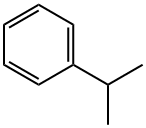
Cumene
- CAS No.
- 98-82-8
- Chemical Name:
- Cumene
- Synonyms
- ISOPROPYLBENZENE;2-PHENYLPROPANE;Cumeen;Isopropylbenzen;Isopropilbenzene;(1-METHYLETHYL)BENZENE;CUMOL;CUMENE;NSC 8776;Cumene,99%
- CBNumber:
- CB2191522
- Molecular Formula:
- C9H12
- Molecular Weight:
- 120.19
- MOL File:
- 98-82-8.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
- Modify Date:
- 2024/3/14 15:18:26
| Melting point | −96 °C(lit.) |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 152-154 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 0.864 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor density | 4.1 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 8 mm Hg ( 20 °C) |
| refractive index |
n |
| Flash point | 115 °F |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | 0.05g/l |
| form | Liquid |
| pka | >14 (Schwarzenbach et al., 1993) |
| color | Clear colorless |
| Odor | Strong, slightly irritant; fragrant; aromatic. |
| Odor Threshold | 0.0084ppm |
| explosive limit | 0.8-6.0%(V) |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in alcohol, ether, acetone, benzene, carbon tetrachloride. Insoluble in water. |
| Merck | 14,2617 |
| BRN | 1236613 |
| Henry's Law Constant | 13.0, 15.3, and 23.9 at 28.0, 35.0, and 46.1 °C, respectively (headspace method, Hansen et al., 1993) |
| Exposure limits |
Flammable liquid; flash point (closed cup)
36°C (97°F) (NFPA 1986), 39°C (102°F)
(Merck 1996), 35.5°C (96°F) (Meyer 1989);
vapor pressure 8 torr at 20°C (68°F); vapor
density 4.1 (air=1); the vapor is heavier than
air and may travel a considerable distance
to a nearby ignition source and flash back;
autoignition temperature 425°C (797°F); fire- extinguishing agent: dry chemical, foam, or
CO2; use a water spray to keep fire- exposed
containers cool and to disperse the vapors。 Cumene forms explosive mixtures in the air within the range 0.9–6.5% by volume in air. Cumene may form peroxide on prolonged exposure to air. It should be tested for peroxides before it is subjected to distillation or evaporation。. |
| Dielectric constant | 2.4(20℃) |
| Stability | Stable, but may form peroxides in storage if in contact with the air. Test for the presence of peroxides before heating or distilling. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| InChIKey | RWGFKTVRMDUZSP-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| LogP | 3.55 at 20℃ |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 98-82-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Benzene, (1-methylethyl)-(98-82-8) |
| IARC | 2B (Vol. 101) 2013 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Cumene (98-82-8) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |     GHS02,GHS07,GHS08,GHS09 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H226-H304-H335-H411 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P210-P233-P240-P273-P301+P310-P331 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | Xn,N,T,F | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 10-37-51/53-65-39/23/24/25-23/24/25-11 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 24-37-61-62-45-36/37-16 | |||||||||
| OEB | A | |||||||||
| OEL | TWA: 50 ppm (245 mg/m3) [skin] | |||||||||
| RIDADR | UN 1918 3/PG 3 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 1 | |||||||||
| RTECS | GR8575000 | |||||||||
| F | 10 | |||||||||
| Autoignition Temperature | 797 °F | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 3 | |||||||||
| PackingGroup | III | |||||||||
| HS Code | 29027000 | |||||||||
| Toxicity | LD50 orally in rats: 2.91 g/kg (Smyth) | |||||||||
| IDLA | 900 ppm [10% LEL] | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Cumene price More Price(12)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | PHR1210 | Cumene Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material | 98-82-8 | 3X1.2ML | ₹8189.18 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | C87657 | Cumene 98% | 98-82-8 | 1L | ₹2794.8 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 8.02681 | Cumene for synthesis | 98-82-8 | 100ML | ₹5040 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 8.02681 | Cumene for synthesis | 98-82-8 | 1L | ₹5200 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 40669 | Cumene solution certified reference material, 5000?μg/mL in methanol | 98-82-8 | 1ML | ₹5639.2 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
Cumene Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Cumene is a common name for isopropylbenzene, an organic
compound. Cumene is a volatile colorless liquid at room
temperature with a characteristic sharp, penetrating, aromatic
odor. It is insoluble in water but is soluble in alcohol and many
other organic solvents. Cumene is structurally a member of the
alkyl aromatic family of hydrocarbons, which also includes
toluene (methylbenzene) and ethylbenzene.Cumene can be
found in crude oil, refined fuels, and is a part of processed highoctane
gasoline.
