Mercury chloride
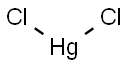
- CAS No.
- 7487-94-7
- Chemical Name:
- Mercury chloride
- Synonyms
- HgCl2;MERCURIC CHLORIDE;Mercury dichloride;MERCURY(II) CHLORIDE;MERCURIC BICHLORIDE;LHGG;Sulem;tl898;TL 898;Sulema
- CBNumber:
- CB1134977
- Molecular Formula:
- Cl2Hg
- Molecular Weight:
- 271.5
- MOL File:
- 7487-94-7.mol
- Modify Date:
- 2025/1/27 9:38:02
| Melting point | 277 °C(lit.) |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 302 °C |
| Density | 5.44 |
| bulk density | 2000kg/m3 |
| vapor pressure | 1.3 mm Hg ( 236 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.859 |
| Flash point | 302°C |
| storage temp. | Store at RT. |
| solubility | H2O: soluble |
| form | powder |
| color | White |
| Specific Gravity | 5.44 |
| PH | 3.2 (15g/L in H2O) |
| Odor | odorless |
| Water Solubility | 7.4 g/100 mL (20 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,5876 |
| Dielectric constant | 3.2(Ambient) |
| Stability | Stable, but moisture sensitive and light sensitive - decomposes in sunlight. Incompatible with strong acids, ammonia, carbonates, metallic salts, alkalies, phosphites, phosphates, sulfites, sulfates, arsenic, antimony, bromides. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7487-94-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Mercury dichloride(7487-94-7) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Mercuric chloride (7487-94-7) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |     GHS05,GHS06,GHS08,GHS09 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H300-H314-H341-H361f-H372-H410 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P260-P273-P280-P303+P361+P353-P304+P340+P310-P305+P351+P338 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | T+,N,T | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 28-34-48/24/25-50/53-51/53-48/21/22-25-68-62-27-24/25 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 36/37/39-45-60-61-28-26-36/37 | |||||||||
| RIDADR | UN 1624 6.1/PG 2 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 3 | |||||||||
| RTECS | OV9100000 | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 6.1 | |||||||||
| PackingGroup | II | |||||||||
| Hazardous Substances Data | 7487-94-7(Hazardous Substances Data) | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Mercury chloride price More Price(25)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 215465 | Mercury(II) chloride ACS reagent, ≥99.5% | 7487-94-7 | 100G | ₹6256.85 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 215465 | Mercury(II) chloride ACS reagent, ≥99.5% | 7487-94-7 | 500G | ₹19181.9 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 1.04417 | Mercury(II) chloride fine cryst. EMPLURA? | 7487-94-7 | 100G | ₹18780 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 1.04417 | Mercury(II) chloride fine cryst. EMPLURA? | 7487-94-7 | 1044171000 | ₹74510.01 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| ALFA India | ALF-010808-36 | Mercury(II) chloride, Puratronic™, 99.999% (metals basis) | 7487-94-7 | 500g | ₹49903 | 2022-05-26 | Buy |
Mercury chloride Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Chemical Properties
Mercuric chloride,HgC12, is white crystals that are soluble in water and alcohol that melt at 276℃ and boil at 302℃. Highly toxic and corrosive, it is used in the manufacture of mercury compounds, in organic synthesis, as a reagent and catalyst, as a fungicide, insecticide, and wood preservative, and for many other purposes.
Uses
Preserving (kyanizing) wood and anatomical specimens; also embalming; disinfecting; browning and etching steel and iron; intensifier in photography; white reserve in fabric printing; tanning leather; electroplating aluminum; depolarizer for dry batteries; freeing gold from lead; magic photograms; mordant for rabbit and beaver furs; staining wood and vegetable ivory pink; manufacture of ink for mercurography; treating seed potatoes; manufacture of other mercury Compounds. As an important reagent In animal chemistry.
Definition
ChEBI: A mercury coordination entity made up of linear triatomic molecules in which a mercury atom is bonded to two chlorines. Water-soluble, it is highly toxic. Once used in a wide variety of applications, including preserving wood and anatomical specimens, emba ming and disinfecting, as an intensifier in photography, as a mordant for rabbit and beaver furs, and freeing gold from lead, its use has markedly declined as less toxic alternatives have been developed.
General Description
An odorless white crystalline solid. Density 5.4 g / cm3. Melting point 277°C. Slightly volatile at ordinary temperatures. Can be sublimed unchanged. Corrosive to the mucous membranes. Toxic by inhalation (dusts, etc.), ingestion, and skin absorption. Used in photography, disinfectants, wood preservatives, fungicides.
