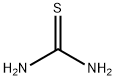
Thiourea
- CAS No.
- 62-56-6
- Chemical Name:
- Thiourea
- Synonyms
- Isothiourea;THIO;THIOCARBAMIDE;THU;250g;Thiurea;(NH2)2CS;2-Thiourea;THIOUREA DIOXID;Thiourea, reagent grade, ACS
- CBNumber:
- CB9854008
- Molecular Formula:
- CH4N2S
- Molecular Weight:
- 76.12
- MOL File:
- 62-56-6.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
- Modify Date:
- 2023/12/22 17:53:22
| Melting point | 170-176 °C (lit.) |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 263.89°C (estimate) |
| Density | 1.405 |
| refractive index | 1.5300 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | water: soluble137g/L at 20°C |
| form | Crystals |
| pka | -1.0(at 25℃) |
| Specific Gravity | 1.406 |
| color | White to almost white |
| Odor | Odorless |
| PH Range | 5 - 7 |
| PH | 6-8 (50g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
| Water Solubility | 13.6 g/100 mL (20 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,9367 |
| BRN | 605327 |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with strong acids, strong bases, strong oxidizing agents, metallic salts, proteins, hydrocarbons. May react violently with acrolein. |
| InChIKey | UMGDCJDMYOKAJW-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| LogP | -1.050 (est) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 62-56-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| IARC | 3 (Vol. Sup 7, 79) 2001 |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Thiourea(62-56-6) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Thiourea (62-56-6) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |    GHS07,GHS08,GHS09 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Warning | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H302-H351-H361fd-H411 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P201-P202-P264-P273-P301+P312-P308+P313 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | Xn,N,Xi | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 22-40-51/53-63-43-38 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 36/37-61 | |||||||||
| RIDADR | UN 2811 6.1/PG 3 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 2 | |||||||||
| RTECS | YU2800000 | |||||||||
| Autoignition Temperature | 440 °C Dust | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 6.1 | |||||||||
| PackingGroup | III | |||||||||
| HS Code | 29309070 | |||||||||
| Toxicity | LD50 orally in wild Norway rats: 1830 mg/kg (Dieke) | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Thiourea price More Price(37)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | T8656 | Thiourea ACS reagent, ≥99.0% | 62-56-6 | 50G | ₹3052.65 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | T7875 | Thiourea ReagentPlus?, ≥99.0% | 62-56-6 | 5G | ₹2284.08 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | T8656 | Thiourea ACS reagent, ≥99.0% | 62-56-6 | 100G | ₹5444.98 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | T8656 | Thiourea ACS reagent, ≥99.0% | 62-56-6 | 500G | ₹8800.73 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | T7875 | Thiourea ReagentPlus?, ≥99.0% | 62-56-6 | 100G | ₹4145.98 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
Thiourea Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Thiourea appears as white crystal/powder, is combustible, and on contact with fire, gives off irritating or toxic fumes/gases. Thiourea is a reducing agent used primarily in the production of bleached recycled pulp. In addition, it is also effective in the bleaching of stone groundwood, pressurised groundwood. Thiourea undergoes decomposition on heating and produces toxic fumes of nitrogen oxides and sulphur oxides. It reacts violently with acrolein, strong acids, and strong oxidants. The main application of thiourea is in textile processing and also is commonly employed as a source of sulphide. Thiourea is a precursor to sulphide to produce metal sulphides, for example, mercury sulphide, upon reaction with the metal salt in aqueous solution. The industrial uses of thiourea include production of flame-retardant resins and vulcanisation accelerators. Thiourea is used as an auxiliary agent in diazo paper, light-sensitive photocopy paper, and almost all other types of copy paper. Thiourea is used in many industrial applications, including as a chemical intermediate or catalyst, in metal processing and plating, and in photoprocessing.
Chemical Properties
Thiourea consists of colorless, lustrous crystals or powder with a bitter taste.
Uses
The product is wildly used in pharmaceutical industry, agricultural, chemicals, metallurgical industry, petroleum and so on. It is also main material for producing thiourea dioxide(CH1N2O2S).
Production Methods
Thiourea is formed by heating ammonium thiocyanate at 170 °C (338 °F). After about an hour, 25% conversion is achieved. With HCl, thiourea forms thiourea hydrochloride; with mercuric oxide, thiourea forms a salt; and with silver chloride, it forms a complex salt.
Definition
ChEBI: The simplest member of the thiourea class, consisting of urea with the oxygen atom substituted by sulfur.
Preparation
Thiourea is manufactured by heating ammonium thiocyanate at 140-145??C
for about 4 hours; equilibrium is established when about 25% of the
thiocyanate is converted to thiourea.Thiourea may also be prepared by the interaction of cyanamide and hydrogen sulphide:
Thiourea closely resembles urea in that reaction with formaldehyde gives
methylol derivatives and then resinous condensates which on continued
heating yield network structures. Thiourea-formaldehyde resins are slower
curing than urea-formaldehyde resins and the hardened products are more
brittle and more water-resistant. At one time thiourea-formaldehyde resins
were added to urea-formaldehyde resins to give mouldings and laminates
with improved water-resistance. These mixed resins have now been largely
superseded by melamine-formaldehyde resins which give products with better
resistance to heat.
General Description
White or off-white crystals or powder. Sinks and mixes with water.
Air & Water Reactions
Water soluble.
