Thiosulfan
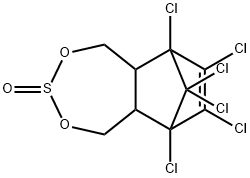
- CAS No.
- 115-29-7
- Chemical Name:
- Thiosulfan
- Synonyms
- ENDOSULFAN;thionate;Benzoepin;ENDOSULFANE;FAN;3-oxide;6,7,8,9,10,10-Hexachloro-1,5,5a,6,9,9a-hexahydro-6,9-methano-2,4,3-benzo[e]-dioxathiepin-3-oxide;Hilda;oms570;ensure
- CBNumber:
- CB6153380
- Molecular Formula:
- C9H6Cl6O3S
- Molecular Weight:
- 406.93
- MOL File:
- 115-29-7.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
- Modify Date:
- 2024/12/18 14:15:30
| Melting point | 106°C |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 106 °C(Press: 0.70 Torr) |
| Density | 1.7450 |
| vapor pressure | 8.3 x 10-4 Pa (25 °C) for 2:l mixture of α- and β-isomers |
| Flash point | -26 °C |
| storage temp. | APPROX 4°C |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Sparingly) |
| Water Solubility | <0.1 g/100 mL at 23 ºC |
| Merck | 13,3608 |
| BRN | 2062338 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 115-29-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Endosulfan(115-29-7) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Endosulfan (115-29-7) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |   GHS06,GHS09 |
|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H300+H310+H330-H410 |
| Precautionary statements | P260-P262-P273-P280-P302+P352+P310-P304+P340+P310 |
| Hazard Codes | T,N,Xn,F,T+ |
| Risk Statements | 24/25-36-50/53-67-65-62-51/53-48/20-38-11-26/28-21 |
| Safety Statements | 28-36/37-45-60-61-62-63-33-29-16-9 |
| RIDADR | UN 2761 |
| OEB | D |
| OEL | TWA: 0.1 mg/m3 [skin] |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | RB9275000 |
| HazardClass | 6.1(a) |
| PackingGroup | II |
| HS Code | 29209090 |
| Hazardous Substances Data | 115-29-7(Hazardous Substances Data) |
| Toxicity | LD50 orally in male, female rats: 43, 18 mg/kg (Gaines) |
Thiosulfan Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Endosulfan (70) [115-29-7], 6,7,8,9,10,10- hexachloro-1,5,5a,6,9,9a-hexahydro-6,9-methano-2,4,3,- benzo-dioxathiepine 3-oxide (IUPAC) [The technical product is a mixture of two isomers: α-endosulfan: 3α,5αβ,6α, 9α,9αβ (64–67%) (70a) and β-endosulfan 3α,5aα,6β,9β, 9aα, (29–32%) (70b)]; [959-98-8] (formerly [33213-66- 0]) (β-endosulfan);[33213-65-9] (formerly [891-86-1] and [19670-15-6]) (β-endosulfan) is the adduct of hexachlorocyclopentadiene and 1,4-dihydroxy-2-butene reacted further with SOCl2 to produce 6,7,8,9,10,10-hexachloro- 1,5,5a,6,9,9a-hexahydro-6,9-methano-2,4,3-benzodioxa thiepin-3-oxide. The technical product is a brownish solid, mp 70–100 ?C, vapor pressure 1.3 mPa at 25 ?C, soluble in petroleum solvents but having low solubility in water. It consists of about four parts of α-isomer (mp 108 ?C, cis with regard to the sulfite group) and one part of the β-isomer (mp 206 ?C, trans with regard to the sulfite group). The α-isomer, which is somewhat more insecticidal, is slowly converted to the more stable β-isomer at high temperature, and both isomers are oxidized slowly to endosulfan sulfate [1031-07-8] (mp 181 ?C). In acid media, both isomers form endosulfan diol [2157-19-9] (mp 203 ?C).
Chemical Properties
(commercial product): Brown crystals. Mixture of two isomers.
Uses
Insecticide.
Definition
ChEBI: A cyclic sulfite ester that is 1,5,5a,6,9,9a-hexahydro-6,9-methano-2,4,3-benzodioxathiepine 3-oxide substituted by chloro groups at positions 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 and 10.
General Description
Endosulfan is a pesticide. It is a cream- to brown-coloured solid that may appear in the form of crystals or flakes. It has a smell like turpentine, but does not burn. It does not occur naturally in the environment. It is a restricted use pesticide, meaning that it can only be used by professional applicators.
