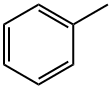
Toluene
- CAS No.
- 108-88-3
- Chemical Name:
- Toluene
- Synonyms
- TOL;METHYLBENZENE;TOLUNE;TOLUOL;Toluen;JB;PHENYLMETHANE;Methane, phenyl-;tolueno;caswellno859
- CBNumber:
- CB4233905
- Molecular Formula:
- C7H8
- Molecular Weight:
- 92.14
- MOL File:
- 108-88-3.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
- Modify Date:
- 2023/11/28 16:31:44
| Melting point | -93 °C (lit.) |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 110-111 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 0.865 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| vapor density | 3.2 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 22 mm Hg ( 20 °C) |
| refractive index |
n |
| Flash point | 40 °F |
| storage temp. | 0-6°C |
| pka | 40(at 25℃) |
| form | Liquid |
| color | Colorless |
| Specific Gravity | 0.865~0.870(20/20℃)(Ph.Eur.) |
| Odor | Aromatic, benzene-like odor detectable at 0.16 to 37 ppm (mean = 1.6 ppm) |
| Relative polarity | 0.099 |
| explosive limit | 7% |
| Odor Threshold | 0.33ppm |
| Water Solubility | 0.5 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,9529 |
| BRN | 635760 |
| Henry's Law Constant | 1.05 at 40 °C, 1.68 at 50 °C, 2.62 at 60 °C, 3.15 at 70 °C, 3.97 at 80 °C (headspace-GC, Vane et al., 2001) |
| Exposure limits | TLV-TWA 100 ppm (~375 mg/m3) (ACGIH, NIOSH, and MSHA), 200 ppm (~750 mg/ m3) OSHA; ceiling 300 ppm, peak 500 ppm/ 15 min (OSHA); STEL 150 ppm (ACGIH). |
| Dielectric constant | 2.4(20℃) |
| LogP | 2.73 at 20℃ |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 108-88-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| IARC | 3 (Vol. 47, 71) 1999 |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Toluene(108-88-3) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Toluene (108-88-3) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |    GHS02,GHS07,GHS08 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H225-H304-H315-H336-H361d-H373-H412 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P201-P210-P273-P301+P310+P331-P302+P352-P308+P313 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | F,Xn,T | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 11-38-48/20-63-65-67-39/23/24/25-23/24/25 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 36/37-46-62-45-16-7 | |||||||||
| OEB | A | |||||||||
| OEL | TWA: 100 ppm (375 mg/m3), STEL: 150 ppm (560 mg/m3) | |||||||||
| RIDADR | UN 1294 3/PG 2 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 2 | |||||||||
| RTECS | XS5250000 | |||||||||
| F | 3-10 | |||||||||
| Autoignition Temperature | 480 °C | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 3 | |||||||||
| PackingGroup | II | |||||||||
| HS Code | 29023000 | |||||||||
| Toxicity | LD50 orally in rats: 7.53 g/kg (Smyth) | |||||||||
| IDLA | 500 ppm | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Toluene price More Price(120)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | V800429 | Toluene LR, ≥99% | 108-88-3 | 6X500ML | ₹3298.28 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | V800430 | Toluene suitable for HPLC, ≥99.8% | 108-88-3 | 6X1L | ₹8672.1 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | V800429 | Toluene LR, ≥99% | 108-88-3 | 4X2.5L | ₹7870.65 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | V800428 | Toluene AR, ≥99.5% | 108-88-3 | 6X500ML | ₹3575.7 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | V800428 | Toluene AR, ≥99.5% | 108-88-3 | 4X2.5L | ₹8055.6 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
Toluene Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Toluene is a clear, colourless liquid with a sweet, benzene-like odour. Toluene occurs naturally
in crude oil and in the toluene tree. It is also produced in the process of making
gasoline and other fuels from crude oil and making coke from coal. Toluene is used in
making paints, paint thinners, fingernail polish, lacquers, adhesives, and rubber and in
some printing and leather tanning processes. Toluene is also used in the production of
polymers used to make nylon, plastic soda bottles, and polyurethanes and for pharmaceuticals,
dyes, cosmetic nail products, and the synthesis of organic chemicals.
Toluene has been reported as the most commonly abused hydrocarbon solvent, primarily
through ‘glue sniffing’. The common possibilities of exposure to high levels of toluene
include indoor air from the use of household products such as paints, paint thinners, adhesives,
synthetic fragrances, and many other sources.
