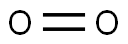산소, 냉각된 액체
|
|
산소, 냉각된 액체 속성
- 녹는점
- −218 °C(lit.)
- 끓는 점
- −183 °C(lit.)
- 밀도
- 1.429(0℃)
- 증기 밀도
- 1.11 (vs air)
- 증기압
- >760 mmHg at 20 °C
- 저장 조건
- -20°C
- 용해도
- 20°C, 101kPa의 압력에서 1부피는 약 32부피의 물에 용해됩니다.
- 물리적 상태
- 무색 가스
- 색상
- 무색의 기체, 액체 또는 육각형 결정
- 냄새
- 무취가스
- 생물학적 소스
- rabbit
- 수용성
- 1vol 가스는 32부피의 H2O(20°C), 7부피의 알코올(20°C)에 용해됩니다. 가용성 기타 유기 액체, 일반적으로 H2O보다 용해도가 더 높음 [MER06]
- Merck
- 13,7033
- Dielectric constant
- 1.5(-193℃)
- 안정성
- 안정적인. 연소를 강력하게 지원합니다. 인, 유기 물질, 많은 금속 분말과 호환되지 않습니다.
- 표면장력
- 15.85 mN/m at 80.0K
- CAS 데이터베이스
- 7782-44-7(CAS DataBase Reference)
- NIST
- Oxygen(7782-44-7)
- 위험 및 안전 성명
- 위험 및 사전주의 사항 (GHS)
| 위험품 표기 | O,C | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 위험 카페고리 넘버 | 8-52/53-34-48/20/22-37 | ||
| 안전지침서 | 17-45-36/37/39-26-61 | ||
| 유엔번호(UN No.) | UN 1072 2.2 | ||
| WGK 독일 | - | ||
| RTECS 번호 | RS2060000 | ||
| F 고인화성물질 | 4.5-31 | ||
| 위험 등급 | 2.2 | ||
| 유해 물질 데이터 | 7782-44-7(Hazardous Substances Data) | ||
| 독성 | OSHA recommends a minimum oxygen concentration of 19.5% for human occupancy. | ||
| 기존화학 물질 | KE-27737 |
산소, 냉각된 액체 C화학적 특성, 용도, 생산
순도시험
이 품목의 채취량은 온도 20℃, 압력 760mmHg에서의 용량으로 환산하여야 한다.
(1) 이산화탄소 : 이산화탄소검지관의 양단을 절단하여 그 일단을 이 품목의 용기와 연결하고 다른 끝을 적당한 유량계에 연결한다. 이 품목 약 1050±50mL를 검지관에 알맞은 유속으로 통과시켰을 때, 그 양은 300μL/L 이하이어야 한다.
(2) 일산화탄소 : 일산화탄소검지관의 양단을 절단하여 그 일단을 이 품목의 용기와 연결하고 다른 끝을 적당한 유량계에 연결한다. 이 품목 약 1050±50mL를 검지관에 알맞은 유속으로 통과시켰을 때, 그 양은 10μL/L 이하이어야 한다.
(3) 냄새 : 이 품목 용기의 밸브를 조용히 열어 얼굴에 산소가 직접 닿지 않게 조심하면서 냄새를 맡아보았을 때, 인지할 수 있는 냄새는 나지 않아야 한다.
확인시험
이 품목을 불꽃을 끈 나무조각과 접촉시키면 격렬한 불꽃을 일으킨다.
정량법
장 치 : A는 이방콕크 a가 달린 100mL 가스뷰렛으로 b~c, d~e 및 e~f 사이는 0.1mL 눈금이고 c~d 사이는 2mL 눈금이다. A는 수준관 B와 두꺼운 고무관으로 연결하고 A 및 B의 대략 반 용량의 염화암모늄․암모니아시액을 채운다. 가스피펫 C의 흡수구 g에는 지름 2mm이하의 구리선을 코일 모양으로 가늘게 감은 것을 위까지 가득 채우고 다시 염화암모늄․암모니아시액 125mL를 넣어 고무마개 i를 막고 A와 두꺼운 고무관으로 연결한다.
