1-Butanol
- CAS No.
- 71-36-3
- Chemical Name:
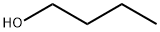
- 1-Butanol
- Synonyms
- n-Butanol;BuOH;NBA;n-BuOH;n-Butyl alcohol;Normal Butanol;butanols;1-Butano;Butanol-1;1-Butyl alcohol
- CBNumber:
- CB9113046
- Molecular Formula:
- C4H10O
- Molecular Weight:
- 74.12
- MOL File:
- 71-36-3.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
- Modify Date:
- 2024/7/29 15:17:36
| Melting point | -90 °C (lit.) |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 116-118 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 0.81 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| vapor density | 2.55 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 6.7 hPa (20 °C) |
| refractive index |
n |
| FEMA | 2178 | BUTYL ALCOHOL |
| Flash point | 95 °F |
| storage temp. | Store at +5°C to +30°C. |
| solubility | water: soluble |
| form | Liquid |
| pka | 15.24±0.10(Predicted) |
| color | APHA: ≤10 |
| Relative polarity | 0.586 |
| PH | 7 (70g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
| Odor | Alcohol-like; pungent; strong; characteristic; mildly alcoholic, non residual. |
| explosive limit | 1.4-11.3%(V) |
| Odor Threshold | 0.038ppm |
| Odor Type | fermented |
| Water Solubility | 80 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Sensitive | Moisture Sensitive |
| λmax |
λ: 215 nm Amax: 1.00 λ: 220 nm Amax: 0.50 λ: 240 nm Amax: 0.10 λ: 260 nm Amax: 0.04 λ: 280-400 nm Amax: 0.01 |
| Merck | 14,1540 |
| JECFA Number | 85 |
| BRN | 969148 |
| Henry's Law Constant | 49.2 at 50 °C, 92.0 at 60 °C, 152 at 70 °C, 243 at 80 °C (headspace-GC, Hovorka et al., 2002) |
| Exposure limits | TLV-TWA 300 mg/m3 (100 ppm) (NIOSH), 150 mg/m3 (50 ppm) (ACGIH); IDLH 8000 ppm (NIOSH). |
| Dielectric constant | 17.1(25℃) |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with strong acids, strong oxidizing agents, aluminium, acid chlorides, acid anhydrides, copper, copper alloys. Flammable. |
| LogP | 0.88 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 71-36-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | 1-Butanol(71-36-3) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 1-Butanol (71-36-3) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |    GHS02,GHS05,GHS07 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H226-H302-H315-H318-H335-H336 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P210-P233-P280-P301+P312-P303+P361+P353-P305+P351+P338 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | Xn,T,F | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 10-22-37/38-41-67-39/23/24/25-23/24/25-11 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 13-26-37/39-46-7/9-45-36/37-16-7 | |||||||||
| RIDADR | UN 1120 3/PG 3 | |||||||||
| OEL | Ceiling: 50 ppm (150 mg/m3) [skin] | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 1 | |||||||||
| RTECS | EO1400000 | |||||||||
| Autoignition Temperature | 649 °F | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HS Code | 2905 13 00 | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 3 | |||||||||
| PackingGroup | III | |||||||||
| Toxicity | LD50 orally in rats: 4.36 g/kg (Smyth) | |||||||||
| IDLA | 1,400 ppm | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
1-Butanol price More Price(70)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | W217820 | Butyl alcohol ≥99.5%, FCC, FG | 71-36-3 | 1SAMPLE-K | ₹5272.5 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | W217820 | Butyl alcohol ≥99.5%, FCC, FG | 71-36-3 | 1KG | ₹5905.2 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | W217820 | Butyl alcohol ≥99.5%, FCC, FG | 71-36-3 | 4KG | ₹12665.1 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | W217820 | Butyl alcohol ≥99.5%, FCC, FG | 71-36-3 | 8KG | ₹20268.6 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | W217820 | Butyl alcohol ≥99.5%, FCC, FG | 71-36-3 | 20KG | ₹40115.4 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
1-Butanol Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
n-Butyl alcohol is a colourless flammable liquid with strong alcoholic odour. n-Butyl alcohol is a highly refractive liquid and burns with a strongly luminous flame. It is incompatible with strong acids, strong oxidising agents, aluminium, acid chlorides, acid anhydrides, copper, and copper alloys. n-Butyl alcohol has an extensive use in a large number of industries. For instance, it is used as solvent in industries associated with the manufacturing of paints, varnishes, synthetic resins, gums, pharmaceuticals, vegetable oils, dyes, and alkaloids. n-Butyl alcohol finds its use in the manufacture of artificial leather, rubber, plastic cements, shellac, raincoats, perfumes, and photographic films.
Chemical Properties
1-Butanol is a colorless, volatile liquid with a rancid sweet odor. The air odor threshold of 1-butanol was reported to be 0.83 ppm ; others have identified the minimum concentration with identifiable odor as 11 and 15 ppm.
