3, m.p. = 3027°C), with a cubic crystal lattice similar to that of
diamond, also called cubic boron nitride (CBN) or borazon;
Pyrolitic boron nitride
(PBN). From a chemical point of view, boron nitride oxidizes readily in air at temperatures
above 1100°C, forming a thing protective layer of boric acid (H3BO3) on its surface that prevents further oxidation as long as it coats the material. Boron nitride is stable in reducing
atmospheres up to 1500°C.
Boron nitride Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
1of3
chevron_rightPreparation Products
| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PERFECT CHEMICAL | +91-9820465461 +91-9820465461 | Mumbai, India | 391 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Kiran Lights Laboratories | 91-9987701501 | Maharashtra, India | 262 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Innovative | 07942565925 | Mumbai, India | 617 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Gautam Zen International (P) Ltd | 91-33-40335200 | Kolkata, India | 68 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Brisben Chemicals | 08048963750 | Mumbai, India | 509 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Scientific OEM | +91-22- 2343 7546 / 2341 3094 | New Delhi, India | 1996 | 38 | Inquiry |
| ALPHA CHEMIKA | +91-22-22061123 +91-22-66382501 | Mumbai, India | 1681 | 43 | Inquiry |
| CHEMSWORTH | +91-261-2397244 | New Delhi, India | 6707 | 30 | Inquiry |
| Otto Chemie Pvt. Ltd. | +91 9820041841 | Mumbai, India | 5873 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Sisco Research Laboratories Pvt. Ltd. | +91-22-4268 5800 | Mumbai, India | 4317 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Supplier | Advantage |
|---|---|
| PERFECT CHEMICAL | 58 |
| Kiran Lights Laboratories | 58 |
| Innovative | 58 |
| Gautam Zen International (P) Ltd | 58 |
| Brisben Chemicals | 58 |
| Scientific OEM | 38 |
| ALPHA CHEMIKA | 43 |
| CHEMSWORTH | 30 |
| Otto Chemie Pvt. Ltd. | 58 |
| Sisco Research Laboratories Pvt. Ltd. | 58 |
Related articles
- Boron nitride-based nanocomposite hydrogels: properties and medical applications
- Boron nitride-based nanocomposite hydrogels offer biodegradable, biocompatible properties for wound healing, cancer treatment,....
- Jan 12,2024
- Boron nitride-based materials: synthesis and applications in water purification
- Boron nitride materials are promising for water purification and membrane separation due to their unique properties.
- Aug 7,2023
- What is Boron nitride?
- Boron nitride is a material in which the extra electron of nitrogen (with respect to carbon) enables it to form structures tha....
- Jul 14,2020
10043-11-5(Boron nitride)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




