Oxamyl
- CAS No.
- 23135-22-0
- Chemical Name:
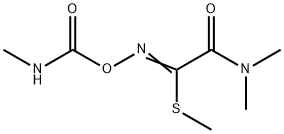
- Oxamyl
- Synonyms
- oxamil;Blade;d 1410;d-1410;VYDATE;OXAMYL;dpx1410;vydateg;vydatek;vydatel
- CBNumber:
- CB7311293
- Molecular Formula:
- C7H13N3O3S
- Molecular Weight:
- 219.26
- MOL File:
- 23135-22-0.mol
- Modify Date:
- 2024/3/14 15:18:27
| Melting point | 100°C |
|---|---|
| Density | 0.9700 |
| vapor pressure | 5.1×10-5Pa (25 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.6630 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 0-6°C |
| solubility | Chloroform: Slightly Soluble,Methanol: Slightly Soluble |
| pka | 10.48±0.46(Predicted) |
| Water Solubility | 28 g/100 mL |
| BRN | 2212753 |
| Stability | Hygroscopic |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 23135-22-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Oxamyl(23135-22-0) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Oxamyl (23135-22-0) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |   GHS06,GHS09 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H300+H330-H312-H411 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P273-P280-P301+P310+P330-P302+P352+P312-P304+P340+P310 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | T+;N,N,T+ | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 21-26/28-51/53 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 36/37-45-61 | |||||||||
| RIDADR | UN 2811 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 3 | |||||||||
| RTECS | RP2300000 | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 6.1(a) | |||||||||
| PackingGroup | I | |||||||||
| Toxicity | LD50 orally in rats: 5 mg/kg (Fahmy) | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Oxamyl Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Oxamyl, is also called N,N-dimethyl-2-methylcarbamoyloxyimino- 2-(methylthio)acetamide (IUPAC), consists of colorless crystals, which are readily soluble in water, methanol, ethanol, acetone, and fairly soluble in toluene. Oxamyl is produced by chlorination of the oxime of methylglycolate, reaction with methanethiol and alkali, and conversion to the carbamate with methyl isocyanate.
Uses
Oxamyl is a pesticide used in the treatment and protection of crops from parasites and insects.
Agricultural Uses
Insecticide, Nematicide, Acaricide: A systemic and contact insecticide/acaricide and nematicide, oxamyl is a restricted use pesticide used on apples, bananas, carrots, celery, citrus, cotton, cucumbers, eggplants, garlic, ginger, muskmelon (including cantaloupe and honeydew melon), onion (dry bulb), peanuts, pears, peppers, peppermint, pineapples, plantains, potatoes, pumpkins, soybeans, spearmint, squash, sweet potatoes, tobacco, tomatoes, watermelons, yams. Oxamyl is also used on non-bearing apple, cherry, citrus, peach, pear, and tobacco. It is applied directly onto plants or the soilsurface. It is available in both liquid and granular form, but the granular form is banned in the U.S. It has no residential use. Registered for use in EU countries[115
Trade name
BLADE®; D-1410®; DPX 1410®; INSECTICIDE-NEMACIDE 1410®; OXAMYL CARBAMATE INSECTICIDE®; THIOXAMYL®; VYDATE®; VYDATE® 10G; VYDATE L®; VYDATE INSECTICIDE/NEMATICIDE®; VYDATE OXAMYL INSECTICIDE/NEMATOCIDE®[C]
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion, skin contact, and inhalation. Experimental reproductive effects. Moderately toxic by skin contact. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of NOx and SOx
Potential Exposure
Oxamyl is a white crystalline solid. Sulfur or garlic-like odor. Molecular weight=219.3
Environmental Fate
Soil. Oxamyl rapidly degraded in a loamy sand and fine sand soil at 25°C to carbon
dioxide and the intermediate methyl N-hydroxy-N,N-dimethyl-1-thiooxaminidate (Rajagopol
et al., 1984). The reported half-life in soil is approximately one week (Worthing
and Hance, 1991). Ou and Rao (1986) reported a half-life in soil of 8–50 days. The reported
half-lives of oxamyl in Pitstone, Devizes, Sutton Veany and Mepal soils at 15°C were
reported to be 10.2–13.1, 6.2, 7.1 and 17.8 days, respectively (Bromilow et al., 1980).
Smelt et al. (1987) reported that oxamyl degraded at a higher rate in field plots after
repeated applications of this nematocide than in soils that received no treatment. The
repeated applications of oxamyl to soils probably induced microbial activity, which
resulted in the accelerated disappearance of this compound.
Harvey and Han (1978) reported a half-life of 8 days for oxamyl in soil.
Groundwater. According to the U.S. EPA (1986) oxamyl has a high potential to leach
to groundwater.
Plant. Dislodgable residues of oxamyl on cotton leaf 0, 24, 48, 72 and 96 hours after
application (0.41 kg/ha) were 1.5, 1.1, 1.2, 0.85 and 0.76 mg/m2, respectively (Buck et al.,
1980).
Chemical/Physical. The hydrolysis half-lives of oxamyl in a sterile 1% ethanol/water
solution at 25°C and pH values of 4.5, 6.0, 7.0 and 8.0, were 300, 17, 1.6 and 0.20 weeks,
respectively (Chapman and Cole, 1982). Under alkaline conditions, oxam
Metabolic pathway
Oxamyl degrades in soils, plants and animals following common metabolic pathways. Primary degradation reactions include the hydrolysis of the carbamate ester to yield the corresponding oxyimidothioate and nitrile. Other major metabolic reactions include N-demethylation and the hydration/oxidation of the nitriles to the corresponding amides and acids. The majority of the oxamyl metabolites are recovered as conjugates in plants and animals. No metabolites containing the oxidised thiomethyl group were observed. The primary degradation/metabolic pathways of oxamyl are presented in Scheme 1.
Shipping
UN2811 Toxic solids, organic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required. UN2991 Carbamate pesticides, liquid, toxic, flammable, flash point <23°C, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous material, 3-Flammable liquid.
Incompatibilities
Compounds of the carboxyl group react with all bases, both inorganic and organic (i.e., amines) releasing substantial heat, water and a salt that may be harmful. Incompatible with arsenic compounds (releases hydrogen cyanide gas), diazo compounds, dithiocarbamates, isocyanates, mercaptans, nitrides, and sulfides (releasing heat, toxic, and possibly flammable gases), thiosulfates and dithionites (releasing hydrogen sulfate and oxides of sulfur).
Waste Disposal
Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal 2264 Oxamyl practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant (≥100 kg/mo) must conform with EPA regulations governing storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal. Small quantities may be treated with alkali and buried in a landfill. In accordance with 40CFR165, follow recommendations for the disposal of pesticides and pesticide containers. Must be disposed properly by following package label directions or by contacting your local or federal environmental control agency, or by contacting your regional EPA office.
Oxamyl Preparation Products And Raw materials
23135-22-0(Oxamyl)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




