Aspartame
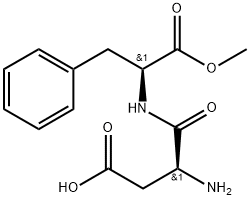
- CAS No.
- 22839-47-0
- Chemical Name:
- Aspartame
- Synonyms
- APM;ASPARTAME POWDER;ASP-PHE METHYL ESTER;ASPARTAM;(S)-3-AMino-4-(((S)-1-Methoxy-1-oxo-3-phenylpropan-2-yl)aMino)-4-oxobutanoic acid;Asp-Phe-OMe;Glycopeptide;Equal;Protein sugar;ASPARTAME-ACESULFAMESALT
- CBNumber:
- CB4345527
- Molecular Formula:
- C14H18N2O5
- Molecular Weight:
- 294.31
- MOL File:
- 22839-47-0.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
- Modify Date:
- 2024/7/8 20:25:11
| Melting point | 242-248 °C |
|---|---|
| alpha | 15.5 º (c=4, 15N formic acid) |
| Boiling point | 436.08°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.2051 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 14.5 ° (C=4, 15mol/L Formic Acid) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Sparingly soluble or slightly soluble in water and in ethanol (96 per cent), practically insoluble in hexane and in methylene chloride. |
| pka | pKa 3.19±0.01 (H2O t=25.0 I=0.100(NaCl))(Approximate);7.87±0.02(H2O t=25.0 I=0.100(NaCl))(Approximate) |
| form | Powder |
| color | White |
| Odor | odorless with a sweet taste |
| PH | pH(8g/l, 25℃) : 4.5~6.0 |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in formic acid, dimethyl sulfoxide. Sparingly soluble in water and ethanol. |
| Merck | 14,839 |
| BRN | 2223850 |
| Sequence | H-Asp-Phe-OMe |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| InChIKey | IAOZJIPTCAWIRG-QWRGUYRKSA-N |
| LogP | 0.542 (est) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 22839-47-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | L-Phenylalanine, L-.alpha.-aspartyl-, 2-methyl ester (22839-47-0) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |  GHS07 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Warning | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H315-H319-H335 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P280-P304+P340-P305+P351+P338 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 22-24/25 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 2 | |||||||||
| RTECS | WM3407000 | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HS Code | 29242990 | |||||||||
| Toxicity | TDLo orl-wmn: 3710 mg/kg:SKN AIMEAS 104,207,86 | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Aspartame price More Price(10)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | A5139 | Asp-Phe methyl ester ≥98% | 22839-47-0 | 1G | ₹4784.65 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | WH0010461M1 | Monoclonal Anti-MERTK antibody produced in mouse clone 2D2, purified immunoglobulin, buffered aqueous solution | 22839-47-0 | 100μG | ₹48018.6 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | PHR1381 | Aspartame Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material | 22839-47-0 | 1G | ₹8237.83 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | A5139 | Asp-Phe methyl ester ≥98% | 22839-47-0 | 5G | ₹12535.35 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | A5139 | Asp-Phe methyl ester ≥98% | 22839-47-0 | 25G | ₹44220.13 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
Aspartame Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Aspartame is the most popular artificial sweetener in the United States. It is sold as sweeteners such as NutraSweet and Equal, but it is also incorporated into thousands of food products.
Chemical Properties
Aspartame (N-L-aspartyl-L-phenylalanine-1-methyl ester, 3-amino-N-(a-carbomethoxy-
phenethyl)-succinamic acid-N-methyl ester) is an intense sweetener widely
used in foods and beverages. Its solubility in water is approximately 10 g/L at room
temperature. Aspartame is not fully stable under common processing and storage
conditions of foods and beverages with the highest stability around pH 4.3.
Aspartame is about 200 times sweeter than sucrose with a clean, but slightly
lingering sweetness. It is used as the single sweetener, but often also in blends with other intense sweeteners owing to synergistic taste enhancement and taste quality
improvement often seen in such blends.
In the European Union, aspartame is approved as E 951 for a large number of
food applications. In the United States, it is approved as a multipurpose sweetener
for food and beverage uses and it is also approved in many other countries.
History
Aspartame was discovered accidentally in 1965 during a search for drugs to treat gastric ulcers. James M. Schlatter, an organic chemist working for G. D. Searle & Company, was using aspartyl-phenylalanine methyl ester (aspartame) in a synthesis procedure and inadvertently got some of the compound on his hands.
Uses
Aspartame is a high-intensity sweetener that is a dipeptide, provid- ing 4 cal/g. it is synthesized by combining the methyl ester of phenylalanine with aspartic acid, forming the compound n-l-alpha- aspartyl-l-phenylalanine-1-methyl ester. it is approximately 200 times as sweet as sucrose and tastes similar to sugar. it is compara- tively sweeter at low usage levels and at room temperature. its mini- mum solubility is at ph 5.2, its isoelectric point. its maximum solubility is at ph 2.2. it has a solubility of 1% in water at 25°c. the solubility increases with temperature. aspartame has a certain insta- bility in liquid systems which results in a decrease in sweetness. it decomposes to aspartylphenylalanine or to diketropiperazine (dkp) and neither of these forms is sweet. the stability of aspartame is a function of time, temperature, ph, and water activity. maximum stability is at approximately ph 4.3. it is not usually used in baked goods because it breaks down at the high baking temperatures. it contains phenylalanine, which restricts its use for those afflicted with phenylketonuria, the inability to metabolize phenylalanine. uses include cold breakfast cereals, desserts, topping mixes, chew- ing gum, beverages, and frozen desserts. the usage level ranges from 0.01 to 0.02%.
