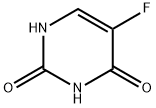
5-Fluorouracil
- CAS No.
- 51-21-8
- Chemical Name:
- 5-Fluorouracil
- Synonyms
- 51-21-8;5-FU;FLUOROURACIL;5-FLUOROPYRIMIDINE-2,4(1H,3H)-DIONE;FU;Efudex;Efudix;Adrucil;Fluracil;Fluoracil
- CBNumber:
- CB8162744
- Molecular Formula:
- C4H3FN2O2
- Molecular Weight:
- 130.08
- MOL File:
- 51-21-8.mol
- Modify Date:
- 2024/11/16 15:32:52
| Melting point | 282-286 °C (dec.) (lit.) |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 190-200°C/0.1mmHg |
| Density | 1.4593 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | H2O: 10 mg/mL, clear |
| form | powder |
| pka | pKa 8.0±0.1 (H2O) (Uncertain);3.0±0.1(H2O) (Uncertain) |
| color | white |
| PH | 4.3-5.3 (10g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
| Water Solubility | 12.2 g/L 20 ºC |
| Sensitive | Air Sensitive |
| Merck | 14,4181 |
| BRN | 127172 |
| Stability | Stable. Light sensitive. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong bases. |
| InChIKey | GHASVSINZRGABV-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 51-21-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| IARC | 3 (Vol. 26, Sup 7) 1987 |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | 2,4-Pyrimidinedione, 5-fluoro-(51-21-8) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 5-Fluorouracil (51-21-8) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |   GHS06,GHS08 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H301-H351 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P201-P202-P264-P270-P280-P301+P310 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | Xn,T,C,Xi | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 22-20/21/22-52-25 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 36-36/37-36/37/39-22-45-26 | |||||||||
| RIDADR | UN 2811 6.1/PG 3 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 3 | |||||||||
| RTECS | YR0350000 | |||||||||
| F | 10-23 | |||||||||
| Hazard Note | Irritant/Highly Toxic | |||||||||
| TSCA | T | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 6.1 | |||||||||
| PackingGroup | III | |||||||||
| HS Code | 29335995 | |||||||||
| Toxicity | LD50 orally in Rabbit: 230 mg/kg | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
5-Fluorouracil price More Price(22)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | PHR1227 | Fluorouracil Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material | 51-21-8 | 500MG | ₹11355.43 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | F8423 | Fluorouracil meets USP testing specifications | 51-21-8 | 5G | ₹12535.35 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | F6627 | 5-Fluorouracil ≥99% (HPLC), powder | 51-21-8 | 1G | ₹2706.25 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | F8423 | Fluorouracil meets USP testing specifications | 51-21-8 | 10G | ₹23306.23 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | F6627 | 5-Fluorouracil ≥99% (HPLC), powder | 51-21-8 | 5G | ₹9320.33 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
5-Fluorouracil Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) is a prodrug form of the thymidylate synthase inhibitor fluorodeoxyuridylate (FdUMP). It is also converted to the active metabolites FUTP and FdUTP, which induce RNA and DNA damage, respectively. In vivo, 5-FU (15 mg/kg) when administered in combination with docetaxel reduces tumor growth in B88 and CAL 27 oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) mouse xenograft models. Formulations containing 5-FU have been used in the treatment of colorectal, breast, gastric, and pancreatic cancers.
Chemical Properties
White or almost white, crystalline powder
Uses
5-Fluorouracil is used as an antitumor agent in the treatment of anal, breast, colorectal, oesophageal, stomach, pancreatic and skin cancers. It finds application as a suicide inhibitor due to its irreversible inhibition of thymidylate synthase. It is also used in the treatment of actinic keratoses and bowen's disease. Further, it serves as a potent antineoplastic agent in clinical use. In addition to this, it acts as a DNA synthesis inhibitor.
Indications
Fluorouracil (5-fluorouracil, 5-fluorouracil, Efudex,
Adrucil) is a halogenated pyrimidine analogue that
must be activated metabolically. The active metabolite
that inhibits DNA synthesis is the deoxyribonucleotide
5-fluoro-2'deoxyuridine-S'-phosphate (FdUMP). 5-
Fluorouracil is selectively toxic to proliferating rather
than non-proliferating cells and is active in both the G1-
and S-phases. The target enzyme inhibited by 5-fluorouracilfluorouracil is thymidylate synthetase.
methylenetetrahydrofolate dihydrofolate
The carbon-donating cofactor for this reaction is
N5,N10 methylenetetrahydrofolate, which is converted
to dihydrofolate. The reduced folate cofactor occupies
an allosteric site on thymidylate synthetase, which allows
for the covalent binding of 5-FdUMP to the active
site of the enzyme.
