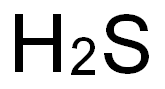황화 수소
|
|
황화 수소 속성
- 녹는점
- −85 °C(lit.)
- 끓는 점
- −60 °C(lit.)
- 밀도
- dgas 1.19 (air = 1.00)
- 증기 밀도
- 1.19 (15 °C, vs air)
- 증기압
- 252 psi ( 21 °C)
- 인화점
- -17℃
- 저장 조건
- 2-8°C
- 용해도
- soluble in H2O
- 물리적 상태
- 무색 가스
- 산도 계수 (pKa)
- 7(at 25℃)
- 색상
- colorless gas; flammable
- 수소이온지수(pH)
- pKa1= 6.90, pKa2 = 13.48(25℃)
- Flame Color
- Blue
- 냄새
- Strong rotten egg odor detectable at 0.001 to 0.1 ppm (mean = 0.0094 ppm); olfactory fatigue occurs quickly at high concentrations
- Odor Threshold
- 0.00041ppm
- 폭발한계
- 6%
- 수용성
- 1g은 H2O에 용해됩니다: 187mL(10°C), 242mL(20°C), 314(30°C) [MER06]
- Merck
- 13,4823
- BRN
- 3535004
- Dielectric constant
- 9.3(-84℃)
- 안정성
- 안정적인. 가연성이 높습니다. 공기와 폭발성 혼합물을 형성할 수 있음. 폭 넓은 폭발 한계에 유의하십시오. 강한 산화제, 많은 금속과 호환되지 않습니다. 금속 산화물, 구리, 불소, 나트륨, 에탄알과 격렬하게 반응할 수 있습니다.
- CAS 데이터베이스
- 7783-06-4(CAS DataBase Reference)
안전
- 위험 및 안전 성명
- 위험 및 사전주의 사항 (GHS)
| 위험품 표기 | F+,T+,N,F | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 위험 카페고리 넘버 | 12-26-50-40-36/37-19-11 | ||
| 안전지침서 | 9-16-36-38-45-61-28-26 | ||
| 유엔번호(UN No.) | UN 1053 2.3 | ||
| OEL | Ceiling: 10 ppm (15 mg/m3) [10-minute] | ||
| WGK 독일 | 2 | ||
| RTECS 번호 | MX1225000 | ||
| 자연 발화 온도 | 260 °C | ||
| DOT ClassificationII | 2.3, Hazard Zone B (Gas poisonous by inhalation) | ||
| 위험 등급 | 2.3 | ||
| 유해 물질 데이터 | 7783-06-4(Hazardous Substances Data) | ||
| 독성 | LC50 in mice, rats (ppm): 634, 712 (1 hr inhalation) (Vernot); LC50 in rats (ppm): 444 (4 hr inhalation) (Tansy) | ||
| IDLA | 100 ppm | ||
| 기존화학 물질 | KE-20209 | ||
| 유해화학물질 필터링 | 2019-1-941 | ||
| 사고대비 물질 필터링 | 50 | ||
| 함량 및 규제정보 | 물질구분: 유독물질; 혼합물(제품)함량정보: 황화수소[Hydrogen sulfide; 7783-06-4] 및 이를 1% 이상 함유한 혼합물 |
황화 수소 C화학적 특성, 용도, 생산
개요
Hydrogen Sulfide is a colorless, very poisonous, flammable gas with the characteristic foul odor of rotten eggs. It often results from the bacterial breakdown of organic matter in the absence of oxygen, such as in swamps and sewers where anaerobic digestion can take place. It also occurs in volcanic gases, “natural gas”, and some well waters. Hydrogen sulfide has numerous names, some of which are archaic.Small amounts of hydrogen sulfide occur in crude oil, but natural gas can contain up to 90%. About 10% of the total global emission of H2S is due to human activity.