Air & Water Reactions
Sightly soluble in water. Slowly hydrolyzes to form sulfur dioxide and a diol; hydrolyzes more rapidly under basic or acidic conditions.
Reactivity Profile
Thiosulfan is an organochlorine, cyclodiene derivative. Thiosulfan is also a sulfite ester. Halogenated aliphatic or cyclic alkane compounds are moderately or very reactive. Reactivity generally decreases with increased degree of substitution of halogen for hydrogen atoms. As Thiosulfan is rather highly substituted Thiosulfan may be resistant to reaction. However, materials in this group are incompatible with strong oxidizing and reducing agents. Also, they may be incompatible with many amines, nitrides, azo/diazo compounds, alkali metals, and epoxides. As an ester, Thiosulfan will hydrolyze to form sulfur dioxide and diol; reaction is more rapid under basic conditions.
Hazard
Toxic by ingestion, inhalation, and skin absorption; use may be restricted. Lower respiratory tract irritant; liver and kidney damage. Questionable carcinogen.
Health Hazard
Thiosulfan is very toxic. The probable oral lethal dose is 50 to 500 mg/kg, or 1 teaspoonful to 1 ounce for a 150 lb. person.
Fire Hazard
Container may explode in heat of fire. Fire or run off from fire control water may release irritating or poisonous gases. Slowly oxidizes in air. Do not store at temperature below 20F.
Agricultural Uses
Insecticide, Acaricide: A U.S. EPA restricted Use Pesticide (RUP). Not approved for use in EU countries. Globally banned as of April 29, 2010. Endosulfan was added to the list of Stockholm Convention Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs): Annex A (Elimination). Endosulfan is a chlorinated hydrocarbon insecticide and acaricide of the cyclodiene subgroup which acts as a poison to a wide variety of insects and mites on contact. Although it may also be used as a wood preservative, it is used primarily on a wide variety of food crops including tea, coffee, fruits, and vegetables, as well as on rice, cereals, maize, sorghum, or other grains. Formulations of endosulfan include emsulsifiable concentrate, wettable powder, ultra-low volume (ULV) liquid, and smoke tablets. It is compatible with many other pesticides and may be found in formulations with dimethoate, malathion, methomyl, monocrotophos, pirimicarb, triazophos, fenoprop, parathion, petroleum oils, and oxine-copper. It is not compatible with alkaline materials. Technical endosulfan is made up of a mixture of two molecular forms (isomers) of endosulfan, the alpha-and beta-isomers.
Trade name
AFIDEN®; BEOSIT®; BIO 5,462®; CHLORTHIEPIN®; CLEAN-CROP®; CRISUFAN®; CYCLODAN®; DE-PESTER®; DESTROY®; DEVISULPHAN®; DISSULFAN CE®; ENDOCEL® ENDOCIDE®; ENDOSOL®; END-O-SULFAN®; ENDOTAF®; ENDOX®; ENSURE®; E-Z FLO®; FMC 5462®; HEXASULFAN®; HILDAN®; HOE 2671®; INSECTO®; INSECTOPHENE®; KENDAN®; KERNTOX®; KOP-THIODAN®; MALIX®; MALUX; MAUX®; MOS-570; METHOFAN®; NCI-C00566; NIA 5462®, NIAGARA 5,462; NIAGARA 5,462®[C]; PHASER®; RASAYANSULFAN; ROCKY®; THIFOR®; THIDAN®; THIMUL®; THIODAN®; α-THIODAN®; β-THIODAN®; THIONEX; α-THIONEX®; β-THIONEX®; THIOKILL®; THIOFOR®; THIONEX®; THIOSULFAN®; THIOSULFAN THIONEL®; THISULFAN TIOVEL; TIONEL; TIOVEL®
Pharmacology
The rat LD50 values are 43, 18 mg/kg (oral) and 130,
74 mg/kg (dermal). The α-isomer has somewhat greater
insecticidal activity and is slowly converted to the more
stable β-isomer at a high temperature. Both isomers
oxidize slowly in air and in biological systems to endosulfan
sulfate [1031-07-8], mp 181–182 ?C. In acid media, both
isomers form endosulfan diol [2157-19-9], mp 203–205 ?C.
Endosulfan is a broad-spectrum insecticide used to control
pests of vegetables, fruit, field crops, and ornamentals.
Unlike other cyclodiene insecticides, it is biodegradable by
hydrolysis at the sulfite ester bonds and is more readily
metabolized. It is also less persistent on plant surfaces,
and 50% of the residues are lost in 3–7 days. Volatilization
may be the major route of loss.