General Description
White to nearly white crystalline powder; practically odorless. Used as an anti neoplastic drug, chemosterilant for insects.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
5-Fluorouracil may be sensitive to prolonged exposure to light. Solutions discolor on storage. 5-Fluorouracil can react with oxidizing agents and strong bases. Incompatible with methotrexate sodium.
Hazard
Questionable carcinogen.
Health Hazard
Minimum toxic dose in humans is approximately 450 mg/kg (total dose) over 30 days for the ingested drug. Intravenous minimum toxic dose in humans is a total dose of 6 mg/kg over three days. Depression of white blood cells occurred after intravenous administrative of a total dose of 480 mg/kg over 32 days. Occasional neuropathy and cardiac toxicity have been reported. Do not use during pregnancy. Patients with impaired hepatic or renal function, with a history of high-dose pelvic irradiation or previous use of alkylating agents should be treated with extreme caution. Patients with nutritional deficiencies and protein depletion have a reduced tolerance to 5-Fluorouracil.
Fire Hazard
Emits very toxic fumes of flourides and nitrogen oxides when heated to decomposition. Avoid decomposing heat.
Biological Activity
Anticancer agent. Metabolized to form fluorodeoxyuridine monophosphate (FdUMP), fluorodeoxyuridine triphosphate (FdUTP) and fluorouridine (FUTP). FdUMP inhibits thymidylate reductase causing a reduction in dTMP synthesis. FUTP and FdUTP are misincorporated into RNA and DNA respectively.
Mechanism of action
Another action proposed for 5-fluorouracil may involve
the incorporation of the nucleotide 5-fluorouridine
triphosphate (5-FUTP) into RNA. The cytotoxic
role of these “fraudulent” 5-fluorouracil-containing
RNAs is not well understood.
Several possible mechanisms of resistance to 5-fluorouracil
have been identified, including increased synthesis
of the target enzyme, altered affinity of thymidylate
synthetase for FdUMP, depletion of enzymes
(especially uridine kinase) that activate 5-fluorouracil
to nucleotides, an increase in the pool of the normal
metabolite deoxyuridylic acid (dUMP), and an increase
in the rate of catabolism of 5-fluorouracil.
The drug has been administered orally, but absorption
by this route is erratic. The plasma half-life of 5-
fluorouracil after intravenous injection is 10 to 20 minutes.
It readily enters CSF. Less than 20% of the parent
compound is excreted into the urine, the rest being
largely metabolized in the liver.
Mechanism of action
5-Fluorouracil (FU) is converted intracellularly to several active metabolites: fluorodeoxyuridine monophosphate (FdUMP), fluorodeoxyuridine triphosphate (FdUTP), and fluorouridine triphosphate (FUTP). The active metabolites of 5-FU disrupt RNA synthesis (FUTP), inhibit the action of thymidylate synthase (TS)—a nucleotide synthetic enzyme (FdUMP)—and can also be directly misincorporated into DNA (FdUTP). The rate-limiting enzyme in 5-FU catabolism is dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPD), which converts 5-FU to dihydrofluorouracil (DHFU). Over 80% of administered 5-FU is normally catabolized primarily in the liver, where DPD is abundantly expressed.
5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) is converted to three major active metabolites: (1) fluorodeoxyuridine monophosphate (FdUMP), (2) fluorodeoxyuridine triphosphate (FdUTP), and (3) fluorouridine triphosphate (FUTP). The main mechanism of 5-FU activation is conversion to fluorouridine monophosphate (FUMP) either directly by orotate phosphoribosyl transferase (OPRT), or indirectly via fluorouridine (FUR) through the sequential action of uridine phosphorylase (UP) and uridine kinase (UK). FUMP is then phosporylated to fluorouridine diphosphate (FUDP), which can be either further phosphorylated to the active metabolite fluorouridine triphosphate (FUTP), or converted to fluorodeoxyuridine diphosphate (FdUDP) by ribonucleotide reductase (RR). In turn, FdUDP can either be phosphorylated or dephosphorylated to generate the active metabolites FdUTP and FdUMP respectively. An alternative activation pathway involves the thymidine phosphorylase catalyzed conversion of 5-FU to fluorodeoxyuridine (FUDR), which is then phosphorylated by thymidine kinase (TK) to the thymidylate synthase (TS) inhibitor, FdUMP. Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPD)-mediated conversion of 5-FU to dihydrofluorouracil (DHFU) is the rate-limiting step of 5-FU catabolism in normal and tumor cells.