화학적 성질
Hydrogen sulfide is a colourless gas with strong odour of rotten eggs (odour threshold ca 0.2 ppt).물리적 성질
H2S is soluble in carbon disulfide, methanol, acetone and alkanolamines. A solution of hydrogen sulfide in water is initially clear but over time turns cloudy. This is due to the slow reaction of hydrogen sulfide with the oxygen dissolved in water, yielding elemental sulfur, which precipitates out.출처
Reported found in heated French beans, beef broth, vapors of canned beef, canned beef, beef extract, heated beef fat, raw beef, beer, bread, heated Brussels sprouts, cabbage, cooked celery, cheddar cheese, cooked and raw chicken, chives, heated coconut, codfish, ground and roast coffee, heated corn, heated egg, grapefruit juice, cooked herring, citrus juices, strawberry, cabbage, onion, potato, rutabaga, tomato, blue cheese, buttermilk, raw and boiled eggs, coffee, potato chips, rice, soybeans, okra, sweet corn, sake, squid, shrimps, cooked, fatty fish and other natural sources역사
Hydrogen sulfide is a colorless, flammable, toxic gas with the characteristic odor of rotten eggs.It is produced naturally from the anaerobic bacterial decomposition of organic wastes, occurs in volcanic gases and hot springs, is a product of animal digestion, and is generated in industrial processes. Hydrogen is a natural component of natural gas and petroleum; it is only a small fraction of oil (hundreds of ppm), but may form an appreciable component of natural gas. Natural gas typically contains up to 5% hydrogen sulfide. Natural gas is considered sour if the hydrogen sulfide content exceeds 5.7 mg of H2S per cubic meter of natural gas. The process for removing hydrogen sulfide from sour gas is referred to as sweetening the gas. Because hydrogen sulfide is associated with anaerobic respiration in sewers and swamps, it is referred to as sewer gas, swamp gas, or stink damp.용도
Hydrogen sulfide is used as an analyticalreagent and in the manufacture of heavywater. It occurs in natural gas and sewer gas.It is formed by the reaction of a metal sulfidewith dilute mineral acid, and in petroleumrefining.생산 방법
Hydrogen sulfide is produced during anaerobic respiration (fermentation). Anaerobic respirationenables organisms, primarily bacteria and other microbes, to meet their energy needsusing sulfate, elemental sulfur, and sulfur compounds as electron acceptors instead of oxygen.제조 방법
By far the largest industrial route toH2S occurs in petroleum refineries. The “hydrodesulfurization” process liberates sulfur from petroleum by the action of hydrogen. The resulting H2S is converted to elemental sulfur by partial combustion via the Claus process that is a major source of elemental sulfur (In the Claus process, hydrogen sulfide is catalytically reacted with oxygen from the air to produce sulfur and sulfur dioxide). Other anthropogenic sources of hydrogen sulfide include coke ovens, paper-mills (using the sulfate method), and tanneries, where Na2S is used for processing cowhide to form leather. H2S arises from virtually anywhere where elemental sulfur comes in contact with organic material, especially at high temperatures.정의
ChEBI: A sulfur hydride consisting of s single sulfur atom bonded to two hydrogen atoms. A highly poisonous, flammable gas with a characteristic odour of rotten eggs, it is often produced by bacterial decomposition of organic matter in the absence of oxygen.화학 반응
Fluorine, chlorine, bromine, and iodine react with H2S to form the corresponding halogen acid. Metal sulfides are formed when H2S is passed into solutions of the heavy metals, such as Ag, Pb, Cu, and Mn. This reaction is responsible for the tarnishing of Ag and is the basis for the separation of these metals in classical wet qualitative analytical methods. Hydrogen sulfide reacts with many organic compounds.공기와 물의 반응
Highly flammable; a flame can very easily flash back to the source of leak. Soluble in water to a maximum of 0.4% by mass at room temperature .반응 프로필
