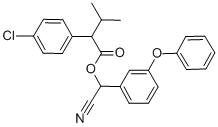
Fenvalerate
- CAS No.
- 51630-58-1
- Chemical Name:
- Fenvalerate
- Synonyms
- SANMARTON;fenkill;phenvalerate;DUFON;FENNY;ARFEN;fenkem;Tirade;Pydrin;S-5602
- CBNumber:
- CB7281563
- Molecular Formula:
- C25H22ClNO3
- Molecular Weight:
- 419.9
- MOL File:
- 51630-58-1.mol
- Modify Date:
- 2024/7/2 8:55:16
| Melting point | 54-59℃ |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 300°C |
| Density | d23 1.17 |
| vapor pressure | 1.92×10-5 Pa (20 °C) |
| refractive index | nD20 1.5533 |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,2-8°C |
| solubility |
DMSO:1.0(Max Conc. mg/mL);2.38(Max Conc. mM) DMF:30.0(Max Conc. mg/mL);71.44(Max Conc. mM) Ethanol:5.0(Max Conc. mg/mL);11.91(Max Conc. mM) |
| form | Solid |
| color | Off-white to light yellow |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in 100% ethanol (>25 mg/ml), water (0.001 g/L) at 20°C, and DMSO. |
| Merck | 13,4038 |
| BRN | 2025982 |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Benzeneacetic acid, 4-chloro-«alpha»-(1-methylethyl)-, cyano(3-phenoxyphenyl)methyl ester(51630-58-1) |
| IARC | 3 (Vol. 53) 1991 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Fenvalerate (51630-58-1) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |   GHS06,GHS09 |
|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H301-H315-H319-H335-H410 |
| Precautionary statements | P261-P264-P273-P301+P310-P302+P352-P305+P351+P338 |
| Hazard Codes | T,N |
| Risk Statements | 25-36/37/38-50/53-57 |
| Safety Statements | 26-45-60-61 |
| RIDADR | UN 2811 6.1/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | CY1576350 |
| HazardClass | 6.1(b) |
| PackingGroup | III |
| HS Code | 29269090 |
| Toxicity | LD50 orally in rats: 451 mg/kg (DMSO); >3200 mg/kg (aqueous suspension), Shell Technical Data Bulletin |
Fenvalerate price More Price(2)
Fenvalerate Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Fenvalerate is a yellow-brown viscous liquid that is practically soluble in water. It is stable to moderate heat and light and is rapidly hydrolysed in basic environments (above pH 8). Fenvalerate is a racemic mixture of four stereoisomers in equal proportions owing to the presence of two chiral centres. It is a synthetic type II pyrethroid.
Fenvalerate is registered as an insecticide for a wide array of crop uses, as well as a termiticide and insect repellent.
Chemical Properties
It is an ester of 2-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-methylbutyric acid and alpha-cyano-3-phenoxybenzyl alcohol but lacks a cyclopropane ring. However, in terms of its insecticidal behaviour, it belongs to the pyrethroid insecticides. Technical grade fenvalerate is a yellow or brown viscous liquid having a specific gravity of 1.175 at 25°C. The vapour pressure is 0.037 mPa at 25°C, and it is relatively non-volatile. It is practically insoluble in water (approximately 2 μg/L) but soluble in organic solvents such as acetone, xylene, and kerosene. It is stable to light, heat, and moisture but unstable in alkaline media.
Uses
Fenvalerate controls a wide range of insect pests in fruit, vines, olives, hops, nuts, vegetables, cotton, oilseed rape, sunflowers, alfalfa, cereals, maize, sorghum, potatoes, beets, soyabeans, tobacco, sugar cane and ornamentals. It is also used in public health situations and in animal houses.
Definition
ChEBI: A carboxylic ester obtained by formal condensation between 2-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-methylbutyric acid and cyano(3-phenoxyphenyl)methanol.
General Description
A clear viscious yellow liquid with a mild odor. Used as broad spectrum insecticide.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water. Rapidly hydrolyzed by alkaline solution.
Reactivity Profile
A pyrethroid. Phenvalerate is an ester and nitrile. Esters react with acids to liberate heat along with alcohols and acids. Strong oxidizing acids may cause a vigorous reaction that is sufficiently exothermic to ignite the reaction products. Heat is also generated by the interaction of esters with caustic solutions. Flammable hydrogen is generated by mixing esters with alkali metals and hydrides. Nitriles may polymerize in the presence of metals and some metal compounds. They are incompatible with acids; mixing nitriles with strong oxidizing acids can lead to extremely violent reactions. Nitriles are generally incompatible with other oxidizing agents such as peroxides and epoxides. The combination of bases and nitriles can produce hydrogen cyanide. Nitriles are hydrolyzed in both aqueous acid and base to give carboxylic acids (or salts of carboxylic acids).
Hazard
Questionable carcinogen.
Contact allergens
Fenvalerate is an insecticide of the synthetic pyrethroid group, which induced sensitization in farmers.
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion, intravenous, and intracerebral routes. Moderately toxic by skin contact.Experimental reproductive effects. Mutation data reported. Highly toxic to fish and bees. Corrosive, causes eye damage. A skin irritant. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of Cl-, NOx, and CN-. See also CYANIDE.
