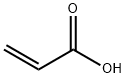
Acrylic acid
- CAS No.
- 79-10-7
- Chemical Name:
- Acrylic acid
- Synonyms
- Acrylate;2-PROPENOIC ACID;Glacial acrylic acid;PROPENOIC ACID;CH2=CHCOOH;Propensαure;Acroleic acid;prop-2-enoicacid;acrylated MonoMers;2-Propenoic acid (I)
- CBNumber:
- CB7307797
- Molecular Formula:
- C3H4O2
- Molecular Weight:
- 72.06
- MOL File:
- 79-10-7.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
- Modify Date:
- 2024/7/24 13:33:21
| Melting point | 13 °C (lit.) |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 139 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 1.051 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| vapor density | 2.5 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 4 mm Hg ( 20 °C) |
| refractive index |
n |
| Flash point | 130 °F |
| storage temp. | Store at +15°C to +25°C. |
| solubility | 1000g/l |
| form | Liquid |
| pka | 4.25(at 25℃) |
| color | Clear |
| Odor | Acrid odor |
| PH Range | 1 - 2 |
| PH | 3.68(1 mM solution);3.14(10 mM solution);2.63(100 mM solution); |
| explosive limit | 3.9-19.8%(V) |
| Water Solubility | MISCIBLE |
| Sensitive | Air Sensitive |
| λmax | 231nm(lit.) |
| Merck | 14,130 |
| BRN | 635743 |
| Exposure limits | TLV-TWA 10 ppm (30 mg/m3) (ACGIH). |
| Stability | Stability Unstable - may contain p-methoxyphenol as an inhibitor. Prone to hazardous polymerization. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong bases, amines. Contact with oxidizers may cause fire. Light and air sensitive. Hygroscopic. |
| LogP | 0.46 at 25℃ |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 79-10-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| IARC | 3 (Vol. 19, Sup 7, 71) 1999 |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | 2-Propenoic acid(79-10-7) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Acrylic acid (79-10-7) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |     GHS02,GHS05,GHS07,GHS09 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H226-H302+H312+H332-H314-H335-H410 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P210-P273-P280-P303+P361+P353-P304+P340+P310-P305+P351+P338 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | C,N | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 10-20/21/22-35-50 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 26-36/37/39-45-61 | |||||||||
| OEB | B | |||||||||
| OEL | TWA: 2 ppm (6 mg/m3) [skin] | |||||||||
| RIDADR | UN 2218 8/PG 2 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 1 | |||||||||
| RTECS | AS4375000 | |||||||||
| F | 8-13 | |||||||||
| Autoignition Temperature | 744 °F | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 8 | |||||||||
| PackingGroup | II | |||||||||
| HS Code | 29161110 | |||||||||
| Toxicity | LD50 orally in rats: 2.59 g/kg (Smyth) | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Acrylic acid price More Price(20)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 8.00181 | Acrylic acid (stabilised with hydroquinone monomethyl ether) for synthesis | 79-10-7 | 100ML | ₹5350 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 8.00181 | Acrylic acid (stabilised with hydroquinone monomethyl ether) for synthesis | 79-10-7 | 500ML | ₹6170 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 8.00181 | Acrylic acid (stabilised with hydroquinone monomethyl ether) for synthesis | 79-10-7 | 1L | ₹8910 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 147230 | Acrylic acid anhydrous, contains 200?ppm MEHQ as inhibitor, 99% | 79-10-7 | 5G | ₹297.69 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 147230 | Acrylic acid anhydrous, contains 200?ppm MEHQ as inhibitor, 99% | 79-10-7 | 100G | ₹596.46 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
Acrylic acid Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Acrylic acid (IUPAC: prop-2-enoic acid) is an organic compound with the formula CH2=CHCO2H. It is the simplest unsaturated carboxylic acid, consisting of a vinyl group connected directly to a carboxylic acid terminus. This colorless liquid has a characteristic acrid or tart smell. It is miscible with water, alcohols, ethers, and chloroform. More than one billion kilograms are produced annually.