HYDROGEN SULFIDE reacts as an acid and as a reducing agent. Explodes on contact with oxygen difluoride, bromine pentafluoride, chlorine trifluoride, dichlorine oxide, silver fulminate. May ignite and explode when exposed to powdered copper in oxygen [Mertz, V. et al., Ber., 1880, 13, p. 722]. May react similarly with other powdered metals. Ignites on contact with metal oxides and peroxides (barium peroxide, chromium trioxide, copper oxide, lead dioxide, manganese dioxide, nickel oxide, silver oxide, silver dioxide, thallium trioxide, sodium peroxide, mercury oxide, calcium oxide) [Mellor, 1947, vol. 10, p. 129, 141]. Ignites with silver bromate, lead(II) hypochlorite, copper chromate, nitric acid, lead(IV) oxide and rust. May ignite if passed through rusty iron pipes [Mee, A. J., School Sci. Rev., 1940, 22(85), p. 95]. Reacts exothermically with bases. The heat of the reaction with soda lime, sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, barium hydroxide may lead to ignition or explosion of the unreacted portion in the presence of air / oxygen [Mellor, 1947, vol. 10, p. 140].위험도
Highly flammable, dangerous fire risk, explosive limits in air 4.3–46%. Toxic by inhalation, strong irritant to eyes and mucous membranes.건강위험
The acute toxicity of hydrogen sulfide by inhalation is moderate. A 5-min exposure to 800 ppm has resulted in death. Inhalation of 1000 to 2000 ppm may cause coma after a single breath. Exposure to lower concentrations may cause headache, dizziness, and upset stomach. Low concentrations of H2S (20 to 150 ppm) can cause eye irritation, which may be delayed in onset. Although the odor of hydrogen sulfide is detectable at very low concentrations, it rapidly causes olfactory fatigue at higher levels, and therefore is not considered to have adequate warning properties. Hydrogen sulfide has not been shown to be carcinogenic or to have reproductive or developmental effects in humans화재위험
Compound is heavier than air and may travel a considerable distance to source of ignition and flash back. HYDROGEN SULFIDE forms explosive mixtures with air over a wide range. Also reacts explosively with bromine pentafluoride, chlorine trifluoride, nitrogen triiodide, nitrogen trichloride, oxygen difluoride, and phenyl diazonium chloride. When heated to decomposition, HYDROGEN SULFIDE emits highly toxic fumes of oxides of sulfur. Incompatible with many materials including strong oxidizers, metals, strong nitric acid, bromine pentafluoride, chlorine trifluoride, nitrogen triiodide, nitrogen trichloride, oxygen difluoride and phenyl diazonium chloride. Avoid physical damage to containers; sources of ignition; storage near nitric acid, strong oxidizing materials, and corrosive liquids or gases.인화성 및 폭발성
Hydrogen sulfide is flammable in air in the range of 4.3 to 45.5% (NFPA rating = 4). Combustion products (sulfur oxides) are also toxic by inhalation. In the event of a hydrogen sulfide fire, stop the flow of gas if possible without risk of harmful exposure and let the fire burn itself out.농업용
Hydrogen sulphide (H2S) is a colorless, poisonous, flammable gas with an odor of rotting eggs. It is found in cesspools and mines and is a by-product of decomposed substances containing sulphur. It is one of the gaseous end-products of the reduction of sulphate in highly degraded paddy fields. Hydrogen sulphide is also produced in the laboratory for use as an analytical reagent.Materials Uses
Dry hydrogen sulfide is satisfactorily handled under pressure at normal ambient temperatures in carbon steel or black iron piping. Carbon steels in wet applications are known to be subject to sulfide stress cracking and low- temperature brittle fracture under some conditions of temperature, stress, and pressure. While hydrogen sulfide itself is relatively noncorrosive to steel in many uses, factors such as impurities, pH, erosive conditions, and high thermal or mechanical stresses in the metal can cause severe corrosion problems. High-strength steels are subject to crack formation when exposed to hydrogen sulfide.환경귀착