Potential Exposure
Fenvalerate is one of the most versatile synthetic pyrethroid insecticides. It is mostly used in agriculture and on cattle, but also in homes and gardens. It acts as a stomach poison against a wide variety of leaf and fruit eating such as bollworm fruit and shoot borers and aphids. Crops on which it is used include cotton, cauliflower, okra, vines and fruits. It is also used in public health and animal husbandry. It is effective against pests whose strains are resistant to organochlorine, organophosphorus, and carbamate insecticides. Not used in EU countries
Environmental Fate
Soil. Fenvalerate is moderately persistent in soil. The percentage of the initial dosage (1 ppm) remaining after 8 weeks of incubation in an organic and mineral soil were 58 and 12%, respectively, while in sterilized controls 100 and 91% remained, respectively (Chapman et al., 1981).
In a sugarcane runoff plot, fenvalerate was applied at a rate of 0.22 kg/ha 4 times each year in 1980 and 1981. Runoff losses in 1980 and 1981 were 0.08 and 0.56 of the applied amount, respectively (Smith et al., 1983).
Plant. Dislodgable residues of fenvalerate on cotton leaf 0, 24, 48, 72 and 96 hours after application (0.22 kg/ha) were 0.85, 0.36, 0.38, 0.28 and 0.28 μg/m2, respectively (Buck et al., 1980).
Surface Water. In an estuary, the half-life of fenvalerate was 27–42 days (Schimmel et al., 1983).
Chemical/Physical. Undergoes hydrolysis at the ester bond (Hartley and Kidd, 1987). Decomposes gradually at 150–300°C (Windholz et al., 1983) probably releasing toxic fumes of nitrogen and chlorine.
Metabolic pathway
After foliar treatment of 14C-fenvalerate on wheat plants, the amount of residual radioactivity in the grain and hull is below the limit of reliable measurement. Individual degradation products accounting for more than 1% of the applied radioactivity are not present in the foliage or straw. Important degradation pathways include decarboxylation and ester cleavage.
Shipping
UN3349 Pyrethroid pesticide, solid toxic, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous material. UN3352 Pyrethroid pesticide, liquid toxic, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials.
Incompatibilities
ncompatible with oxidizers, chlorates nitrates, peroxides, sulfuric acid, caustics, ammonia, aliphatic amines, alkanolamines, isocyanates, alkylene oxides, epichlorohydrin. Moisture may cause hydrolysis or other forms of decomposition. Emulsifiable concentrate is corrosive
Waste Disposal
Incineration would be an effective disposal procedure where permitted. If an efficient incinerator is not available, the product should be mixed with large amounts of combustible material and contact with the smoke should be avoided. In accordance with 40CFR165, follow recommendations for the disposal of pesticides and pesticide containers
References
[1] http://www.toxipedia.org
[2] Y. Xia, Q. Bian, L. Xu, S. Cheng, L. Song, J. Liu, W. Wu, S. Wang and X. Wang, Genotoxic effects on human spermatozoa among pesticide factory workers exposed to fenvalerate, Toxicology, 2004, vol. 203, 49-60
[3] Terry R Roberts, David H Hutson, Philip W Lee, Peter H Nicholls and Jack R Plimmer, Metabolic Pathways of Agrochemicals: Part 2: Insecticides and Fungicides, 1999
Fenvalerate Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
1of6
chevron_rightPreparation Products
1of2
chevron_right| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gujarat Chemicals GUJCHEM | +91-9825114095 +91-9825114095 | Gujarat, India | 42 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Bharat Rasayan | +91-9619772584 +91-9619772584 | Maharashtra, India | 23 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Shree Vallabh Chemicals | +91-8849453471 +91-9975490440 | Gujarat, India | 43 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Kilpest India limited | +91-7552586536 +91-7552586536 | Madhya Pradesh, India | 38 | 58 | Inquiry |
| ENTOMIC CHEMICALS | +91-9425149263 +91-9425149263 | Madhya Pradesh, India | 39 | 58 | Inquiry |
| General Crop Science | +91-9810438260 +91-9896700555 | Haryana, India | 31 | 58 | Inquiry |
| SD Agro Chemicals | +91-9650182828 +91-9871331171 | Uttar Pradesh, India | 42 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Unique Farm Aid Pvt Ltd | +91-9873006591 +91-9873006592 | New Delhi, India | 31 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Gujarat Insecticides Ltd | +91-2646662200 +91-2646668200 | Gujarat, India | 6 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Aimco Pesticides Limited | +91-9444137807 +91-9825358545 | Maharashtra, India | 22 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Supplier | Advantage |
|---|---|
| Gujarat Chemicals GUJCHEM | 58 |
| Bharat Rasayan | 58 |
| Shree Vallabh Chemicals | 58 |
| Kilpest India limited | 58 |
| ENTOMIC CHEMICALS | 58 |
| General Crop Science | 58 |
| SD Agro Chemicals | 58 |
| Unique Farm Aid Pvt Ltd | 58 |
| Gujarat Insecticides Ltd | 58 |
| Aimco Pesticides Limited | 58 |
51630-58-1(Fenvalerate)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




