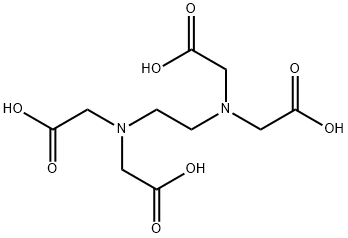
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
- CAS No.
- 60-00-4
- Chemical Name:
- Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
- Synonyms
- EDTA;EDTA ACID;Trilon B;EDETIC ACID;Trilon;Titriplex;VERSENE;Ethylenediaminetetraacetate;([2-(Bis-carboxymethyl-amino)-ethyl]-carboxymethyl-amino)-acetic acid;HAMPENE ACID
- CBNumber:
- CB9853940
- Molecular Formula:
- C10H16N2O8
- Molecular Weight:
- 292.24
- MOL File:
- 60-00-4.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
- Modify Date:
- 2024/8/1 23:06:22
| Melting point | 250 °C (dec.) (lit.) |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 434.18°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.46 g/cm3 at 20 °C |
| vapor pressure | <0.013 hPa (20 °C) |
| refractive index |
n |
| Flash point | >400°C DIN 51758 |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | 3 M NaOH: 100 mg/mL |
| pka | pKa 2 (Uncertain);10.26 (Uncertain) |
| form | crystalline |
| color | White to almost white |
| Odor | Odorless |
| PH Range | 2.5 at 10 g/l at 23 °C |
| PH | 2.5 (10g/l, H2O, 23℃)(slurry) |
| Water Solubility | 0.5 g/L (25 ºC) |
| λmax | λ: 280 nm Amax: ≤0.25 |
| Decomposition | 240 °C |
| Merck | 14,3517 |
| BRN | 1716295 |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with copper, copper alloys, nickel, aluminium, strong oxidizing agents, strong bases |
| LogP | -0.836 (est) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 60-00-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | N,N'-1,2-Ethane diylbis-(N-(carboxymethyl)glycine)(60-00-4) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (60-00-4) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |  GHS07 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Warning | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H319 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P264-P280-P305+P351+P338-P337+P313 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | Xi | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 36-52/53-36/37/38-36/38 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 26-61-37/39-36 | |||||||||
| RIDADR | UN 3077 9 / PGIII | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 2 | |||||||||
| RTECS | AH4025000 | |||||||||
| F | 3 | |||||||||
| Autoignition Temperature | >200 °C | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HS Code | 2922 49 85 | |||||||||
| Toxicity | LD50 orally in Rabbit: 2580 mg/kg | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid price More Price(64)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | RDD017 | Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid anhydrous, free-flowing, powder, Redi-Dri?, ACS reagent, 99.4-100.6% | 60-00-4 | 500G | ₹12059.05 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | RDD017 | Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid anhydrous, free-flowing, powder, Redi-Dri?, ACS reagent, 99.4-100.6% | 60-00-4 | 1KG | ₹17817.95 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | EDS | Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid BioUltra, anhydrous, ≥99% (titration) | 60-00-4 | 100G | ₹2800 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | PHR2586 | Edetic Acid | 60-00-4 | 1G | ₹20415.95 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | EDS | Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid BioUltra, anhydrous, ≥99% (titration) | 60-00-4 | 500G | ₹9070 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid (EDTA) is a common polydentate ligand. In EDTA, the hydrogen atoms are easily removed
in solution to produce anionic EDTA4-. In its anionic form Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid (EDTA) has six binding atoms, two
nitrogen and four oxygen.
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid (EDTA) binds to a metal ion at the six binding sites, wrapping itself around the metal ion,
forming a very stable complex.the strong grasp of Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid (EDTA) on the metal ion is analogous
to a crab or lobster clamping down on an object with its claw, hence the name chelation.
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid (EDTA) is such an effective chelating agent because it can deactivate a metal at up to six sites.
Chemical Properties
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid is a solid.