Hydrogen sulfide is a colorless, flammable compressed liquid gas with a characteristic odor of rotten eggs. The solubility of hydrogen sulfide in water is 3980 mg l-1 at 20 ℃ and it is soluble in certain polar organic solvents, notably methanol, acetone, propylene carbonate, sulfolane, tributyl phosphate, various glycols and glycol ethers, gasoline, kerosene, crude oil, and carbon disulfide. The calculated vapor pressure at 21.9 ℃ is 1929 Pa. Boiling point and melting point of the substance are -60.33 ℃ and-85.49 ℃, respectively. Based on the estimated Henry’s law constant of 468 atm mol-1 for hydrogen sulfide, volatilization from water and soil is high.저장
cylinders of hydrogen sulfide should be stored and used in a continuously ventilated gas cabinet or fume hood. Local fire codes should be reviewed for limitations on quantity and storage requirements.Purification Methods
Wash it, then pass the gas through a train of tubes containing saturated Ba(OH)2 (2x), water (2x), and dilute HCl [Goates et al. J Am Chem Soc 73 707 1951]. It is available in gas cylinders. HIGHLY POISONOUS.비 호환성
Hydrogen sulfide is incompatible with strong oxidizers. It will attack many metals, forming sulfides. Liquid hydrogen sulfide will attack some forms of plastics, rubber, and coatings. H2S reacts violently with a variety of metal oxides, including the oxides of chromium, mercury, silver, lead, nickel, and iron.폐기물 처리
To respond to a release, use appropriate protective equipment and clothing. Positive pressure air-supplied respiratory protection is required. Close cylinder valve and ventilate area. Remove cylinder to a fume hood or remote area if it cannot be shut off. Disposal Excess hydrogen sulfide should be returned to the manufacturer, according to your institution's waste disposal guidelines. For more information on disposal procedures, see Chapter 7 of this volume.황화 수소 준비 용품 및 원자재
원자재
준비 용품
염화니켈 헥사히드레이트
디메피퍼레이트
CALCIUM IODIDE HYDRATE
2-클로로페노티아진
p-멘타-6,8-다이엔-2-온, (R)-(-)
3-메르캅토프로피온산
Konjac glucomannan
시스테아민
아미디노티오요소
산화 니켈
실리콘 카바이드
Vidarabine
카보닐 황화합물
설프로포스
티오카보히드라지드
디티존
N-오메가-아세틸히스타민
초산납
p-Mentha-8-thiol-3-one
1,7-헵탄디올
이황화몰리브덴
4(5)-시아노메틸리미다졸
4-이미다졸아세트산 염화수소산염
디페닐티오카르바지드
메트리뷰진
프로필메르캅탄
카르본(에스)
L-시스테인
디에틸 티오포스포릴 염화물
타르타르산 칼륨
티오황산 암모늄
4-이미다졸 아크릴산
싸이오사이안산 칼륨
4-이미다졸메탄올염화수소산염
디알킬디티오인산
삼차뷰틸 머캡탄
5-아미노-1,2,3-티아디아졸
염산 L-시스테인 모노수화물
NIZA티딘
Difurfuryldisulfide
황화 수소 공급 업체
글로벌( 72)공급 업체
| 공급자 | 전화 | 이메일 | 국가 | 제품 수 | 이점 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hubei Jusheng Technology Co.,Ltd. | 18871490254 |
linda@hubeijusheng.com | CHINA | 28172 | 58 |
| Hubei xin bonus chemical co. LTD | 86-13657291602 |
linda@hubeijusheng.com | CHINA | 22963 | 58 |
| Hefei TNJ Chemical Industry Co.,Ltd. | +86-0551-65418671 +8618949823763 |
sales@tnjchem.com | China | 34563 | 58 |
| SUZHOU SENFEIDA CHEMICAL CO.,LTD | +86-0512-83500002 +8618501500038 |
3899766280@qq.com | China | 26362 | 58 |
| XIAMEN AMITY INDUSTRY AND TRADE CO., LTD. | +8618950047208 |
ellena@amitychem.com | China | 43416 | 58 |
| Mainchem Co., Ltd. | +86-0592-6210733 |
sale@mainchem.com | China | 32343 | 55 |
| Guangdong wengjiang Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. | 0751-2886750 13927877953 |
3005811397@qq.com | China | 13317 | 58 |
| Shanghai T&W Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | +86 21 61551611 |
China | 9891 | 58 | |
| Shanghai Meishui Chemical Technology Co., Ltd | 021-60549325 18616193163 |
China | 4526 | 56 | |
| Chizhou Kailong Import and Export Trade Co., Ltd. | |
xg01_gj@163.com | China | 9484 | 50 |
황화 수소 관련 검색:
클로르아민 T S-에틸 트리플루오로 티오 아세테이트 트리플루오로메탄술폰산무수물 4,4'-디클로로디페닐 술폰 클로로카보닐슬페닐클로라이드 유황 수소 펜타플루오로페닐 설파이드
Triethylsilyl trifluoromethanesulfonate
Tosylmethyl isocyanide
4-Fluorophenyl sulfone
TrimethylSilyl Trifluoromethanesulfonate
Ethyl trifluoromethanesulfonate
Diethylaminosulfur trifluoride
N-Phenyl-bis(trifluoromethanesulfonimide)
Trifluoromethanesulfonic acid tert-butyldimethylsilyl ester
2-Bromothioanisole
Methyl trifluoromethanesulfonate