Chemical Properties
Toluene is a clear, colorless, flammable liquid with a sweet/pungent odor. It is extensively used as a solvent in different industries, i.e., rubber chemical manufacturing, drugs and pharmaceuticals, thinner for inks, paints dyes, and perfume manufacturing. It is a natural constituent of crude oil and is produced from petroleum refi ning and coke-oven operations. Toluene occurs naturally as a component of crude oil and occurs in petroleum refi ning and coke oven operations. Occupational workers associated with several kinds of activities, such as manufacturing of dyes, printing inks, painting automobile mechanics, gasoline manufacturers, shippers, and retailers, adhesives and coatings manufacturers and applicators, audio-equipment product workers, chemical industry workers, coke-oven workers, fabric manufacturers (fabric coating), sites of hazardous wastes, linoleum manufacturers, in pharmaceutical manufacturing, printing works, shoe manufacturing industry, become exposed to toluene.
Physical properties
Colorless, clear, flammable liquid with a pleasant, sweet or paint-like odor similar to benzene. At 40 °C, the lowest concentration at which an odor was detected were 960 μg/L. Similarly at 25 °C, the lowest concentration at which a taste was detected was 960 μg/L (Young et al., 1996). Experimentally determined detection and recognition odor threshold concentrations were 600 μg/m3 (160 ppbv) and 7.0 mg/m3 (1.9 ppmv), respectively (Hellman and Small, 1974). Leonardos et al. (1969) reported higher odor threshold concentrations for toluene derived from coke (4.68 ppmv) and petroleum (2.14 ppmv). The average least detectable odor threshold concentrations in water at 60 °C and in air at 40 °C were 24 and 140 μg/L, respectively (Alexander et al., 1982). An odor threshold concentration of 330 ppbv was determined by a triangular odor bag method (Nagata and Takeuchi, 1990). Cometto-Mu?iz and Cain (1994) reported an average nasal pungency threshold concentration of 29,574 ppmv.
History
Toluene is a clear, flammable, aromatic hydrocarbon liquid with a smell similar to benzene.
It is also called methylbenzene, indicating that a methyl group has been added to one of
benzene’s carbon atoms. Toluene was first isolated by Pierre-Joseph Pelletier (1788–1842) and
Philippe Walter (1810–1847) in 1837. The name toluene comes from the South American
tree Toluifera balsamum. Henri-Etienne Sainte-Claire Deville (1818–1881) isolated toluene
from the tree’s gum, Tolu balsam, in 1841.
The main source of toluene is from the catalytic reforming of naphthas during petroleum
processing. During this process cycloalkanes are dehydrated, forming aromatics such as
toluene and xylene along with hydrogen. Toluene can also be obtained from the pyrolysis of
gasoline. It is a by-product when styrene is produced and can also be produced from coal tar,
which was its main source in the first half of the 20th century.
Uses
Toluene is derived from coal tar as well aspetroleum. It occurs in gasoline and manypetroleum solvents. Toluene is used to producetrinitrotoluene (TNT), toluene diisocyanate,and benzene; as an ingredient fordyes, drugs, and detergents; and as an industrialsolvent for rubbers, paints, coatings, andoils.
Preparation
Toluene is the starting material for the production of tolylene diisocyanate (TDI),the process may be varied to give products of differing isomer contents. The nitration of toluene (with a nitrating mixture containing 20% nitric acid, 60% sulphuric acid and 20% water at 30-45°C) gives a mixture of 2-nitrotoluene (about 60%) and 4- nitrotoluene (40%). If this mixture is nitrated further (with a mixture of 35% nitric acid and 65% sulphuric acid at 65-80°C) without separation, the product is a mixture of2,4-dinitrotoluene (about 80%) and 2,6-dinitrotoluene (20%). If, on the other hand, the mixed mononitrates are separated (by distillation), then further nitration of the 2-nitrotoluene yields a mixture of 2,4-dinitrotoluene (about 65%) and 2,6-dinitrotoluene (35%) whilst further nitration of the 4-nitrotoluene gives only 2,4-dinitrotoluene.
Production Methods
Benzene is produced from toluene through a process called hydrodealkylation. In thisprocess, toluene reacts with hydrogen in the presence of a chromium, platinum, or molybdenumcatalysts at temperatures of several hundred degrees Celsius and pressures of about50 atmospheres: C6H5CH3 + H2 → C6H6 + CH4. Toluene can also be used to producephenol, (C6H5OH), benzoic acid (C6H5COOH), and benzaldehyde (C6H5CHO). Nitratedforms of toluene produce explosive compounds; the most common of these is TNT (SeeTrinitrotoluene).