Chemical Properties
Acrylic acid is a colorless, flammable, and corrosive liquid or solid (below 13 C) with an irritating, rancid, odor. Sinks and mixes with water; irritating vapor is produced.
Uses
Acrylic acid is produced by oxidation of acrolein or hydrolysis of acrylonitrile. It is used in the manufacture of plastics; in paints, polishes, and adhesives; and as coatings for leather.
Production Methods
Acrylic acid is produced from propene which is a by product of ethylene and gasoline production. CH2=CHCH3 + 1.5 O2→ CH2=CHCO2H + H2O Because acrylic acid and its esters have long been valued commercially, many other methods have been developed but most have been abandoned for economic or environmental reasons. An early method was the hydrocarboxylation of acetylene ("Reppe chemistry") : HCCH + CO + H2O → CH2=CHCO2H This method requires nickel carbonyl and high pressures of carbon monoxide. It was once manufactured by the hydrolysis of acrylonitrile which is derived from propene by ammoxidation, but was abandoned because the method cogenerates ammonium derivatives. Other now abandoned precursors to acrylic acid include ethenone and ethylene cyanohydrin.
Definition
An unsaturated liquid carboxylic acid with a pungent odor. The acid and its esters are used to make ACRYLIC RESINS.
General Description
Acrylic acid is a colorless liquid with a distinctive acrid odor. Flash point 130°F. Boiling point 286°F. Freezing point 53°F. Corrosive to metals and tissue. Prolonged exposure to fire or heat can cause polymerization. If polymerization takes place in a closed container, violent rupture may occur. The inhibitor (usually hydroquinone) greatly reduces the tendency to polymerize.
Air & Water Reactions
Flammable. Soluble in water. The presence of water, due to different solubilities of the acid and inhibitor (partitioning one from the other), may initiate polymerization.
Reactivity Profile
ACRYLIC ACID may polymerize violently especially when the frozen acid is partially thawed (freezing point 12°C or 53°F). Frozen acid should be melted at room temperature and the process should be well stirred. Do not use heat during the melting process [Kirk-Othmer, 3rd ed., Vol. 1, 1978, p. 330]. Corrodes iron and steel and polymerization may occur on contact with iron salts. The uninhibited acid polymerizes exothermically at ambient temperature and explodes if confined. The inhibitor (usually hydroquinone) greatly reduces the tendency to polymerize. Explosive polymerization can also occur with strong bases, amines, ammonia, oleum, chlorosulfonic acid, and peroxides. Mixing with 2-aminoethanol, 28% ammonium hydroxide, ethylenediamine or ethyleneimine in a closed container causes an increase in temperature and pressure. Can react violently with oxidizing reagents and strong bases [Bretherick, 5th ed., 1995, p. 419].
Health Hazard
Acrylic acid is a corrosive liquid that cancause skin burns. Spill into the eyes candamage vision. The vapors are an irritantto the eyes. The inhalation hazard is oflow order. An exposure to 4000 ppm for4 hours was lethal to rats. The oral LD50values reported in the literature show widevariation. The dermal LD50 value in rabbitsis 280 mg/kg.
Fire Hazard
Combustible liquid; flash point (closed cup)
54°C (130°F), (open cup) 68°C (155°F);
vapor pressure 31 torr at 25°C (77°F); vapor
density 2.5 (air=1); autoignition temperature 360°C (680°F). Vapors of acrylic acid
form explosive mixtures with air within the
range 2.9–8.0% by volume in air. Fireextinguishing agent: water spray, “alcohol”
foam, dry chemical, or CO2; use a water
spray to flush and dilute the spill and to disperse the vapors.
Acrylic acid may readily polymerize at
ambient temperature. Polymerization may
be inhibited with 200 ppm of hydroquinone
monomethyl ether (Aldrich 2006). In the
presence of a catalyst or at an elevated temperature, the polymerization rate may accelerate, causing an explosion. The reactions of
acrylic acid with amines, imines, and oleum
are exothermic but not violent. Acrylic acid
should be stored below its melting point with
a trace quantity of polymerization inhibitor.
Its reactions with strong oxidizing substances
can be violent.
