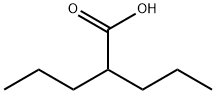
2-Propylpentanoic acid
- CAS No.
- 99-66-1
- Chemical Name:
- 2-Propylpentanoic acid
- Synonyms
- VALPROIC ACID;valproate;VPA;DIVALPROEX;Valproic;depakote;Depakene;Depakine;Mylproin;2-PropyL
- CBNumber:
- CB7149528
- Molecular Formula:
- C8H16O2
- Molecular Weight:
- 144.21
- MOL File:
- 99-66-1.mol
- Modify Date:
- 2024/7/5 11:27:04
| Melting point | -21.25°C (estimate) |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 220 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 0.9 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| vapor pressure | 0.01 hPa (20 °C) |
| refractive index |
n |
| Flash point | 232 °F |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | H2O: slightly soluble |
| form | Liquid |
| pka | 4.6(at 25℃) |
| color | Clear colorless to pale yellow |
| explosive limit | 1%(V) |
| Odor Threshold | 0.0033ppm |
| Water Solubility | slightly soluble |
| Merck | 14,9913 |
| BRN | 1750447 |
| BCS Class | 1,2 |
| LogP | 1.59 at 22.1℃ and pH5 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 99-66-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Valproic Acid(99-66-1) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Valproic acid (99-66-1) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |   GHS07,GHS08 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H302-H315-H319-H360D | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P201-P301+P312+P330-P302+P352-P305+P351+P338-P308+P313 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | Xn,T,F | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 22-36/37/38-39/23/24/25-23/24/25-11-34-61 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 26-45-36/37-16-7-36/37/39-53 | |||||||||
| RIDADR | UN 1230 3/PG 2 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 3 | |||||||||
| RTECS | YV7875000 | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 8 | |||||||||
| PackingGroup | III | |||||||||
| HS Code | 29159080 | |||||||||
| Toxicity | LD50 orally in rats: 670 mg/kg (Jenner) | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
2-Propylpentanoic acid price More Price(7)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | V-006 | Valproic acid solution 1.0?mg/mL in methanol, ampule of 1?mL, certified reference material, Cerilliant? | 99-66-1 | 1ML | ₹10041.5 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | PHR1061 | Valproic acid Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material | 99-66-1 | 1G | ₹8530.1 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | P6273 | 2-Propylpentanoic acid | 99-66-1 | 100ML | ₹19485 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 8.14439 | 2-Propylvaleric acid for synthesis | 99-66-1 | 25ML | ₹14059.99 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| TCI Chemicals (India) | P0823 | 2-Propylvaleric Acid min. 99.0 % | 99-66-1 | 25ML | ₹3100 | 2022-05-26 | Buy |
2-Propylpentanoic acid Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Valproic acid and its salts are a new group of antiepileptic drugs that differs from the
known drugs both structurally and in terms of its mechanism of action. It is believed that
it acts on the metabolism of the GABA system. Valproic acid has been shown to elevate
the level of GABA in the brain by means of competitive inhibition of GABA transaminase
and the dehydrogenase of succinic semialdehyde.
This drug not only exhibits anticonvulsant action, but also betters the mental condition
of the patient.
Chemical Properties
Colorless Liquid
Uses
2-Propylpentanoic acid has been used as a supplement in mouse embryonic fibroblast - conditioned medium (MEF-CM)?to feed the cells.
Definition
ChEBI: A branched-chain saturated fatty acid that comprises of a propyl substituent on a pentanoic acid stem.
Biological Functions
Although it is marketed as both valproic acid
(Depakene) and as sodium valproate (Depakote), it is
the valproate ion that is absorbed from the gastrointestinal
tract and is the active form.
As with several other AEDs, it is difficult to ascribe
a single mechanism of action to valproic acid.This compound
has broad anticonvulsant activity, both in experimental
studies and in the therapeutic management of
human epilepsy.Valproic acid has been shown to block
voltage-dependent sodium channels at therapeutically
relevant concentrations. In several experimental studies,
valproate caused an increase in brain GABA; the
mechanism was unclear.There is evidence that valproate may also inhibit T-calcium channels and that this may
be important in its mechanism of action in patients with
absence epilepsy.
General Description
Clear colorless liquid.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Fire Hazard
2-Propylpentanoic acid is combustible.
Pharmacokinetics
Valproate undergoes rapid and complete absorption, which is only slightly slowed by food. It is 90% protein bound, and its clearance is dose-dependent because of an increase in the free fraction of the drug at higher doses. It is metabolized almost entirely by the liver, with 30 to 50% of an orally administered dose being eliminated in the urine as its acyl glucuronide conjugate, 40% from mitochondrial β-oxidation, approximately 15 to 20% by ω-oxidation, and less than 3% is excreted unchanged in urine. Its major active metabolite is (E)-2-ene valproate (trans 2-ene valproate). Its 4-ene metabolite has been proposed to be a reactive metabolite responsible for the hepatotoxicity of valproate. Other metabolites found in the urine include 3-oxo- and 4-hydroxyvalproate. The elimination half-life for valproate ranged from 9 to 16 hours following oral dosing regimens of 250 to 1,000 mg. Patients who are not taking enzyme-inducing AEDs (carbamazepine, phenytoin, and phenobarbital) will clear valproate more rapidly; therefore, monitoring of AED plasma concentrations should be intensified whenever concurrent AEDs are introduced or withdrawn.
