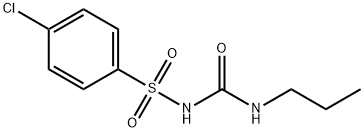
CHLORPROPAMIDE
- CAS No.
- 94-20-2
- Chemical Name:
- CHLORPROPAMIDE
- Synonyms
- p607;P-607;u-3818;u-9818;Adiaben;Asucrol;Catanil;Glisema;Meldian;Oradian
- CBNumber:
- CB8677954
- Molecular Formula:
- C10H13ClN2O3S
- Molecular Weight:
- 276.74
- MOL File:
- 94-20-2.mol
- Modify Date:
- 2024/7/2 8:55:37
| Melting point | 128 °C |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 302°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.3046 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.6300 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Room Temperature |
| solubility | Chloroform (Sparingly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | pKa 4.8 (Uncertain) |
| color | White to Light Yellow |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in ethanol (1:12), acetone (1:5), chloroform (1:9) and solutions of alkali hydroxides. Does not mix well with water. |
| Merck | 14,2186 |
| Stability | Stable. Combustible. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 94-20-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Chloropropamide (94-20-2) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |   GHS07,GHS08 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Warning | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H302-H361f-H373 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P202-P260-P264-P270-P301+P312-P308+P313 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | Xn | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 20/21/22-40 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 22-36 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 3 | |||||||||
| RTECS | YS6650000 | |||||||||
| HS Code | 29350090 | |||||||||
| Toxicity | LD50 i.p. in rats: 580 mg/kg (Goldenthal) | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
CHLORPROPAMIDE price More Price(3)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | PHR1284 | Chlorpropamide Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material | 94-20-2 | 1G | ₹8107.93 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | C1290 | Chlorpropamide analytical standard, ≥97% | 94-20-2 | 25G | ₹12221.43 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| TCI Chemicals (India) | C1220 | 1-(4-Chlorophenylsulfonyl)-3-propylurea | 94-20-2 | 25G | ₹4000 | 2022-05-26 | Buy |
CHLORPROPAMIDE Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Chemical Properties
white crystalline powder
Uses
Chlorpropamide is a sulfonylurea derivative. Chlorpropamide is a long acting hyopglycemic agent. Chlorpropamide is used in the treatment of diabetes metilus type 2. Chlorpropamide acts to increase the secretion of insulin and is not effective in patients who do not have pancreatic beta cell function.
Definition
ChEBI: An N-sulfonylurea that is urea in which a hydrogen attached to one of the nitrogens is substituted by 4-chlorobenzenesulfonyl group and a hydrogen attached to the other nitrogen is substituted by propyl group. Chlorpropamide is a hypogly aemic agent used in the treatment of type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus not responding to dietary modification.
General Description
Chlorpropamide is 4-chloro-N-[(propylamino)carbonyl]benzenesulfonamide; or 1-[(p-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl]-3-propylurea; or 1-(p-chlorobenzenesulfonyl)-3-propylurea(Diabinese, generic). The p-chlorophenyl moiety is quite resistantto P450-mediated hydroxylations; hence, blood levelsof the drug are sustained for a markedly long length of time,as aliphatic hydroxylation constitutes most of the clearance,and this happens relatively slowly. Although the -hydroxyland (ω–1)-hydroxyl metabolites (the latter formed in muchgreater portion) exert hypoglycemic potencies not much lessthan does the parent drug, elimination of these by conversion to the corresponding glucuronides occurs more rapidly thanhydroxylation of chlorpropamide, so blood levels of thesemetabolites remain low, and thus they probably do not makean appreciable contribution to the hypoglycemic action ofthis drug in clinical application. Removal of the entire propylside chain (oxidative N-dealkylation) also occurs to a significantextent (up to 20% of an orally administered dose), creatingthe inactive metabolite p-chlorobenzenesulfonylurea,about 10% of which degrades to the corresponding benzenesulfonamide.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
A halogenated amide. Organic amides/imides react with azo and diazo compounds to generate toxic gases. Flammable gases are formed by the reaction of organic amides/imides with strong reducing agents. Amides are very weak bases (weaker than water). Imides are less basic yet and in fact react with strong bases to form salts. That is, they can react as acids. Mixing amides with dehydrating agents such as P2O5 or SOCl2 generates the corresponding nitrile. The combustion of these compounds generates mixed oxides of nitrogen (NOx).
Fire Hazard
Flash point data for CHLORPROPAMIDE are not available; however, CHLORPROPAMIDE is probably combustible.
Purification Methods
Crystallise the urea from aqueous EtOH. [Beilstein 11 IV 119.]
CHLORPROPAMIDE Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
Preparation Products
| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kothari Phytochemicals and Industries Ltd. | +91-9244448844 +91-9331023407 | West Bengal, India | 18 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Quantum Drugs Chemicals | +91 9443396658 +91 9362944455 | Tamil Nadu, India | 6 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Medilink Pharmachem | +91 (79) 3007-0133 | New Delhi, India | 424 | 50 | Inquiry |
| OCEAN TRADING CORPORATION | +91(22) 24921669 | New Delhi, India | 6211 | 58 | Inquiry |
| TCI Chemicals (India) Pvt. Ltd. | 1800 425 7889 | New Delhi, India | 6778 | 58 | Inquiry |
| SynZeal Research Pvt Ltd | +1 226-802-2078 | Gujarat, India | 6522 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Triveni chemicals | 08048762458 | New Delhi, India | 6093 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Pharmaffiliates Analytics and Synthetics P. Ltd | +91-172-5066494 | Haryana, India | 6773 | 58 | Inquiry |
| PNR Impex | 07942548368 | Mumbai, India | 81 | 58 | Inquiry |
| A.J Chemicals | 91-9810153283 | New Delhi, India | 6124 | 58 | Inquiry |
94-20-2(CHLORPROPAMIDE)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