Physical properties
Clear, colorless liquid with a rancid sweet odor similar to fusel oil. Experimentally determined detection and recognition odor threshold concentrations were 900 μg/m3 (300 ppbv) and 3.0 mg/m3 (1.0 ppmv), respectively (Hellman and Small, 1974). Odor threshold concentration in water is 500 ppb (Buttery et al., 1988). The least detectable odor threshold in concentration water at 60 °C was 0.2 mg/L (Alexander et al., 1982). Cometto-Mu?iz et al. (2000) reported nasal pungency threshold concentrations ranging from approximately 900 to 4,000 ppm.
Occurrence
1-Butanol is a natural product found in Vitis rotundifolia, Cichorium endivia, peppermint oil from Brazil, Achillea ageratum, tea, apple aroma, American cranberry, black currants, guava fruit, papaya, cooked asparagus, tomato, Swiss cheese, Parmesan cheese, heated butter, cognac, Armagnac, rum and cider.
Uses
1-Butanol is used in the production of butylacetate, butyl glycol ether, and plasticizerssuch as dibutyl phthalate; as a solvent in thecoating industry; as a solvent for extractionsof oils, drugs, and cosmetic nail products;and as an ingredient for perfumes and flavor.
1-Butanol occurs in fusel oil and as aby-product of the fermentation of alcoholicbeverages such as beer or wine. It is presentin beef fat, chicken broth, and nonfilteredcigarette smoke (Sherman 1979).
Production Methods
The principal commercial source of 1-butanol is n-butyraldehyde obtained from the oxo reaction of propylene, followed by hydrogenation in the presence of a catalyst . 1-Butanol has also been produced from ethanol via successive dehydrogenation to acetaldehyde, followed by an aldol process. The earliest commercial route to 1-butanol, which is still used extensively in many Third World countries, employs fermentation of molasses or corn products with Clostridium acetobutylicum .
Definition
ChEBI: 1-Butanol is a primary alcohol that is butane in which a hydrogen of one of the methyl groups is substituted by a hydroxy group. It it produced in small amounts in humans by the gut microbes. It has a role as a protic solvent, a human metabolite and a mouse metabolite. It is a primary alcohol, a short-chain primary fatty alcohol and an alkyl alcohol.
General Description
Colorless liquid. Used in organic chemical synthesis, plasticizers, detergents, etc.
Air & Water Reactions
Highly flammable. Soluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
1-Butanol attacks plastics. [Handling Chemicals Safely 1980. p. 236]. Mixtures with concentrated sulfuric acid and strong hydrogen peroxide can cause explosions. May form explosive butyl hypochlorite by reacting with hypochlorous acid. May form butyl explosive butyl hypochlorite with chlorine.
Hazard
Toxic on prolonged inhalation, irritant to eyes. Toxic when absorbed by skin. Flammable, moderate fire risk. Eye and upper respiratory tract irritant.
Health Hazard
The toxicity of 1-butanol is lower than thatof its carbon analog. Target organs are theskin, eyes, and respiratory system. Inhalationcauses irritation of the eyes, nose, and throat.It was found to cause severe injury to rabbits’eyes and to penetrate the cornea uponinstillation into the eyes. Chronic exposureof humans to high concentrations may causephotophobia, blurred vision, and lacrimation.
A concentration of 8000 ppm was maternallytoxic to rats, causing reduced weightgain and feed intake. Teratogenicity wasobserved at this concentration with a slightincrease in skeletal malformations (Nelsonet al. 1989).
In a single acute oral dose, the LD50 value(rats) is 790 mg/kg; in a dermal dose theLD50 value (rabbits) is 4200 mg/kg.
n-Butanol is oxidized in vivo enzymaticallyas well as nonenzymatically and iseliminated rapidly from the body in the urineand in expired air. It inhibits the metabolismof ethanol caused by the enzyme alcoholdehydrogenase.
Based on the available data, the useof n-butanol as an ingredient is consideredsafe under the present practices andconcentrations in cosmetic nail products(Cosmetic, Toiletry and Fragrance Association1987a).
Fire Hazard
HIGHLY FLAMMABLE: Will be easily ignited by heat, sparks or flames. Vapors may form explosive mixtures with air. Vapors may travel to source of ignition and flash back. Most vapors are heavier than air. They will spread along ground and collect in low or confined areas (sewers, basements, tanks). Vapor explosion hazard indoors, outdoors or in sewers. Runoff to sewer may create fire or explosion hazard. Containers may explode when heated. Many liquids are lighter than water.
Safety Profile
A poison by intravenous route. Moderately toxic by skin Review: Group 3 IMEMDT 7,56,87; Animal Inadequate Evidence IMEMDT 39,67,86* contact, ingestion, subcutaneous, and intraperitoneal routes. Human systemic Reported in EPA TSCA Inventory. Community fight-To-Ihow List. OSHA PEL: TWA 10 pprn Classifiable as a Carcinogen DFG MAK: 2 ppm (11 mg/m3) DOT CLASSIFICATION: 3; Label: Flammable Liquid ingestion, inhalation, skin contact, and intraperitoneal routes. Experimental reproductive effects. A skin and eye irritant. Questionable carcinogen. A flammable fight fire, use foam, CO2, dry chemical. Incompatible with oxidzing materials. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid and irritating fumes. See also ESTERS. effects by inhalation: conjunctiva irritation, unspecified respiratory system effects, and nasal effects. Experimental reproductive Though animal experiments have shown the butyl alcohols to possess toxic properties, they have produced few cases of poisoning in industry, probably because of their low reported to have resulted in irritation of the eyes, with corneal inflammation, slight headache and H2ziness, slight irritation of the nose and throat, and dermatitis about fingers. Keratitis has also been reported. Mutation data reported.