Pharmacology
Local inflammatory reactions characterized by erythema, edema, crusting, burning, and pain are common (and, some would argue, desirable) but may be minimized by reduced frequency of application or use in combination with a topical corticosteroid.
Clinical Use
5-Fluorouracil (FU) is widely used in the treatment of a range of cancers including breast and cancers of the aerodigestive tract, but has had the greatest impact in colorectal cancer. 5-FU-based chemotherapy improves overall and disease-free survival of patients with resected stage III colorectal cancer. Nonetheless, response rates for 5-FU-based chemotherapy as a first-line treatment for advanced colorectal cancer are only between 10 and 15%. Combination of 5-FU with newer chemotherapies, such as irinotecan and oxaliplatin, has improved the response rates for advanced colorectal cancer to between 40 and 50%.
Side effects
Patients who are genetically deficient in this enzyme will experience a more pronounced effect from this drug and are at significant risk for use-limiting toxicity. In general, women clear fluorouracil faster than men do. Dosage adjustments usually are not required in hepatic or renal dysfunction. Major toxicities are related to bone marrow depression, stomatitis/esophagopharyngitis, and potential GI ulceration. Nausea and vomiting are common. Solutions of fluorouracil are light sensitive, but discolored products that have been properly stored and protected from light are still safe to use.
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion, intraperitoneal, subcutaneous, and intravenous routes. Moderately toxic by parented and rectal routes. Experimental teratogenic and reproductive effects. Human systemic effects: EKG changes, bone marrow changes, cardiac, pulmonary, and gastrointestinal effects. Human mutation data reported. A human skin irritant. Questionable carcinogen. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of Fand NOx.
Potential Exposure
This material is used as an antineo plastic drug for cancer treatment and as a chemosterilant for insects.
Shipping
UN2811 Toxic solids, organic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required.
Incompatibilities
Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explo sions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides, methotrexrate sodium, sources of heat.
5-Fluorouracil Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
1of2
chevron_rightPreparation Products
1of2
chevron_right| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jigs Chemical ltd | +919099003427 | Gujarat, India | 239 | 58 | Inquiry |
| JSK Chemicals | +919879767970 | Gujarat, India | 3753 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Rivashaa Agrotech Biopharma Pvt. Ltd. | +91-26463395 +91-7926462688 | Gujarat, India | 1615 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Aspen Biopharma Labs Pvt Ltd | +91-9248058660 +91-9248058662 | Telangana, India | 234 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Pallav Chemicals And Solvents Pvt Ltd | +91-9136093115 +91-9136093115 | Maharashtra, India | 1364 | 58 | Inquiry |
| SS Reagents and Chemicals | +91-7981238883 +91-7981238883 | Hyderabad, India | 404 | 58 | Inquiry |
| TCI Chemicals (India) Pvt. Ltd. | 1800 425 7889 | New Delhi, India | 6768 | 58 | Inquiry |
| A.J Chemicals | 91-9810153283 | New Delhi, India | 6100 | 58 | Inquiry |
| CLEARSYNTH LABS LTD. | +91-22-45045900 | Hyderabad, India | 6257 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Central Drug House(P) Ltd. | 91-11-49404040 | New Delhi, India | 6157 | 58 | Inquiry |
Related articles
- The structure and mechanism of action of 5-Fluorouracil
- 5-Fluorouracil is the third most commonly used chemotherapeutic agent in the treatment of solid malignancies across the world.
- Dec 4,2023
- Side effects related to 5-Fluorouracil
- 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) is a commonly used chemotherapeutic drug that is widely prescribed for the treatment of various types of....
- Oct 23,2023
- The pharmaceutical analysis of 5-fluorouracil
- 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) is widely used in the treatment of cancer
- Jun 6,2022
Related Qustion
- Q:What conditions can 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) Injection be used to treat?
- A:5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) injection is not only used as an anticancer agent for the treatment of many types of cancers such as bre....
- Nov 5,2024
- Q:What cancers does 5-fluorouracil treat for?
- A:5-fluorouracil (5-FU) is a drug given as an injection to treat cancers of the breast, colon, rectum, stomach, and pancreas.
- Aug 29,2024
51-21-8(5-Fluorouracil)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