Cumene is manufactured by reacting benzene with
propylene at elevated temperature and pressure in the presence
of a catalyst. It is considered an environmental pollutant
because it is a natural component of petroleum and is present
in tobacco smoke. Cumene vapor can be absorbed by the respiratory tract. Sufficiently high levels of exposure to cumene
causes central nervous system (CNS) depression leading to
death, internal bleeding of numerous organs, as well as irritation
of the eyes and respiratory system, skin, and mucous
membranes. Cumene is a high production volume chemical.
Chemical Properties
cumene is oxidized to its hydroperoxide, which is used to produce propene oxide. The alcohol produced is subsequently converted back to cumene over a copper-chromium oxide catalyst to be reused in the process. The advantage of this process is that cumene is easier to hydroperoxidate (more stable).
Physical properties
Colorless liquid with an aromatic odor. Experimentally determined detection and recognition odor threshold concentrations were 40 μg/m3 (8 ppbv) and 230 μg/m3 (47 ppbv), respectively (Hellman and Small, 1974). The taste threshold concentration in water is 60 ppb (Young et al., 1996).
Uses
Around 98% of cumene is used in the production of phenol and its coproduct, acetone, using cumene hydroperoxide as chemical intermediate. However, the demand for cumene is largely dependent on the performance of phenol’s derivatives, which have resulted in healthy growth rates in demand for cumene. It is also used as a starting material in the production of acetophenone, α-methylstyrene, diisopropylbenzene, and dicumylperoxide. Cumene is used as a thinner for paints, lacquers, and enamels. It is also used in the manufacture of acetophenone, methylstyrene, and other chemicals commonly found in home cleaning products. Minor uses of cumene include as a constituent of some petroleum-based solvents, such as naphtha; in gasoline blending diesel fuel and highoctane aviation fuel; and as a raw material for peroxides and oxidation catalysts such as polymerization catalysts for acrylic and polyester-type resins. It is also a good solvent for fats and resins and has been suggested as a replacement for benzene in many of its industrial applications.
General Description
Pharmaceutical secondary standards for application in quality control, provide pharma laboratories and manufacturers with a convenient and cost-effective alternative to the preparation of in-house working standards.
Air & Water Reactions
Flammable. Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Mixing CUMENE in equal molar portions with any of the following substances in a closed container caused the temperature and pressure to increase: chlorosulfonic acid, nitric acid, oleum, NFPA 1991.
Hazard
Toxic by ingestion, inhalation, and skin absorption; a narcotic. Moderate fire risk. Eye, skin, and upper respiratory tract irritant, and central nervous system impairment. Possible carcinogen.
Health Hazard
Narcotic action with long-lasting effects; depressant to central nervous system. Acute (short-term) inhalation exposure to cumene may cause headaches, dizziness, drowsiness, slight incoordination, and unconsciousness in humans. Cumene has a potent central nervous system (CNS) depressant action characterized by a slow induction period and long duration of narcotic effects in animals. Cumene is a skin and eye irritant. No information is available on the chronic (long-term), reproductive, developmental, or carcinogenic effects of cumene in humans. Animal studies have reported increased liver, kidney, and adrenal weights from inhalation exposure to cumene. EPA has classified cumene as a Group D, not classifiable as to human carcinogenicity.
Fire Hazard
HIGHLY FLAMMABLE: Will be easily ignited by heat, sparks or flames. Vapors may form explosive mixtures with air. Vapors may travel to source of ignition and flash back. Most vapors are heavier than air. They will spread along ground and collect in low or confined areas (sewers, basements, tanks). Vapor explosion hazard indoors, outdoors or in sewers. Runoff to sewer may create fire or explosion hazard. Containers may explode when heated. Many liquids are lighter than water.