조작법 : a를 열고 B를 내려 g 중의 액을 a의 콕크까지 빨아올린 다음 a를 닫고 다음에 a의 검체도입관 h에 통하는 구멍을 열고 B를 올려 염화암모늄․암모니아시액을 A 및 h에 가득 채운 다음 a를 닫고 검체용기를 h에 연결하고 다시 a를 열어 B를 내리면서 이 품목 약 100mL를 정밀하게 취한다. a의 c에 통하는 구멍을 열고 B를 올려 이 품목을 g에 보내고 a를 닫고 c를 5분간 앞뒤로 조용하게 흔들어 준다. 흡수되지 않고 남은 가스를 a를 열고 B를 내려서 A에 다시 되돌려 보내고 그 용량을 측정한다. 이 조작을 반복하여 흡수되지 않고 남은 가스의 양이 항량이 되었을 때 그 용량을 측정하여 V(mL)로 하고, 다음 계산식에 따라 함량을 구한다. 다만, C중의 염화암모늄․암모니아시액을 새로 갈아넣어 시험할 때는 적어도 위의 조작을 4회 반복하여 그 정량값을 취한다. V 및 이 품목의 채취량을 20℃에서 기압 760mmHg의 용량으로 환산한다.
개요
Oxygen is a very prevalent and important element and is necessary for sustaining life on this planet. This element is the third most abundant in mass behind helium and hydrogen in the universe. The diatomic form (O2) is the most common pure form. With a boiling point at -183 °C, O2 exists as a colorless and odorless gas at standard temperature and pressure. In the process of cellular respiration, the highly reactive O2 is used as the oxidant in breaking down food molecules to produce energy. In turn, photosynthetic organisms generate O2 by using energy from the sun and water. Other allotropes of pure oxygen exist, including the trioxygen (O3) form known as ozone, as well as other, less common allotropes of oxygen such as O4 and O8. These oxygen allotropes are formed under high pressure and low temperatures and are solid.화학적 성질
Oxygen, O2, is a colorless, tasteless, gaseous element essential to almost all forms of life. It promotes respiration and combustion. Oxygen comprises 20% of the earth's atmosphere and is the most abundant element in seawater and in the earth's crust. It is slightly soluble in water and alcohol, but combines readily with most other elements to form oxides. The electrolysis of water produces both oxygen and hydrogen.
물리적 성질
There are three allotropes (different forms) of oxygen: (1) atomic oxygen (O), sometimesreferred to as nascent or “newborn” oxygen; (2) diatomic oxygen (O2), or molecular oxygen(gas); and (3) ozone (O3), also a gas.The atmospheric oxygen that we breathe is a very reactive nonmetal and is colorless, odorless,and tasteless, but it is essential to all living organisms. It readily forms compounds withmost other elements. With six electrons in its outer valence shell, it easily gains two moreelectrons to form a negative (–2) ion; or as covalent, it can share electrons with other elementsto complete its outer shell.
Almost all the oxygen in the atmosphere (?21%) is the allotropic form of molecular oxygen(O2). This essential gas we breathe is the result of photosynthesis, which is how green plants(with chlorophyll) use the energy of the sun to convert carbon dioxide (CO2) and water tostarches and sugars with molecular oxygen as the by-product.
Liquid oxygen has a slightly bluish cast to it. As it boils, pure oxygen gas is released. Themelting point for oxygen is –218.79°C, its boiling point is –182.95°C, and its density is0.001429 g/cm3.
Isotopes
There are a total of 15 isotopes of oxygen, three of which are stable. The stableones are O-16, which accounts for 99.762% of all the oxygen on Earth; O-17, whichcontributes only 0.038% of the Earth’s oxygen; and O-18, which makes up just 0.200%of Earth’s oxygen.Characteristics
Oxygen is, without a doubt, the most essential element on Earth. It is required to supportall plant and animal life, and it forms more compounds with other elements than any otherelement.Oxygen is soluble in both water and alcohol. Contrary to what many people believe, oxygenis NOT combustible (it will not burn), but rather it actively supports the combustion ofmany other substances. After all, if oxygen burned, every time a fire was lit, all the O2 in theatmosphere would be consumed!
Burning is a form of oxidation wherein oxygen chemically combines with a substance rapidlyenough to produce adequate heat to cause fire and light, or to maintain a fire once started.The oxidation of iron is called rusting. Rusting in an example of “slow oxidation,” which isthe reaction of O2 with Fe to form Fe2O3 or Fe3O4. This chemical reaction is so slow that theheat it produces is dissipated; thus, there is no fire.
Recently a new allotrope of oxygen was discovered. When O2 is subjected to great pressure,it is converted intoO4, which is a deep red solid that is a much more powerful oxidizer thanthe other forms of oxygen.
