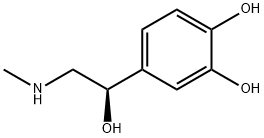
L(-)-Epinephrine
- CAS No.
- 51-43-4
- Chemical Name:
- L(-)-Epinephrine
- Synonyms
- EPINEPHRINE;ADRENALINE;L-ADRENALINE;ADRENALIN;Epinefrina;EPINEPHRIN;EPINEPHERINE;L-EPINEPHRINE;Adrenaline Base;(-)-EPINEPHRINE
- CBNumber:
- CB8322199
- Molecular Formula:
- C9H13NO3
- Molecular Weight:
- 183.2
- MOL File:
- 51-43-4.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
- Modify Date:
- 2024/8/28 13:53:27
| Melting point | 215 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
|---|---|
| alpha | -51.5 º (c=4, 1M HCl, dry sub) |
| Boiling point | 316.88°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.1967 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | -51.5 ° (C=4, 1mol/L HCl) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Practically insoluble in water, in ethanol (96 per cent) and in methylene chloride. It dissolves in hydrochloric acid. |
| pka | 8.66(at 25℃) |
| form | Fine Crystalline Powder |
| color | White to light beige |
| optical activity | -53.222~25 (c 1.2, 0.5 mol dm-3 HCl)-50.617 (c 7.5, 0.37 mol dm-3 HCl), L +50.5 (HCl) |
| Water Solubility | <0.01 g/100 mL at 18 ºC |
| Sensitive | Air & Light Sensitive |
| Decomposition | > 212°C |
| Merck | 14,3619 |
| BRN | 2368277 |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with acids, acid chlorides, acid anhydrides, oxidizing agents. Light sensitive. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 51-43-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | L-adrenaline(51-43-4) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Epinephrine (51-43-4) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |  GHS06 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H301+H331-H310 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P261-P262-P280-P301+P310-P302+P352+P310-P304+P340+P311 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | T | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 23/24/25-52/53-36/37/38-33 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 36/37/39-45-61-26-23 | |||||||||
| RIDADR | UN 2811 6.1/PG 2 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 3 | |||||||||
| RTECS | DO2625000 | |||||||||
| F | 8-10-23 | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 6.1 | |||||||||
| PackingGroup | II | |||||||||
| HS Code | 29373100 | |||||||||
| Toxicity | LD50 i.p. in mice: 4 mg/kg (Lands) | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
L(-)-Epinephrine price More Price(7)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | E4250 | (−)-Epinephrine | 51-43-4 | 1G | ₹3193.38 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | E4250 | (−)-Epinephrine | 51-43-4 | 5G | ₹10023.95 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | E4250 | (−)-Epinephrine | 51-43-4 | 10G | ₹16724.63 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| ALFA India | ALF-L04911-14 | L-Adrenaline, 98+% | 51-43-4 | 25g | ₹13418 | 2022-05-26 | Buy |
| ALFA India | ALF-L04911-06 | L-Adrenaline, 98+% | 51-43-4 | 5g | ₹9690 | 2022-05-26 | Buy |
L(-)-Epinephrine Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
The combination of the catechol nucleus, the β-hydroxyl group, and the N-methyl give EPI a direct action and a strong affinity for all adrenergic receptors. Epinephrine and all other catechols are chemically susceptible to oxygen and other oxidizing agents, especially in the presence of bases and light, quickly decomposing to inactive quinones. Therefore, all catechol drugs are stabilized with antioxidants and dispensed in air-tight amber containers.
Chemical Properties
off-white powder
Uses
Endogenous catcholamine with combined α-and β-agonist activity. Principal sympathomimetic hormone produced by the adrenal medulla. Bronchodilator; cardiostimulant; mydriatic; antiglaucoma.
Definition
ChEBI: The R-enantiomer of adrenaline. It is a hormone secreted by the adrenal glands resulting in the 'fight-or-flight' response.
Indications
Epinephrine administered subcutaneously is used to manage severe acute episodes of bronchospasm and status asthmaticus. In addition to its bronchodilator activity through β-adrenoceptor stimulation, a portion of the therapeutic utility of epinephrine in these acute settings may be due to a reduction in pulmonary edema as a result of pulmonary vasoconstriction, the latter effect resulting from α-adrenoceptor stimulation.