History
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid (EDTA) was first synthesized in the early 1930s by the German chemist Ferdinand Münz working for I. G. Farben. Münz, who was looking for a substitute for citric acid to use with dye solutions in the textile industry, was the first to patent a process for Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid (EDTA) synthesis in Germany in 1935. Münz subsequently applied for United States patents in 1936 and 1937 (U.S. Patent Number 2130505); his method involved reacting monochloroacetic acid (C2H3ClO2) and ethylene diamine (C2H8N2). Concurrent with Münz’s work, Frederick C. Bersworth in the United States synthesized Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid (EDTA) using different methods that gave greater yields and made EDTA’s commercial production economically viable. Bersworth syntheses involved reacting formaldehyde, amines, and hydrogen cyanide. Bersworth and Münz obtained patents for Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid (EDTA) production in the 1940s (U.S. Patent Numbers 2407645 and 2461519).
Uses
antispasmodic
Production Methods
Edetic acid may be prepared by the condensation of ethylenediamine
with sodium monochloroacetate in the presence of sodium
carbonate. An aqueous solution of the reactants is heated to about
90°C for 10 hours, then cooled, and hydrochloric acid is added to
precipitate the edetic acid.
Edetic acid may also be prepared by the reaction of ethylenediamine
with hydrogen cyanide and formaldehyde with subsequent
hydrolysis of the tetranitrile, or under alkaline conditions with
continuous extraction of ammonia.
Definition
An organic chelating agent.
General Description
Ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid is a colorless crystalline solid. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid is slightly soluble in water. The primary hazard is the threat to the environment. Immediate steps should be taken to limit its spread to the environment. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid is used in chemical analysis, to make detergents and cleaning compounds, and for many other uses.
Air & Water Reactions
Slightly soluble in water.
Agricultural Uses
EDTA is short for ethylenediamhetetraacetic acid, an amino polycarboxylic acid. It is a tetraprotic acid and is represented as H4Y with four carboxyl groups and two nitrogen atoms acting as ligand sites. Thus the compound is a hexadentate ligand. Ligands include ions such as Cl-, NO2-and CN- or neutral molecules like NH3 and H2O, which possess a lone pair of electrons that can be shared with a metal cation in coordinate covalent bonds.
The water solubility of EDTA is very low and, therefore, its di-sodium salt Na2H2Y.2H2O is commonly used in titrations. The Y4- forms very stable, one-to-one complexes with practically every metal ion in the Periodic Table. The reactions are carried out in a neutral or alkaline medium as the complex decomposes in acidic medium.
(and hence deterioration) of the food product, (d) to increase the storage life of whole blood by removing free calcium ions (Ca2+) to inhibit clotting, and (e) for extracting trace elements, especially copper. EDTA metal complexes, such as NaFeEDTA, MnEDTA, ZnEDTA and CuEDTA are used as fertilizers and foliar sprays.
Biological Activity
Chelating agent; sequesters di- and trivalent metal ions.
Safety Profile
Poison by intraperitoneal route. Experimental teratogenic and reproductive effects. Mutation data reported. A general-purpose chelaung and complexing agent. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx.
Safety
Edetic acid and edetates are widely used in topical, oral, and
parenteral pharmaceutical formulations. They are also extensively
used in cosmetics and food products.
Edetic acid is generally regarded as an essentially nontoxic and
nonirritant material, although it has been associated with doserelated
bronchoconstriction when used as a preservative in
nebulizer solutions. It has therefore been recommended that
nebulizer solutions for bronchodilation should not contain edetic
acid.
Edetates, particularly disodium edetate and edetate calcium
disodium, are used in a greater number and variety of pharmaceutical
formulations than the free acid.
Disodium edetate, trisodium edetate, and edetic acid readily
chelate calcium and can, in large doses, cause calcium depletion
(hypocalcemia) if used over an extended period or if administered
too rapidly by intravenous infusion. If used in preparations for the
mouth, they can also leach calcium from the teeth. In contrast,
edetate calcium disodium does not chelate calcium.
Edetate calcium disodium is nephrotoxic and should be used
with caution in patients with renal impairment.
The WHO has set an estimated acceptable daily intake for
disodium edetate in foodstuffs at up to 2.5 mg/kg body-weight.