용도
Oxygen has many uses due to its high electronegativity with the ability to oxidize manyother substances. Only fluorine has higher electronegativity and is thus a stronger oxidizer.Besides the essential use to support life, oxygen has many other uses.It is used in the smelting process to free metals from their ores. It is particularly importantin the oxygen-converter process in the production of steel from iron ore.
Oxygen is used in making several important synthetic gases and in the production ofammonia, methyl alcohol, and so on.
It is the oxidizer for liquid rocket fuels, and as a gas, oxygen is used in a mixture withhelium to support the breathing of astronauts and divers and to aid patients who have difficultybreathing. It is use to treat (oxidize) sewage and industrial organic wastes.
Oxygen has many uses because of its ability to accept electrons from other elements to formionic bonds or to share electrons with other elements to form covalent bonds.
생산 방법
Oxygen is the most prevalent element in the Earth’s crust, making up 49.2% by weight. It accounts for 20.95% by volume of the Earth’s atmosphere and approximately 65% by weight of the human body.정의
Dioxygen: the normal form of molecularoxygen, O2, used to distinguishit from oxygen atoms or fromozone (O3).일반 설명
Oxygen is a colorless, odorless and tasteless gas. Oxygen will support life. Oxygen is noncombustible, but will actively support the burning of combustible materials. Some materials that will not burn in air will burn in Oxygen. Materials that burn in air will burn more vigorously in Oxygen. As a non-liquid gas Oxygen is shipped at pressures of 2000 psig or above. Pure Oxygen is nonflammable. Under prolonged exposure to fire or intense heat the containers may rupture violently and rocket. Oxygen is used in the production of synthesis gas from coal, for resuscitation and as an inhalant.반응 프로필
Propellant; ignites upon contact with alcohols, alkali metals, amines, ammonia, beryllium alkyls, boranes, dicyanogen, hydrazines, hydrocarbons, hydrogen, nitroalkanes, powdered metals, silanes, or thiols [Bretherick 1979. p.174]. Heat of water will vigorously vaporize liquid Oxygen, pressures may build to dangerous levels if this occurs in a closed container. Liquid Oxygen gives a detonable mixture when combined with powdered aluminum [NFPA 491M. 1991].위험도
Although oxygen itself is not flammable or explosive, as is sometimes believed, its mainhazard is that, in high concentrations, oxygen can cause other materials to burn much morerapidly.Oxygen is toxic and deadly to breathe when in a pure state at elevated pressures. In addition,such pure oxygen promotes rapid combustion and can produce devastating fires, such asthe fire that killed the Apollo 1 crew on a test launch pad in 1967. It spread rapidly because thepure oxygen was at normal pressure rather than the one-third pressure used during flight.
Oxygen used for therapeutic purposes in adults can cause convulsions if the concentrationis too high. At one time, high levels of oxygen were given to premature infants to assist theirbreathing. It was soon discovered that a high concentration of O2 caused blindness in some ofthe infants. This practice has been abandoned, or the oxygen levels have since been reduced,and this is no longer a medical problem.
Oxygen involved in metabolic processes are prone to form “free radicals,” which arethought to cause damage to cells and possibly be associated with cancer and aging.
건강위험
Inhalation of 100% Oxygen can cause nausea, dizziness, irritation of lungs, pulmonary edema, pneumonia, and collapse. Liquid may cause frostbite of eyes and skin.화재위험
Behavior in Fire: Increases intensity of any fire. Mixtures of liquid Oxygen and any fuel are highly explosive.인화성 및 폭발성
Oxygen itself is nonflammable, but at concentrations greater than 25% supports and vigorously accelerates the combustion of flammable materials. Some materials (including metals) that are noncombustible in air will burn in the presence of oxygen.농업용
Oxygen (O) is an odorless, colorless, gaseous element that belongs to group 16 (formerly group VI) of the Periodic Table. It is the most abundant element in the earth's crust (49.2% by weight), is present in the atmosphere (20% by volume) and is a constituent of water. It exists in three isotopes 16, 17 and 18. Oxygen is essential for respiration of most living organisms and for combustion. It is used in metallurgical processes, in high temperature flames (welding) and in medical treatment.The common form of oxygen is di-atomic oxygen (O2) There is also another form - reactive allotrope ozone (O3)C.h emically, oxygen reacts with most other elements forming oxides. For industrial use, it is obtained by fractional distillation of liquid air. This has been replaced by a process which utilizes ambient temperature separation by means of a pressure cycle in which molecular sieves of synthetic zeolite preferentially absorb nitrogen from air, giving 95 % oxygen and 5 % argon.