Contact allergens
Acrylates are esters from acrylic acid. Occupational contact allergies from acrylates have frequently been reported and mainly concern workers exposed to the glues based on acrylic acid, as well as dental workers and beauticians.
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion, skin contact, and intraperitoneal routes. An experimental teratogen. Other experimental reproductive effects. A severe skin and eye irritant. Questionable carcinogen with experimental carcinogenic and tumorigenic data. Corrosive. Flammable liquid. May undergo exothermic polymerization at room temperature. May become explosive if confined. A fire hazard when exposed to heat or flame.
Safety
Acrylic acid is severely irritating and corrosive to the skin and the respiratory tract. Eye contact can result in severe and irreversible injury. Low exposure will cause minimal or no health effects, while high exposure could result in pulmonary edema. The LD50 is 340 mg/kg (rat, oral).
Potential Exposure
Acrylic acid is chiefly used in manufacture of plastics, acrylates, polyacrylic acids, polymer, and resins; as a monomer in the manufacture of acrylic resins and plastic products, leather treatment, and paper coatings. Also, it is used as a tackifier and flocculant.
Environmental Fate
Acrylic acid is corrosive, and its toxicity occurs at the site of contact.
Shipping
UN2218 Acrylic acid, stabilized, Hazard class: 8; Labels: 8-Corrosive material, 3-Flammable liquid
Purification Methods
It can be purified by steam distillation, or vacuum distillation through a column packed with copper gauze to inhibit polymerisation. (This treatment also removes inhibitors such as methylene blue that may be present.) Azeotropic distillation of the water with *benzene converts aqueous acrylic acid to the anhydrous material. [Beilstein 2 H 397, 2 I 186, 2 II 383, 2 III 1215, 2 IV 1455.]
Incompatibilities
May form explosive mixture with air. Light, heat, and peroxides can cause polymerization. Use MEHQ (monomethyl ether of hydroquinone) as an inhibitor. Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides. Incompatible with sulfuric acid, caustics, ammonia, amines, isocyanates, alkylene oxides; epichlorohydrin, toluene diamine, oleum, pyridine, methyl pyridine, n-methyl pyrrolidone, 2-methyl-6-ethyl aniline, aniline, ethylene diamine, ethyleneimine, and 2aminoethanol. Severely corrodes carbon steel and iron; attacks other metals. May accumulate static electrical charges and may cause ignition of its vapors.
Waste Disposal
Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant (≥100 kg/mo) must conform with EPA regulations governing storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal. Incineration. 100 500 ppm potassium permanganate will degrade acrylic acid to a hydroxy acid which can be disposed of at a sewage treatment.
Acrylic acid Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
1of3
chevron_rightPreparation Products
1of8
chevron_right| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANJI BIOSCIENCES | +91-9000100077 +91-9000100077 | Hyderabad, India | 430 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Soham Chemical Industries | +91-7016081644 +91-7016081644 | Mumbai, India | 83 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Nyne Organics Pvt Ltd | +91-9920180386 +91-9920180386 | Mumbai, India | 53 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Chem stride | +91-8169461298 +91-8169461298 | Maharashtra, India | 27 | 58 | Inquiry |
| UNILOSA INTERNATINAL PRIVATE LIMITED | +91-9999069917 +91-9999069917 | New Delhi, India | 152 | 58 | Inquiry |
| PAARICHEM RESOURCES LLP | +91-8104961021 +91-8104961021 | Maharashtra, India | 82 | 58 | Inquiry |
| JSK Chemicals | +919879767970 | Gujarat, India | 3756 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Bharat Petroleum Corporation Limited | +91-22714000 +91-2222713000 | Maharashtra, India | 17 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Gujarat Polysol Chemicals Pvt Ltd | +91-9825117532 +91-9833725951 | Gujarat, India | 5 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Acuro Organics Limited | +91-8882777000 +91-8882777000 | New Delhi, India | 44 | 58 | Inquiry |
Related articles
- Production methods of acrylic acid
- Acrylic acid is an important organic synthesis raw material and a synthetic resin monomer, and is a vinyl monomer with a very ....
- Mar 8,2022