Air & Water Reactions
Slightly soluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Mercury chloride is decomposed by sunlight. Incompatible with formates sulfites, phpophosphites, phosphates, sulfides, albumin, gelatin, alkalis, alkaloid salts, ammonia, lime water, antimony, arsenic, bromides, borax, carbonates, reduced iron, iron, copper, lead and silver salts, infusions of cinchona, oak bark or senna, tannic acids and vegetable astringents. .
Hazard
Toxic by ingestion, inhalation, and skin absorption; a poison.
Health Hazard
Mercury chloride is classified as extremely toxic. All forms of mercury are poisonous if absorbed. Probable oral lethal dose is 5-50 mg/kg; between 7 drops and 1 teaspoonful for a 150 lb. person. Mercury chloride is one of the most toxic salts of mercury. Material attacks the gastrointestinal tract and renal systems.
Fire Hazard
Material may explode on heating, with friction, or contact with alkali metals, sulfides, acetylene, ammonia, and oxalic acid. Upon decomposition highly toxic chloride and mercury fumes are emitted. Avoid formates, sulfites, hypophosphites, phosphates, sulfides, albumin, gelatin, alkalies, alkaloid salts, ammonia, lime water, antimony, arsenic, bromides, borax, carbonates, reduced iron, copper, iron, lead, silver salts, infusions of cinchona, columbo, oak bark or senna, and tannic acid. Mercury chloride may explode with friction or application of heat. Mixtures of Mercury chloride and sodium or potassium are shock sensitive and will explode on impact. Avoid contact with acids or acid fumes.
Safety Profile
A human poison by ingestion. Poison experimentally by ingestion, skin contact, and subcutaneous routes. Human systemic effects by ingestion: respiratory obstruction, nausea or vomiting, urine volume decrease or anuria. Human reproductive effects by ingestion: terminates pregnancy. Experimental teratogenic and reproductive effects. Human mutation data reported. Questionable carcinogen. A severe eye and skin irritant. Reaction with sodmm aci-nitromethanide + acids forms the explosive mercury fulminate. Reacts violently with K, Na. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of Hg.
Potential Exposure
Mercuric chloride is used as dip for bulbs and tubers; for earthworm control; as repellent to ants, roaches, etc.; in preserving wood and anatomical specimens; embalming, browning, etching steel and iron; as a catalyst for organic synthesis; disinfectant, antiseptic, tanning; textile printing aid; manufacture of dyes; in agricultural chemicals; dry batteries; pharmaceuticals, and photographic chemicals
Environmental Fate
Mercury adsorbed from mercuric chloride and 2-methoxyethylmercury chloride (Aretan) solutions by three contrasting soils showed a dependence on soil–solution ratio and initial mercury (Hg) concentration in soil solution. Changing the soil–solution ratio from 1:10 to 1:100 but keeping the initial concentration constant resulted in an increase in initial concentration but, on the other hand, resulted in decrease in Hg adsorption. Upon manipulation of the pH of the surface soils, adsorption of mercuric chloride at 100 mg Hg l-1 concentration increased from ~ 70 to over 95 mg Hg kg-1 when the pH was raised from 5.0 to 8.0. Precipitation of Hg may also have contributed to this trend. Removal of organic matter from soil resulted in large reductions of Hg adsorbed, as much as 95% from the mercuric chloride solutions. Mercuric compounds found in the atmosphere are likely to be transformed by chemical or physical processes. Theoretical calculations on the photodissociation of mercuric compounds have indicated that mercuric chloride and mercuric cyanide are stable, while mercuric hydroxide may dissociate in the gas phase. Exchange reactions between water and mercury compounds are likely to occur in the atmosphere. These exchange reactions eventually result in the release of elemental mercury into the gaseous phase.
Shipping
UN1624 Mercuric chloride, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials.
Purification Methods
It is soluble in EtOH and is extracted into Et2O from an aqueous solution. It is very POISONOUS and 0.2-0.4g is fatal. The antidote is immediate administration of white of egg as an emetic.
Incompatibilities
A strong reducing agent; keep away from oxidizers. Mercuric chloride may explode with friction or application on heat. Mixtures of mercuric chloride and sodium or potassium are shock sensitive and will explode on impact. Avoid contact with acids or acid fumes. Also avoid the presence of formats, sulfites, hypophosphites, phosphates, sulfide; albumin, gelatin, alkalies, alkaloid salts; ammonia, lime water; antimony, arsenic, bromides, borax, carbonates, reduced iron, copper; iron, lead, silver salts; infusions of cinchona; columbo, oak bark or senna; and tannic acid
Mercury chloride Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
Preparation Products
1of2
chevron_right7487-94-7(Mercury chloride )Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