The most popular industrial use of oxygen is in oxygen enrichment of steel blast furnaces. Large quantities of oxygen are used in the synthesis of nitric acid from ammonia, methanol and ethylene oxide, as also in oxy-acetylene welding.
잠재적 노출
Compressed oxygen is used in various oxidation processes, for feedstock; and enrichment purposes; as a medicinal gas; a chemical intermediate; in oxyacetylene welding; in metallurgy. Liquid oxygen is used as a rocket fuel. Oxygen is naturally present at a concentration of 21% in breathing air.Carcinogenicity
Exposure to ionizing radiation is recognized as a cause of cancer, and the production of free radicals in the exposed cells is a part of the process. If hyperoxia causes free radical formation, it may contribute to the occurrence of cancer. Although a direct relation of hyperoxic injury and cancer has not been proven, numerous instances of association in experimental animals exist. Reactive oxidative intermediates have been shown to cause chromosome breaks and damage to DNA that can initiate carcinogenesis. Experimental work done with mouse skin tumors (as models of human tumors) has been both revealing and confusing. A substance may act as a cancer initiator or as a promoter, or sometimes both, depending on intensity and duration of exposure, and the presence of other carcinogenic materials. The same substance can also inhibit cancer growth. Hyperoxia has clearly been involved in modifying the course of tumor development, but the effects have differed under varying circumstances.환경귀착
Atmospheric air contains 20.8% O2. Despite consumption of O2 through respiration and oxidative processes, this concentration remains constant, most likely due to the depleted O2 being replaced by plant-generated O2 in the photosynthetic process. O2 does not bioaccumulate in organisms as pure oxygen.운송 방법
UN1072 Oxygen, compressed & UN1073 Oxygen, refrigerated liquid (cryogenic liquid), Hazard Class: 2.2; Labels: 2.2-Nonflammable compressed gas; 5.1- Oxidizer. Cylinders must be transported in a secure upright position, in a well-ventilated truck. Protect cylinder and labels from physical damage. The owner of the compressed gas cylinder is the only entity allowed by federal law (49CFR) to transport and refill them. It is a violation of transportation regulations to refill compressed gas cylinders without the express written permission of the owner.Purification Methods
Purify it by passing the gas over finely divided platinum at 673oK and Cu(II) oxide (see under nitrogen) at 973o, then condensed in a liquid N2-cooled trap. HIGHLY EXPLOSIVE in contact with organic matter.비 호환성
A strong oxidizer. Reacts violently with nearly every element, combustibles, organics, and reducing materials.폐기물 처리
Return refillable compressed gas cylinders to supplier. Vent to atmosphere.산소, 냉각된 액체 준비 용품 및 원자재
원자재
준비 용품
산소, 냉각된 액체 공급 업체
| 공급자 | 전화 | 이메일 | 국가 | 제품 수 | 이점 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Henan Tianfu Chemical Co.,Ltd. | +86-0371-55170693 +86-19937530512 |
info@tianfuchem.com | China | 21622 | 55 |
| Hubei Jusheng Technology Co.,Ltd. | 18871490254 |
linda@hubeijusheng.com | CHINA | 28172 | 58 |
| Hubei xin bonus chemical co. LTD | 86-13657291602 |
linda@hubeijusheng.com | CHINA | 22963 | 58 |
| Dideu Industries Group Limited | +86-29-89586680 +86-15129568250 |
1026@dideu.com | China | 22866 | 58 |
| Hebei Fengjia New Material Co., Ltd | +86-0311-87836622 +86-18712993135 |
sales01@tairunfaz.com | China | 8051 | 58 |
| PT CHEM GROUP LIMITED | +86-85511178; +86-85511178; |
peter68@ptchemgroup.com | China | 35425 | 58 |
| XIAMEN AMITY INDUSTRY AND TRADE CO., LTD. | +8618950047208 |
ellena@amitychem.com | China | 43416 | 58 |
| Mainchem Co., Ltd. | +86-0592-6210733 |
sale@mainchem.com | China | 32343 | 55 |
| Chemwill Asia Co.,Ltd. | 86-21-51086038 |
chemwill_asia@126.com | CHINA | 23912 | 58 |
| Wuhan eastop Technology Co., ltd.6 | 027-87382885 17702779303 |
service@isotopechina.com | China | 311 | 58 |