Reactivity Profile
Thiocarbamide is a white crystalline material or powder, toxic, carcinogenic. When heated to decomposition Thiocarbamide emits very toxic fumes of oxides of sulfur and oxides of nitrogen. Violent exothermic polymerization reaction with acrylaldehyde (acrolein) [MCA SD-85, 1961], violent decomposition of the reaction product with hydrogen peroxide and nitric acid [Bjorklund G. H. et al., Trans. R. Soc. Can.,1950, 44, p. 28], spontaneous explosion upon grinding with potassium chlorate [Soothill, D., Safety Management, 1992, 8(6), p. 11].
Hazard
A questionable carcinogen. May not be used in food products (FDA); skin irritant (allergenic).
Health Hazard
The acute oral toxicity of thiourea in mostanimals is of low order. The oral LD50 values reported in the literature show variation.Symptoms of chronic effects in rats includebone marrow depression and goiters. Administration of 32.8 mol of thiourea in chickembryos on day 17 of incubation resultedin the accumulation of parabronchial liquidin those embryos (Wittman et al. 1987). Theinvestigators have attributed such changes tothe toxic effects of thiourea, rather to than aretardation of pulmonary development.Dedon and coworkers (1986) observed thepossible protective action of thiourea againstplatinum toxicity. Thiourea and other sulfur-containing nucleophiles have the ability tochelate and remove platinum from biochemical sites of toxicity.Oral administration of thiourea resultedin tumors in the liver and thyroid in rats.It is carcinogenic to animals and has shownsufficient evidence.
Fire Hazard
Noncombustible solid. There is no report of any explosion resulting from reactions of thiourea. Small amounts of thiourea in contact with acrolein may polymerize acrolein, which is a highly exothermic reaction.
Agricultural Uses
Thiourea is a sulphur analogue of urea. It is a crystalline and colorless solid which is relatively insoluble in water. Thiourea, capable of breaking the dormancy of seeds, is used to stimulate seed germination. Seeds are soaked for less than 24 hours before planting.
Contact allergens
Thiourea is used as a cleaner agent for silver and cop- per, and as an antioxidant in diazo copy paper. It can induce (photo-) contact dermatitis.
Potential Exposure
Thiourea is used as rubber antiozonant, toning agent; corrosion inhibitor; and in pharmaceutical manufacture; in the manufacture of photosensitive papers; flame-retardant textile sizes; boiler water treatment. It is also used in photography; pesticide manufacture; in textile chemicals.
Carcinogenicity
Thiourea is reasonably anticipated to be a human carcinogen based on sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity from studies in experimental animals.
Shipping
UN2811 Toxic solids, organic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required. UN3077 Environmentally hazardous substances, solid, n.o.s., Hazard class: 9; Labels: 9-Miscellaneous hazardous material, Technical Name Required.
Purification Methods
Crystallise thiourea from absolute EtOH, MeOH, acetonitrile or water. Dry it under vacuum over H2SO4 at room temperature. [Beilstein 3 IV 342.]
Incompatibilities
Dust may form explosive mixture with air. Reacts violently with acrolein, strong acids (nitric acid). Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides.
Waste Disposal
Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant (≥100 kg/mo) must conform with EPA regulations governing storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal.
Thiourea Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
1of2
chevron_rightPreparation Products
1of8
chevron_right| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UNILOSA INTERNATINAL PRIVATE LIMITED | +91-9999069917 +91-9999069917 | New Delhi, India | 152 | 58 | Inquiry |
| PAARICHEM RESOURCES LLP | +91-8104961021 +91-8104961021 | Maharashtra, India | 82 | 58 | Inquiry |
| JSK Chemicals | +919879767970 | Gujarat, India | 3756 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Annexe Chem Pvt Ltd | +91-9724624061 +91-9898722162 | Gujarat, India | 57 | 58 | Inquiry |
| ShanPar Industries Pvt Ltd | +91-2652638973 +91-9909901206 | Gujarat, India | 115 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Kronox Lab Sciences Pvt Ltd | +91-9313231074 +91-9313231074 | Gujarat, India | 240 | 58 | Inquiry |
| AKASH PHARMA EXPORTS | +91-9388123451 +91-9846039283 | Kerela, India | 470 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Dr Prem's Molecules Pvt. Ltd. | +91 9825310038 | New Delhi, India | 547 | 50 | Inquiry |
| Scientific OEM | +91-22- 2343 7546 / 2341 3094 | New Delhi, India | 1996 | 38 | Inquiry |
| ALPHA CHEMIKA | +91-22-22061123 +91-22-66382501 | Mumbai, India | 1681 | 43 | Inquiry |
| Supplier | Advantage |
|---|---|
| UNILOSA INTERNATINAL PRIVATE LIMITED | 58 |
| PAARICHEM RESOURCES LLP | 58 |
| JSK Chemicals | 58 |
| Annexe Chem Pvt Ltd | 58 |
| ShanPar Industries Pvt Ltd | 58 |
| Kronox Lab Sciences Pvt Ltd | 58 |
| AKASH PHARMA EXPORTS | 58 |
| Dr Prem's Molecules Pvt. Ltd. | 50 |
| Scientific OEM | 38 |
| ALPHA CHEMIKA | 43 |
Related articles
- Thiourea:an organic compound
- Thiourea is an organic compound with the chemical formula (NH2)2CS.It is known for its versatility in various chemical applica....
- Nov 17,2023
- Role of Thiourea in the Kinetic of Growth of the Chemical Bath Deposited ZnS Films
- ZnS films were deposited onto glass substrates by the chemical bath technique at temperatures from 60 to 90°C. Zinc chloride, ....
- Nov 11,2019