Production Methods
Epinephrine is synthesized in the body from the nonessential amino acid tyrosine. Tyrosineundergoes hydroxylation to produce DOPA (3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine). DOPA decarboxylationproduces dopamine, which is hydroxylated to norepinephrine. Norepinephrine, whichis closely related to epinephrine, performs a number of similar functions in the body. The prefix “nor” associated with a compound is used to denote an alkylated nitrogen in the compoundthat has lost an alkyl group. It comes from the German N-ohne-radical, which means Nitrogenwithout the radical. Therefore norepinephrine is epinephrine minus the methyl, CH3, radicalon the nitrogen. The methylation of norepinephrine gives epinephrine.
World Health Organization (WHO)
Epinephrine, first isolated in 1899, is the main hormone secreted by the adrenal medulla. It is widely used as a vasoconstrictor substance and in the treatment of anaphylactic shock. Its use in combination with local anaesthetics to prolong infiltration anaesthesia has been associated with systemic reactions including serious cardiovascular and cerebrovascular incidents. Regulations restricting the concentrations permitted in such preparations have been introduced in many countries but combination products containing epinephrine or levarterenol in concentrations of 1:80,000 or less remain widely available. Representative preparations are included in the WHO Model List of Essential Drugs. (Reference: (WHTAC1) The Use of Essential Drugs, 2nd Report of the WHO Expert Committee, 722, , 1985)
Biological Functions
Epinephrine is found only in very low concentrations in the mammalian CNS, and it is unlikely to play a major role as a neurotransmitter.
General Description
White to nearly-white microcrystalline powder or granules. Odorless. Melting point 211-212°C. Aqueous solutions are slightly alkaline. Slightly bitter, numbing taste.
Air & Water Reactions
L(-)-Epinephrine darkens slowly on exposure to air and light. Water insoluble. Readily soluble in aqueous solutions of inorganic acids. Solutions undergo oxidation in the presence of oxygen.
Reactivity Profile
L(-)-Epinephrine is incompatible with oxidizers, alkalis, copper, iron, silver, zinc and other metals; gum and tannin. L(-)-Epinephrine is also incompatible with acids, acid chlorides and acid anhydrides. L(-)-Epinephrine reacts with salts of sulfurous acid .
Fire Hazard
Flash point data for L(-)-Epinephrine are not available. L(-)-Epinephrine is probably combustible.
Mechanism of action
The effects on pulmonary function are quite rapid, with peak effects occurring within 5 to 15 minutes. Measurable improvement in pulmonary function is maintained for up to 4 hours.The characteristic cardiovascular effects seen at therapeutic doses of epinephrine include increased heart rate, increased cardiac output, increased stroke volume, an elevation of systolic pressure and decrease in diastolic pressure, and a decrease in systemic vascular resistance. The cardiovascular response to epinephrine represents the algebraic sum of both α- and β-adrenoceptor stimulation. A decrease in diastolic blood pressure and a decrease in systemic vascular resistance are reflections of vasodilation, a β2-adrenoceptor response. The increase in heart rate and systolic pressure is the result of either a direct effect of epinephrine on the myocardium, primarily a β1 effect, or a reflex action provoked by a decrease in peripheral resistance, mean arterial pressure, or both. Overt α-adrenoceptor effects, such as systemic vasoconstriction, are not obvious unless large doses are used.
Clinical Use
The ability of epinephrine to stimulate β2-receptors hasled to its use by injection and by inhalation to relaxbronchial smooth muscle in asthma and in anaphylacticreactions. Several OTC preparations (e.g., Primatene, Bronkaid)used for treating bronchial asthma use E. It is also usedin inhibiting uterine contraction. Because of its α-activity, Eis used to treat hypotensive crises and nasal congestion, toenhance the activity of local anesthetics, and as a constrictorin hemorrhage.
In addition, E is used in the treatment of open-angle glaucoma,where it apparently reduces intraocular pressure byincreasing the rate of outflow of aqueous humor from theanterior chamber of the eye. The irritation often experiencedon instillation of E into the eye has led to the developmentof other preparations of the drug that potentially are not asirritating. One such example is dipivefrin.