Preparation
By coupling the amino acids L-phenylalanine and L-aspartic acid, and the esterification of the carboxyl group of the phenylalanine moiety to produce the methyl ester. This esterification can occur before or after coupling. The crystallized slurry is centrifuged and the resulting “wet-cake” is washed to remove impurities.
Production Methods
Aspartame is produced by coupling together L-phenylalanine (or Lphenylalanine methyl ester) and L-aspartic acid, either chemically or enzymatically. The former procedure yields both the sweet aaspartame and nonsweet β-aspartame from which the α-aspartame has to be separated and purified. The enzymatic process yields only α-aspartame.
Definition
ChEBI: A dipeptide composed of methyl L-phenylalaninate and L-aspartic acid joined by a peptide linkage.
General Description
Asp-Phe methyl ester (aspartame, APM, ASP), a dipeptide ester, is made up of phenyl alanine and aspartic acid. Its genotoxic effects have been investigated. Its interaction with certain hydrocolloids has been studied.
Pharmaceutical Applications
Aspartame is used as an intense sweetening agent in beverage
products, food products, and table-top sweeteners, and in
pharmaceutical preparations including tablets, powder mixes,
and vitamin preparations. It enhances flavor systems and can be
used to mask some unpleasant taste characteristics; the approximate
sweetening power is 180–200 times that of sucrose.
Unlike some other intense sweeteners, aspartame is metabolized
in the body and consequently has some nutritive value: 1 g provides
approximately 17 kJ (4 kcal). However, in practice, the small
quantity of aspartame consumed provides a minimal nutritive
effect.
Safety Profile
Human systemic effects byingestion: allergic dermatitis. Experimental reproductiveeffects. When heated to decomposition it emits toxicfumes of NOx.
Environmental Fate
Aspartame is nontoxic. However, individuals with the rare, genetic disease, phenylketonuria (PKU), cannot properly metabolize phenylalanine. Such individuals are detected by testing at birth and placed on special low-phenylalanine diets to control their blood phenylalanine concentrations. Thus, PKU individuals need to be aware that aspartame is a source of phenylalanine.
Metabolic pathway
The rate of aspartame degradation is faster in a phosphate buffer solution than in a citrate buffer solution at the same pH and buffer concentration. The primary mechanism by which aspartame degrades, the formation of diketo piperazine, involves the nucleophilic attack of carbonyl by the free amine, which requires proton transfer.
storage
Aspartame is stable in dry conditions. In the presence of moisture,
hydrolysis occurs to form the degradation products L -aspartyl-Lphenylalanine
and 3-benzyl-6-carboxymethyl-2,5-diketopiperazine
with a resulting loss of sweetness. A third-degradation product is
also known, β-L-aspartyl-L-phenylalanine methyl ester. For the
stability profile at 258℃ in aqueous buffers.
Stability in aqueous solutions has been enhanced by the addition
of cyclodextrins, and by the addition of polyethylene glycol 400
at pH 2. However, at pH 3.5–4.5 stability is not enhanced by the
replacement of water with organic solvents.
Aspartame degradation also occurs during prolonged heat
treatment; losses of aspartame may be minimized by using processes
that employ high temperatures for a short time followed by rapid
cooling.
The bulk material should be stored in a well-closed container, in
a cool, dry place.
Incompatibilities
Differential scanning calorimetry experiments with some directly compressible tablet excipients suggests that aspartame is incompatible with dibasic calcium phosphate and also with the lubricant magnesium stearate. Reactions between aspartame and sugar alcohols are also known.
Regulatory Status
Accepted for use as a food additive in Europe and in the USA. Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (oral powder for reconstitution, buccal patch, granules, syrups, and tablets). Included in nonparenteral medicines licensed in the UK. Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients.
Aspartame Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
1of2
chevron_rightPreparation Products
| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anant Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd | +91-8550986868 +91-9485998001 | Haryana, India | 461 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Rsum Industries Pvt. Ltd. | +91-91062685255 +91-91062685255 | New Delhi, India | 29 | 58 | Inquiry |
| KARPSCHEM LABORATORIES | +91-7249203006 +91-7249203006 | Maharashtra, India | 786 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Medi Pharma Drug House | +919930911911 | Mumbai, India | 143 | 58 | Inquiry |
| HRV Global Life Sciences | +91-9820219686 +91-9820219686 | Telangana, India | 379 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Prakash Chemicals Agencies | +91-8511140657 | Gujarat, India | 106 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Arihant Innochem Pvt Ltd | +91-2267674895 +91-2267674895 | Mumbai, India | 37 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Symbio Generrics (I) Pvt Ltd | +91-8121318328 +91-9099033709 | Karnataka, India | 22 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Triveni Interchem Private Limited (Group Of Triveni... | 08046042087 | Gujarat, India | 497 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Rejoice Life Ingredients | 08048268167 | Delhi, India | 2 | 58 | Inquiry |
Related articles
- Aspartame: Chemical Structure, Digestion and Metabolism
- Aspartame, composed of aspartic acid and phenylalanine, undergoes digestion and metabolism with potential effects on neurotran....
- Jun 20,2024
- Recommended usage of Aspartame
- Based on the lack of toxicity in animal studies, a no-observed effect level of at least 4000 mg kg-1 body weight per day was e....
- Nov 16,2021
- The applications and Health effects of Aspartame
- Aspartame (APM) is an artificial non-saccharide sweetener used as a sugar substitute in some foods and beverages. It is a meth....
- Aug 16,2019
22839-47-0(Aspartame)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