Potential Exposure
Butyl alcohols are used as solvents for paints, lacquers, varnishes, natural and synthetic resins, gums, vegetable oils, dyes, camphor, and alkaloids. They are also used as an intermediate in the manufacture of pharmaceuticals and chemicals; in the manufacture of artificial leather, safety glass; rubber and plastic cements, shellac, raincoats, photographic films, perfumes; and in plastic fabrication.
storage
Store n-butyl alcohol in a cool, dry, well-ventilated location, away from smoking areas. Fire hazard may be acute. Outside or detached storage is preferred. Separate from incompatibles. Containers should be bonded and grounded for transfer to avoid static sparks
Shipping
UN1120 Butanols, Hazard Class: 3; Labels: 3— Flammable liquid. UN1212 Isobutanol or Isobutyl alcohol, Hazard Class: 3; Labels: 3—Flammable liquid
Purification Methods
Dry it with MgSO4, CaO, K2CO3, or solid NaOH, followed by refluxing with, and distillation from, small amounts of calcium, magnesium activated with iodine, or aluminium amalgam. It can also be dried with molecular sieves, or by refluxing with n-butyl phthalate or succinate. (For method, see Ethanol.) n-Butanol can also be dried by efficient fractional distillation, water passing over in the first fraction as a binary azeotrope (contains about 37% water). An ultraviolet-transparent distillate has been obtained by drying with magnesium and distilling from sulfanilic acid. To remove bases, aldehydes and ketones, the alcohol is washed with dilute H2SO4, then NaHSO4 solution; esters are removed by boiling for 1.5hours with 10% NaOH. It has also been purified by adding 2g NaBH4 to 1.5L butanol, gently bubbling with argon and refluxing for 1 day at 50o. Then adding 2g of freshly cut sodium (washed with butanol) and refluxed for 1day. Distil and collect the middle fraction [Jou & Freeman J Phys Chem 81 909 1977]. [Beilstein 1 IV 1506.]
Incompatibilities
Butyl alcohols may form explosive mixture with air. In all cases they are Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides. Attacks some plastics, rubber and coatings. n-Butanol is incompatible with strong acids; halogens, caustics, alkali metals; aliphatic amines; isocyanates. sec-Butanol forms an explosive peroxide in air. Ignites with chromium trioxide. Incompatible with strong oxidizers; strong acids; aliphatic amines; isocyanates, organic peroxides. tert-Butanol is incompatible with strong acids (including mineral acid), including mineral acids; strong oxidizers or caustics, aliphatic amines; isocyanates, alkali metals (i.e., lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium, cesium, francium). isoButanol is incompatible with strong acids; strong oxidizers; caustics, aliphatic amines; isocyanates, alkali metals and alkali earth. May react with aluminum at high temperatur
Waste Disposal
Incineration, or bury absorbed waste in an approved land fill.
1-Butanol Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
1of4
chevron_rightPreparation Products
1of8
chevron_right| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AnalyticsStanza Inc | +91-7032031309 +91-7032031309 | Hyderabad, India | 227 | 58 | Inquiry |
| UNILOSA INTERNATINAL PRIVATE LIMITED | +91-9999069917 +91-9999069917 | New Delhi, India | 152 | 58 | Inquiry |
| JSK Chemicals | +919879767970 | Gujarat, India | 3756 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Ultra Chemical Works | +91-9820078105 +91-9820078105 | Mumbai, India | 124 | 58 | Inquiry |
| GODAVARI BIOREFINERIES LTD | 9769972334 | Maharashtra, India | 26 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Merck Ltd | +91-2262109800 +91-2262109000 | Maharashtra, India | 272 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Bharat Petroleum Corporation Limited | +91-22714000 +91-2222713000 | Maharashtra, India | 17 | 58 | Inquiry |
| The Andhra Petrochemicals Ltd. APL | +919223323806 | Telangana, India | 3 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Silverline Chemicals | +91-9810339289 +91-9810339289 | Haryana, India | 71 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Ridhdhi Sidhdhi Chemicals | +91 9909006960 +91 9909006962 | Gujarat, India | 13 | 58 | Inquiry |
Related articles
- The polarity analysis of 1-Butanol
- 1-Butanol is a vital chemical platform used as feedstock in the plastic industry, plasticizers, paints, binders, and food extr....
- Jan 3,2024
- 1-Butanol: Applications and Toxicity
- 1-Butanol is a primary alcohol with a 4-carbon structure.
- May 8,2023
- What is 1-Butanol?
- What is 1-Butanol?
- Apr 19,2021
71-36-3(1-Butanol)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