Endosulfan is readily hydrolyzed in water to the diol
(74), but it is moderately persistent in soil. Endosulfan (α-
and β-endosulfan) is degraded in soil with DT50 30 to 70
days. The major metabolite is usually endosulfan sulfate
(71), which is degraded more slowly. In the field DT50
for total endosulfan (α- and β-endosulfan and endosulfan
sulfate) is 5 to 8 months.
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion, inhalation, skin contact, intraperitoneal, and subcutaneous routes. Experimental teratogenic and reproductive effects. Questionable carcinogen with experimental tumorigenic and neoplastigenic data. Human systemic effects: convulsions, cyanosis. Human mutation data reported. A central nervous system stimulant producing convulsions. A htghly toxic organochlorine pesticide that does not accumulate significantly in human tissue. Absorption is normally slow, but is increased by alcohols, oil, and emulsifiers. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of Cl and SOx. See also CHLORIDES and SULFITES
Potential Exposure
Those engaged in the manufacture, formulation, and application of this material
Carcinogenicity
Equivocal results have been found in genotoxic
assays, but endosulfan was mutagenic and
clastogenic and induced effects on cell cycle
kinetics in various in vivo and in vitro tests.
In reproductive studies, male rats treated
at 3.0 mg/kg from day 15 to 21 of gestation had
reduced sperm production in adulthood.
The 2003 ACGIH threshold limit
value-time-weighted average (TLV-TWA) is
0.1mg/m3 with a notation for skin absorption.
Metabolic pathway
When endosulfan is incubated with microorganisms, endosulfan is extensively degraded in nitrogen- deficient, carbon-deficient, and nitrogen-rich cultures of Phanerochaete chrysosporium and is primarily oxidized to endosulfan sulfate, which is a terminal end product, or hydrolyzed to the non-sulfur-containing metabolites. An initial hydrolysis of endosulfan results in the formation of the intermediate metabolite or endosulfan diol, which further undergoes oxidation to yield endosulfan hydroxyether followed by the formation of endosulfan lactone or tentatively identified endosulfan dialdehyde.
Shipping
UN2761 Organochlorine pesticides, solid, toxic, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials. UN2811 Toxic solids, organic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required.
Incompatibilities
Those engaged in the manufacture, formulation, and application of this material
Waste Disposal
A recommended method for disposal is burial 18 in deep in noncropland, away from water supplies, but bags can be burned. Large quantities should be incinerated at high temperature in a unit with effluent gas scrubbing. Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant (≥100 kg/ mo) must conform with EPA regulations governing storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal. In accordance with 40CFR165, follow recommendations for the disposal of pesticides and pesticide containers. Must be disposed properly by following package label directions or by contacting your local or federal environmental control agency, or by contacting your regional EPA office.
Thiosulfan Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
1of2
chevron_rightPreparation Products
| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gujarat Chemicals GUJCHEM | +91-9825114095 +91-9825114095 | Gujarat, India | 42 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Kilpest India limited | +91-7552586536 +91-7552586536 | Madhya Pradesh, India | 38 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Unique Farm Aid Pvt Ltd | +91-9873006591 +91-9873006592 | New Delhi, India | 31 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Super Crop Safe Limited | +91-9726022444 +91-9824169514 | Gujarat, India | 38 | 58 | Inquiry |
| CLEARSYNTH LABS LTD. | +91-22-45045900 | Hyderabad, India | 6257 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Triveni chemicals | 08048762458 | New Delhi, India | 6088 | 58 | Inquiry |
| CNC Solutions | 08047630457 | Haryana, India | 1 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Chinraj Enterprises | 08048372642Ext 270 | Karnataka, India | 1 | 58 | Inquiry |
| career henan chemical co | +86-0371-86658258 +8613203830695 | China | 29863 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Xiamen AmoyChem Co., Ltd | +86-86-5926051114 +8615060885618 | China | 6383 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Supplier | Advantage |
|---|---|
| Gujarat Chemicals GUJCHEM | 58 |
| Kilpest India limited | 58 |
| Unique Farm Aid Pvt Ltd | 58 |
| Super Crop Safe Limited | 58 |
| CLEARSYNTH LABS LTD. | 58 |
| Triveni chemicals | 58 |
| CNC Solutions | 58 |
| Chinraj Enterprises | 58 |
| career henan chemical co | 58 |
| Xiamen AmoyChem Co., Ltd | 58 |
115-29-7(Thiosulfan)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