Chemical Reactivity
Reactivity with Water: No reaction; Reactivity with Common Materials: No reaction; Stability During Transport: Stable; Neutralizing Agents for Acids and Caustics: Not pertinent; Polymerization: Not pertinent; Inhibitor of Polymerization: Not pertinent.
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by ingestion. Mdly toxic by inhalation and skincontact. Human systemic effects by inhalation: an antipsychotic, unspecified changes in the sense of smell and respiratory system. An eye and skin irritant. Potential narcotic action. Central nervous system depressant. There is no apparent difference between the toxicity of natural cumene and that derived from petroleum. See also BENZENE and TOLUENE. Flammable liquid when exposed to heat or flame; can react with oxidizing materials. Violent reaction with HNO3, oleum, chlorosulfonic acid. To fight fKe, use foam, CO2, dry chemical.
Potential Exposure
Cumene is used primarily in the manufacture acetone and phenol which are widely used as solvents for paints, laquers, and varnishes and to make plastics. Cumene is used in gasoline blending and as a high-octane gasoline component. It is also found as a component in tobacco smoke.
Carcinogenicity
Cumene was not a developmental toxicant
in either rats or rabbits after exposure to levels
(1200ppm and 2300ppm, respectively) associated
with maternal toxicity.9 Most genotoxic
tests with cumene have been negative.
The LD50 for penetration of rabbit skin
was 12.3 ml/kg after 14 days.4 Contact of the
liquid with the skin causes erythema and irritation.
11 Eye contamination may produce conjunctival
irritation.
It generally is agreed that cumene has no
damaging effect on the hematopoietic system,
despite its chemical similarity to benzene.5
Furthermore, cumene is not anticipated to be
a significant carcinogenic hazard because it is
metabolically similar to toluene, a substance
that showed no carcinogenic activity in 2-year
inhalation studies.
Shipping
UN1918 Cumene, Hazard Class: 3; Labels: 3-Flammable liquid
Incompatibilities
Vapor may form explosive mixture with air. Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, 942 Cumene fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides. Air contact forms cumene hydroperoxide. Attacks rubber. May accumulate static electrical charges, and may cause ignition of its vapors.
Waste Disposal
Dissolve or mix the material with a combustible solvent and burn in a chemical incinerator equipped with an afterburner and scrubber. All federal, state, and local environmental regulations must be observed.
Cumene Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
1of2
chevron_rightPreparation Products
1of3
chevron_right| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SI Group India Limited | +91-2356660401 +91-2356660401 | Maharashtra, India | 32 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Aroma Organics Limited | 91-22-62267700 | Maharashtra, India | 26 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Tejendra Enterprise | 08048372765Ext 159 | Ahmedabad, India | 25 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Oxford laboratories | +91 250 239 0032 | Maharashtra, India | 652 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Supreme (India) International | +91-22- 2828801 | Mumbai, India | 9 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Deepak Nitrite Limited | 08069023791Ext 560 | Hyderabad, India | 84 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Kunjal Synergies Private Limited | 91-33-22881217 | Kolkata, India | 14 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Prasol Chemicals Pvt. Ltd. | 91-22-27782555 | Maharashtra, India | 33 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Innovative Synthetic Molecules | +91 40-24111684 | Hyderabad, India | 527 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Intertrade Exim | 91-22-22696296 | Maharashtra, India | 34 | 58 | Inquiry |
Related articles
- Cumene: Physicochemical properties, Oxidation Mechanism and Uses
- Cumene, also known as isopropylbenzene or 1-methylbenzene, is a flammable, volatile, colourless liquid with an odour similar t....
- Aug 9,2024
- Cumene-Mechanism of toxicity
- Cumene is a common name for isopropylbenzene, an organic compound. Cumene is a volatile colorless liquid at room temperature w....
- Jan 12,2022
- Uses and Benefits of CUMENE
- Cumene, also known as isopropylbenzene, 2-phenylpropane, or (1-methylethyl) benzene, is a colorless, volatile liquid with a ga....
- Nov 27,2019
98-82-8(Cumene)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