Clinical Use
Valproic acid is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal
tract and is highly bound (~90%) to plasma protein,
and most of the compound is therefore retained
within the vascular compartment.Valproate rapidly enters
the brain from the circulation; the subsequent decline
in brain concentration parallels that in plasma, indicating
equilibration between brain and capillary
blood. A large number of metabolites have been identified,
but it is not known whether they play a role in the
anticonvulsant effect of the parent drug. Valproic acid
inhibits the metabolism of several drugs, including phenobarbital,
primidone, carbamazepine, and phenytoin,
leading to an increased blood level of these compounds.
At high doses, valproic acid can inhibit its own metabolism.
It can also displace phenytoin from binding sites
on plasma proteins, with a resultant increase in unbound
phenytoin and increased phenytoin toxicity. In
this instance, the dosage of phenytoin should be adjusted
as required. These examples reinforce the need
to determine serum anticonvulsant levels in epileptic
patients when polytherapy is employed.
Valproic acid has become a major AED against several
seizure types. It is highly effective against absence
seizures and myoclonic seizures. In addition, valproic
acid can be used either alone or in combination with
other drugs for the treatment of generalized tonic–
clonic epilepsy and for partial seizures with complex
symptoms.
Side effects
The most serious adverse effect associated with valproic
acid is fatal hepatic failure. Fatal hepatotoxicity is
most likely to occur in children under age 2 years, especially
in those with severe seizures who are given multiple
anticonvulsant drug therapy. The hepatotoxicity is
not dose related and is considered an idiosyncratic reaction;
it can occur in individuals in other age groups,
and therefore, valproic acid should not be administered
to patients with hepatic disease or significant hepatic
dysfunction or to those who are hypersensitive to it.
Valproic acid administration has been linked to an increased
incidence of neural tube defects in the fetus of
mothers who received valproate during the first
trimester of pregnancy. Patients taking valproate may
develop clotting abnormalities.
Valproic acid causes hair loss in about 5% of patients,
but this effect is reversible. Transient gastrointestinal
effects are common, and some mild behavioral
effects have been reported. Metabolic effects, including
hyperglycemia, hyperglycinuria, and hyperammonemia,
have been reported. An increase in body weight also
has been noted. Valproic acid is not a CNS depressant,
but its administration may lead to increased depression
if it is used in combination with phenobarbital, primidone,
benzodiazepines, or other CNS depressant agents.
Solubility in organics
soluble in most organic solvents, including methanol, chloroform, and ether, solubility in water: 1.27 mg/mL.
2-Propylpentanoic acid Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
Preparation Products
| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| THE MOLECULEZ | +91-7506703683 +91-7506703683 | Maharashtra, India | 79 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Element Chemilink Pvt. Ltd. | +91-6358814008 +91-6358814008 | Gujarat, India | 31 | 58 | Inquiry |
| AARTIA KEM SCIENCE | +91-8291072530 +91-8291072530 | Maharashtra, India | 70 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Chynops Pharma | +919998000404 | Gujarat, India | 39 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Cefa-Cilinas Biotics Pvt Ltd | +91-7875033155 +91-8080701561 | Maharashtra, India | 121 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Sekhment pharmaventures | +91-9030088669 +91-9030088669 | Mumbai, India | 105 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Apotex Pharmachem India Pvt Ltd | +91-8022891034 +91-8022891000 | Karnataka, India | 109 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Roaq Chemicals Pvt Ltd | +91-9227103654 +91-9227103654 | Gujarat, India | 5 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Mascot Industries Pvt., Ltd. | +91-9825849755 +91-9825849755 | Ahmedabad, India | 16 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Chempifine Chemicals | +91-2225667766 +91-2225667766 | Punjab, India | 144 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Supplier | Advantage |
|---|---|
| THE MOLECULEZ | 58 |
| Element Chemilink Pvt. Ltd. | 58 |
| AARTIA KEM SCIENCE | 58 |
| Chynops Pharma | 58 |
| Cefa-Cilinas Biotics Pvt Ltd | 58 |
| Sekhment pharmaventures | 58 |
| Apotex Pharmachem India Pvt Ltd | 58 |
| Roaq Chemicals Pvt Ltd | 58 |
| Mascot Industries Pvt., Ltd. | 58 |
| Chempifine Chemicals | 58 |
99-66-1(2-Propylpentanoic acid)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