Side effects
Patients treated with recommended dosages of epinephrine will complain of feeling nervous or anxious. Some will have tremor of the hand or upper extremity and many will complain of palpitations. Epinephrine is dangerous if recommended dosages are exceeded or if the drug is used in patients with coronary artery disease, arrhythmias, or hypertension. The inappropriate use of epinephrine has resulted in extreme hypertension and cerebrovascular accidents, pulmonary edema, angina, and ventricular arrhythmias, including ventricular fibrillation. At recommended dosages, adverse effects from inhaled isoproterenol are infrequent and not serious. When excessive dosages are used, tachycardia, dizziness, and nervousness may occur, and some patients may have arrhythmias.
Safety Profile
Human poison by subcutaneous route. Experimental poison by ingestion, skin contact, subcutaneous, intraperitoneal, intravenous, and intramuscular routes. Human systemic effects: cardiomyopathy includmg infarction, arrhythmias. An experimental teratogen. Experimental reproductive effects. Mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx. Used as an adrenergic, sympathomimetic, vasoconstrictor, bronchodilator, and cardiac stimulant.
Metabolism
Epinephrine is ultimately metabolized by COMT and MAO to 3-methoxy-4-hydroxy-mandelic acid (vanillylmandelic acid), which is excreted as the sulfate or glucuronide in the urine. Only a very small amount is excreted unchanged.
Purification Methods
L-Adrenaline has been recrystallised from EtOH/AcOH/NH3 [Jensen J Am Chem Soc 57 1765 1935]. Itis sparingly soluble in H2O, readily in acidic or basic solutions but insoluble in aqueous NH3, alkali carbonate solutions, EtOH, CHCl3, Et2O or Me2CO. It has also been purified by dissolving in dilute aqueous acid, then precipitating it by adding dilute aqueous ammonia or alkali carbonates. It is readily oxidised in air and turns brown on exposure to light and air. (Epinephrine readily oxidises in neutral alkaline solution. This can be diminished if a little sulfite is added). Store it in the dark under N2. [Lewis Br J Pharmacol Chemother 9 488 1954]. The hydrogen oxalate salt has m 191-192o(dec, evacuated capillary) after recrystallisation from H2O or EtOH [Pickholz J Chem Soc 928 1945]. [Beilstein 13 H 830, 13 III/IV 2927.]
L(-)-Epinephrine Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
Preparation Products
| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Apex Healthcare Limited | +9199825711244 | Gujarat, India | 22 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Harman Finochem Ltd | +91-2226528080 +91-2226528080 | Maharashtra, India | 37 | 58 | Inquiry |
| S D Fine Chem Limited | +91-9323715856 +91-9323715856 | Maharashtra, India | 368 | 58 | Inquiry |
| TCI Chemicals (India) Pvt. Ltd. | 1800 425 7889 | New Delhi, India | 6778 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Alfa Aesar | 1 800 209 7001 | Maharashtra, India | 6913 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Central Drug House(P) Ltd. | 91-11-49404040 | New Delhi, India | 6160 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Pharmaffiliates Analytics and Synthetics P. Ltd | +91-172-5066494 | Haryana, India | 6773 | 58 | Inquiry |
| SynZeal Research Pvt Ltd | +1 226-802-2078 | Gujarat, India | 6522 | 58 | Inquiry |
| LOBA CHEMIE PVT.LTD. | 91-22-6663 6699 | Mumbai, India | 3077 | 58 | Inquiry |
| ALPHA CHEMIKA | +91-22-22061123 +91-22-66382501 | Mumbai, India | 1681 | 43 | Inquiry |
Related articles
- The Pharmacodynamics of L(-)-Epinephrine and Its Role in Anaphylaxis Management
- L(-)-Epinephrine is a sympathomimetic drug that activates beta-1 and beta-2 receptors, providing relief from asthma, croup, an....
- Dec 26,2023
- L(-)-Epinephrine: Physiological effects and clinical applications
- L(-)-Epinephrine regulates blood pressure, heart rate, metabolism, and the immune system. It is used in resuscitation and anes....
- Aug 2,2023
- Uses of Epinephrine
- Epinephrine stimulates both the alpha- and beta-adrenergic systems, causes systemic vasoconstriction and gastrointestinal rela....
- Dec 22,2021





