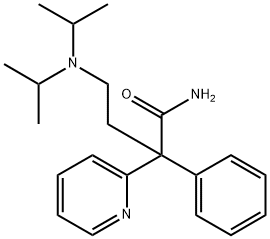
DISOPYRAMIDE
- CAS No.
- 3737-09-5
- Chemical Name:
- DISOPYRAMIDE
- Synonyms
- h3292;sc7031;H 3292;H. 3292;Lispine;SC 7031;Isorythm;Ritmodan;Ritmilen;searle703
- CBNumber:
- CB1285468
- Molecular Formula:
- C21H29N3O
- Molecular Weight:
- 339.48
- MOL File:
- 3737-09-5.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
- Modify Date:
- 2024/7/14 20:44:35
| Melting point | 94.5-950C |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 475.43°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.0779 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.6300 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Inert atmosphere,Room Temperature |
| solubility | Soluble in DMSO (25 mg/ml) and Ethanol (>35 mg/mL) |
| form | solid |
| pka | 10.2; also reported as 10.45(at 25℃) |
| color | White |
| Water Solubility | 6.17mg/L(22.5 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,3360 |
| Stability | Stable for 1 year from date of purchase as supplied. Solutions in DMSO or ethanol may be stored at -20°C for up to 1 month. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 3737-09-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |   GHS07,GHS08 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Warning | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H302-H361 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P201-P301+P312+P330-P308+P313 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | Xn,Xi,T,F | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 22-36/37/38-39/23/24/25-23/24/25-11 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 36-26-45-36/37-16-7 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 3 | |||||||||
| RTECS | UR8432000 | |||||||||
| HS Code | 2933.39.4100 | |||||||||
| Toxicity | LD50 i.p. in mice: 517 mmol/kg (Ruenitz, Mokler) | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
DISOPYRAMIDE price More Price(2)
DISOPYRAMIDE Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Structurally, disopyramide does not belong to any of the known classes of antiarrhythmics; however, being a drug of the class IA sodium channel blockers, it exhibits membranestabilizing action and increases the effective refractory period and duration of an action potential in the atrium and ventricles. It causes a decrease in contractability and excitability of the myocardium, slowing of conductivity, and suppression of sinoatride automatism.
Chemical Properties
Crystalline Solid
Uses
Disopyramide is used for preventing and restoring atrial and ventricular extrasystole and tachycardia in order to prevent atrial flutter and arrhythmia.
Definition
ChEBI: A monocarboxylic acid amide that is butanamide substituted by a diisopropylamino group at position 4, a phenyl group at position 2 and a pyridin-2-yl group at position 2. It is used as a anti-arrhythmia drug.
Pharmacokinetics
Disopyramide phosphate is used orally for the treatment of certain ventricular and atrial arrhythmias. Despite its structural dissimilarity to procainamide, its cardiac effects are very similar. Disopyramide is rapidly and completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Peak plasma level is usually reached within 1 to 3 hours, and a plasma half-life of 5 to 7 hours is common. Approximately half of an oral dose is excreted unchanged in the urine. The remaining drug undergoes hepatic metabolism, principally to the corresponding N-dealkylated form. This metabolite retains approximately half the antiarrhythmic activity of disopyramide and also is subject to renal excretion.
Clinical Use
Disopyramide (Norpace) can suppress atrial and ventricular
arrhythmias and is longer acting than other
drugs in its class.
The indications for use of disopyramide are similar to
those for quinidine, except that it is not approved for
use in the prophylaxis of atrial flutter or atrial fibrillation
after DC conversion.The indications are as follows:
unifocal premature (ectopic) ventricular contractions,
premature (ectopic) ventricular contractions of multifocal
origin, paired premature ventricular contractions
(couplets), and episodes of ventricular tachycardia.
Persistent ventricular tachycardia is usually treated with
DC conversion.
Side effects
The major toxic reactions to disopyramide administration
include hypotension, congestive heart failure, and
conduction disturbances. These effects are the result of
disopyramide’s ability to depress myocardial contractility
and myocardial conduction. Although disopyramide
initially may produce ventricular tachyarrhythmias or
ventricular fibrillation in some patients, the incidence of
disopyramide-induced syncope in long-term therapy is
not known. Most other toxic reactions (e.g., dry mouth,
blurred vision, constipation) can be attributed to the anticholinergic
properties of the drug.
CNS stimulation and hallucinations are rare.The incidence
of severe adverse effects in long-term therapy
may be lower than those observed with quinidine or
procainamide.
Drug interactions
In the presence of phenytoin, the metabolism of disopyramide
is increased (reducing its effective concentration)
and the accumulation of its metabolites is also
increased, thereby increasing the probability of anticholinergic
adverse effects. Rifampin also stimulates the
hepatic metabolism of disopyramide, reducing its
plasma concentration.
Unlike quinidine, disopyramide does not increase
the plasma concentration of digoxin in patients receiving
a maintenance dose of the cardiac glycoside.
Hypoglycemia has been reported with the use of
disopyramide, particularly in conjunction with moderate
or excessive alcohol intake.
Precautions
Disopyramide should not be administered in cardiogenic
shock, preexisting second- or third-degree A-V
block, or known hypersensitivity to the drug. Neither
should it be given to patients who are poorly compensated
or those with uncompensated heart failure or severe
hypotension. Because of its ability to slow cardiac
conduction, disopyramide is not indicated for the treatment
of digitalis-induced ventricular arrhythmias.
Patients with congenital prolongation of the QT interval
should not receive quinidine, procainamide, or disopyramide
because further prolongation of the QT interval
may increase the incidence of ventricular fibrillation.
Because of its anticholinergic properties, disopyramide
should not be used in patients with glaucoma.
Urinary retention and benign prostatic hypertrophy are
also relative contraindications to disopyramide therapy.
Patients with myasthenia gravis may have a myasthenic
crisis after disopyramide administration as a result of
the drug’s local anesthetic action at the neuromuscular
junction.The elderly patient may exhibit increased sensitivity
to the anticholinergic actions of disopyramide.
Caution is advised when disopyramide is used in
conjunction with other cardiac depressant drugs, such as verapamil, which may adversely affect atrioventricular
conduction.
DISOPYRAMIDE Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
1of2
chevron_rightPreparation Products
DISOPYRAMIDE Suppliers
| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TCI Chemicals (India) Pvt. Ltd. | 1800 425 7889 | New Delhi, India | 6778 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Pharmaffiliates Analytics and Synthetics P. Ltd | +91-172-5066494 | Haryana, India | 6773 | 58 | Inquiry |
| A.J Chemicals | 91-9810153283 | New Delhi, India | 6124 | 58 | Inquiry |
| CLEARSYNTH LABS LTD. | +91-22-45045900 | Hyderabad, India | 6351 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Shaanxi Dideu Medichem Co. Ltd | +86-029-81138252 +86-18789408387 | China | 3958 | 58 | Inquiry |
| TargetMol Chemicals Inc. | +1-781-999-5354 +1-00000000000 | United States | 19892 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Career Henan Chemica Co | +86-0371-86658258 +8613203830695 | China | 30250 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Shaanxi Dideu Medichem Co. Ltd | +86-029-89586680 +86-18192503167 | China | 7726 | 58 | Inquiry |
| sgtlifesciences pvt ltd | +8617013299288 | China | 12382 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Aladdin Scientific | +1-+1(833)-552-7181 | United States | 57511 | 58 | Inquiry |
3737-09-5(DISOPYRAMIDE)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




