RETAPAMULIN
|
- ₹0
- Product name: RETAPAMULIN
- CAS: 224452-66-8
- MF: C30H47NO4S
- MW: 517.76
- EINECS:639-491-7
- MDL Number:MFCD11045316
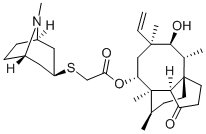
- Synonyms:RETAPAMULIN;RetapaMulin (SB-275833);(3aS,4R,5S,6S,8R,9R,9aR,10R)-2-(exo-8-Methyl-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]octan-3-ylsulfanyl)acetic acid 5-hydroxy-4,6,9,10-tetraMethyl-1-oxo-6-vinylperhydro-3a,9-propanocyclopentacycloocten-8-yl ester;RetapaMulin API;tetapaMulin;(1S,2R,3S,4S,6R,7R,8R,14R)-4-ethenyl-3-hydroxy-2,4,7,14-tetraMethyl-9-oxotricyclo[5.4.3.0^{1,8}]tetradecan-6-yl 2-{[(1R,3S,5S)-8-Methyl-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]octan-3-yl]sulfanyl}acetate;Rebapamulin;SB-275833
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|
Properties
Boiling point :594.9±50.0 °C(Predicted)
Density :1.16±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted)
storage temp. :2-8°C
solubility :insoluble in H2O; ≥114.8 mg/mL in EtOH; ≥16.15 mg/mL in DMSO
form :solid
pka :14.65±0.70(Predicted)
color :White to off-white
InChIKey :STZYTFJPGGDRJD-IFPFAXJDNA-N
CAS DataBase Reference :224452-66-8(CAS DataBase Reference)
Density :1.16±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted)
storage temp. :2-8°C
solubility :insoluble in H2O; ≥114.8 mg/mL in EtOH; ≥16.15 mg/mL in DMSO
form :solid
pka :14.65±0.70(Predicted)
color :White to off-white
InChIKey :STZYTFJPGGDRJD-IFPFAXJDNA-N
CAS DataBase Reference :224452-66-8(CAS DataBase Reference)
Safety Information
| Symbol(GHS): |

|
||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word: | Warning | ||||||||||||||
| Hazard statements: |
|
||||||||||||||
| Precautionary statements: |
|
Description
Antibacterial retapamulin is a derivative of the natural product pleuromutilin and was developed by Glaxo and approved in the US in 2007 for the treatment of skin infections. It has a unique mechanism of action, inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis by inhibiting the larger subunit of the ribosome, and thus has no cross resistance to other antibacterial agents. Pleuromutilin is a tricyclic diterpenoid that was first isolated in 1951 from the edible mushroom Pleurotus mutilus. The first semisynthetic analogs tiamulin and valnemulin, developed for veterinary use, have been shown to interact uniquely with bacterial ribosomes by high affinity binding to a site on the 50S subunit. Binding to this site interferes with ribosomal peptidyl transferase activity, blocks P-site interactions, and prevents the evolution of active 50S ribosomal subunits. Retapamulin, the first pleuromutilin approved for human use, behaves similarly to selectively inhibit bacterial protein synthesis. This novel mechanism of action has been implicated in the lack of in vitro target-specific cross-resistance with other classes of antibiotics.More related product prices
Posaconazole Telithromycin Tafluprost Pirfenidone Amoxicillin Rosuvastatin calcium ISOOCTYL THIOGLYCOLATE RETAPAMULINRelated product price
- Posaconazole
₹3600-53854.38 - Pirfenidone
₹8100-47402.68 - Amoxicillin
₹2016-18099