LD50 (mouse, IP): 0.25 g/kg
LD50 (rat, IP): 0.397 g/kg
Potential Exposure
EDTA is a white, odorless, crystalline material or white powder
Environmental Fate
EDTA can be very persistent in water, including wastewatertreatment plants. EDTA is often found in the receiving waters of many industrial areas, thus being classified as one of the major organic pollutants discharged in waters. The available ecotoxicity data for EDTA indicate that these compounds are slow to degrade under typical environmental conditions but are not expected to bioconcentrate. EDTA compounds range from practically nontoxic to moderately toxic on an acute basis, depending on the salt. Algae and invertebrates are among the most sensitive species based on predictive modeling for acute and chronic endpoints for EDTA, depending on the compound. EDTA and its salts also do not appear to be very toxic for terrestrial wild mammals, and adverse effects from reasonably expected agricultural uses are not expected.
storage
Although edetic acid is fairly stable in the solid state, edetate salts
are more stable than the free acid, which decarboxylates if heated
above 150°C. Disodium edetate dihydrate loses water of crystallization
when heated to 120°C. Edetate calcium disodium is slightly
hygroscopic and should be protected from moisture.
Aqueous solutions of edetic acid or edetate salts may be sterilized
by autoclaving, and should be stored in an alkali-free container.
Edetic acid and edetates should be stored in well-closed
containers in a cool, dry place.
Shipping
UN3082 Environmentally hazardous substances, liquid, n.o.s., Hazard class: 9; Labels: 9-Miscellaneous hazardous material, Technical Name Required
Purification Methods
Dissolve EDTA in aqueous KOH or ammonium hydroxide, and precipitate it twice with dilute HCl or HNO3. Boil it twice with distilled water to remove mineral acid, then recrystallise it from water or dimethylformamide. Dry it at 110o. It also recrystallises from boiling 1N HCl; wash the crystals with distilled H2O and dry them in vacuo. [Ma & Ray Biochemistry 19 751 1980, Beilstein 4 IV 2449.]
Incompatibilities
Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides, copper, copper alloys, and nickel
Regulatory Status
Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (oral, otic, rectal, and topical preparations; submucosal injection preparations). Included in nonparenteral medicines licensed in the UK. Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients.
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
1of4
chevron_rightPreparation Products
1of3
chevron_right| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GLR Innovations | +91 9891111994 | New Delhi, India | 4542 | 58 | Inquiry |
| ANJI BIOSCIENCES | +91-9000100077 +91-9000100077 | Hyderabad, India | 430 | 58 | Inquiry |
| ADVENT CHEMBIO PRIVATE LIMITED | +91-9821524116 +91-9821524116 | Mumbai, India | 353 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Yogi Dye Chem Industries | +91-9821098577 +91-9821098577 | Mumbai, India | 124 | 58 | Inquiry |
| SYNOVA CHEMICALS | +91-9920741772 +91-9920741772 | Mumbai, India | 428 | 58 | Inquiry |
| ALLIPO CHEMICALS | +91-8238998187 +91-8238998187 | Gujarat, India | 32 | 58 | Inquiry |
| UNILOSA INTERNATINAL PRIVATE LIMITED | +91-9999069917 +91-9999069917 | New Delhi, India | 152 | 58 | Inquiry |
| JSK Chemicals | +919879767970 | Gujarat, India | 3756 | 58 | Inquiry |
| AVA CHEMICALS PVT LTD | +91-8879390046 +91-8879390046 | Maharashtra, India | 74 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Kronox Lab Sciences Pvt Ltd | +91-9313231074 +91-9313231074 | Gujarat, India | 240 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Supplier | Advantage |
|---|---|
| GLR Innovations | 58 |
| ANJI BIOSCIENCES | 58 |
| ADVENT CHEMBIO PRIVATE LIMITED | 58 |
| Yogi Dye Chem Industries | 58 |
| SYNOVA CHEMICALS | 58 |
| ALLIPO CHEMICALS | 58 |
| UNILOSA INTERNATINAL PRIVATE LIMITED | 58 |
| JSK Chemicals | 58 |
| AVA CHEMICALS PVT LTD | 58 |
| Kronox Lab Sciences Pvt Ltd | 58 |
Related articles
- EDTA : a chelating agent and anticoagulant
- EDTA is a polyprotic acid containing four carboxylic acid groups and two amine groups with lone-pair electrons that chelate ca....
- Apr 28,2024
- Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid: Application, toxicity and environmental fate
- Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid was developed by Franz Munz in Germany during the 1930s as an alternative to citric acid. EDTA....
- May 9,2023
- The principal toxicity of EDTA
- Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) was developed by Franz Munz in Germany during the 1930s as an alternative to citric aci....
- Oct 18,2021
60-00-4(Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