Definition
ChEBI: The simplest member of the class toluenes consisting of a benzene core which bears a single methyl substituent.
General Description
A clear colorless liquid with a characteristic aromatic odor. Flash point 40°F. Less dense than water (7.2 lb / gal) and insoluble in water. Hence floats on water. Vapors heavier than air. May be toxic by inhalation, ingestion or skin contact. Used in aviation and automotive fuels, as a solvent, and to make other chemicals.
Air & Water Reactions
Highly flammable. Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Toluene reacts vigorously with allyl chloride or other alkyl halides even at minus 70° C in the presence of ethyl aluminum dichloride or ethyl aluminum sesquichloride. Explosions have been reported [NFPA 491M 1991]. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. When added to a tank of sulfur dichloride, the tank over pressurized and ruptured in a reaction thought to be catalyzed by iron or iron(III) chloride [Chem. Eng. News, 1988, 66(32), 2].
Hazard
Flammable, dangerous fire risk. Explosive limits in air 1.27–7%. Toxic by ingestion, inhalation, and skin absorption. Visual impairment, female reproductive effects, and pregnancy loss. Questionable carcinogen.
Health Hazard
Exposures to toluene cause adverse health effects to animals and humans. The symptoms of toxicity and poisoning include, but are not limited to, mild irritation to the skin, headache, nausea, and effects on the CNS. Prolonged exposure to high concentrations of toluene causes disturbances in vision, dizziness, nausea, CNS depression, paresthesia, and sudden collapse. The acute oral LD50 value of toluene in laboratory rats has been reported as 636–7300 mg/kg. Exposure to toluene has been reported to cause rapid and severe corneal damage and conjunctiva infl ammation. The acute dermal LD50 in rabbits was found to be between 1200 and 1400 mg/kg.
Fire Hazard
Toluene is a flammable liquid (NFPA rating = 3), and its vapor can travel a considerable distance to an ignition source and "flash back." Toluene vapor forms explosive mixtures with air at concentrations of 1.4 to 6.7% (by volume). Hazardous gases produced in fire include carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide and dry chemical extinguishers should be used to fight toluene fires.
Flammability and Explosibility
Toluene is a flammable liquid (NFPA rating = 3), and its vapor can travel a considerable distance to an ignition source and "flash back." Toluene vapor forms explosive mixtures with air at concentrations of 1.4 to 6.7% (by volume). Hazardous gases produced in fire include carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide and dry chemical extinguishers should be used to fight toluene fires.
Chemical Reactivity
Reactivity with Water No reaction; Reactivity with Common Materials: No reactions; Stability During Transport: Stable; Neutralizing Agents for Acids and Caustics: Not pertinent; Polymerization: Not pertinent; Inhibitor of Polymerization: Not pertinent.
Potential Exposure
Toluene is used as an industrial chemical, chemical intermediate; solvent, and emulsifier; may be encountered in the manufacture of benzene. It is also used as a chemical feed for toluene diisocyanate, phenol, benzyl and benzoyl derivatives; benzoic acid; toluene sulfonates; nitrotoluenes, vinyltoluene, and saccharin; as a solvent for paints and coatings; or as a component of automobile and aviation fuels.
Carcinogenicity
The IARC has determined that there is evidence for the lack of carcinogenicity of toluene in experimental animals and that there is inadequate evidence for carcinogenicity in humans. Results of in vitro assays generally indicate that toluene is not genotoxic. Reports of increased incidences of sister chromatid exchanges and chromatid breaks in exposed workers are confounded by concurrent exposure to other organic chemicals.
storage
toluene should be used only in areas free of ignition sources, and quantities greater than 1 liter should be stored in tightly sealed metal containers in areas separate from oxidizers.
Shipping
UN1294 Toluene, Hazard Class: 3; Labels: 3-Flammable liquid.
Incompatibilities
Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides. Violent reaction with mixtures of nitric and sulfuric acid.
Waste Disposal
Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant (≥100 kg/mo) must conform with EPA regulations governing storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal.
Toluene Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
1of3
chevron_rightPreparation Products
1of8
chevron_right108-88-3(Toluene)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




