Indigo
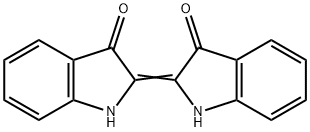
- CAS No.
- 482-89-3
- Chemical Name:
- Indigo
- Synonyms
- INDIGO BLUE;INDIGOTIN;VAT BLUE 1;CI 73000;C.I, vat blue 1;(2,2’-biindoline)-3,3’-dione;otin;AO201;Indig;INDIGO
- CBNumber:
- CB7459700
- Molecular Formula:
- C16H10N2O2
- Molecular Weight:
- 262.26
- MOL File:
- 482-89-3.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
- Modify Date:
- 2024/8/1 14:39:07
| Melting point | >300 °C(lit.) |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 405.51°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.01 g/mL at 20 °C |
| vapor pressure | 0Pa at 100℃ |
| refractive index | 1.5800 (estimate) |
| Flash point | >220℃ |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Room Temperature |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly, Heated, Sonicated), DMF (Slightly) |
| pka | -3.83±0.20(Predicted) |
| form | Powder |
| Colour Index | 73000 |
| color | Dark blue to violet |
| Water Solubility | <0.1 g/100 mL |
| Merck | 14,4943 |
| BRN | 88275 |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| InChIKey | COHYTHOBJLSHDF-BUHFOSPRSA-N |
| LogP | 2.7 at 23℃ |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 482-89-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | c.i. Vat blue 1(482-89-3) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | C.I. Vat Blue 1 (482-89-3) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |  GHS07 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Warning | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H315-H319-H335 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P302+P352-P305+P351+P338 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | Xi,Xn | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 36/38-36/37/38-48/20/21/22 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 26-36 | |||||||||
| RIDADR | UN 3264 8/PG 3 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 1 | |||||||||
| RTECS | DU2988400 | |||||||||
| HS Code | 32041510 | |||||||||
| Toxicity | LD50 oral in mouse: > 32gm/kg | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Indigo price More Price(3)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 229296 | Indigo synthetic, Dye content 95?% | 482-89-3 | 25G | ₹4351.2 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 229296 | Indigo synthetic, Dye content 95?% | 482-89-3 | 100G | ₹14119.2 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| TCI Chemicals (India) | I0212 | Indigo (synthetic) | 482-89-3 | 25G | ₹3800 | 2022-05-26 | Buy |
Indigo Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Indigo, known chemically as indigotin, is a common blue dye that has been highly valued
throughout history and has played a major role in trade and commerce since ancient times.
The term indigo is often used to describe many blue dyes produced from a number of plants.
For example, woad, a blue dye obtained from the plant Isatis tinctoria, was used throughout
the Mediterannean and Europe and is often identified as indigo. True indigo comes from
the leguminous plant of the genus Indigofera.
The Indigofera genus includes several hundred
species, and indigo has been obtained from a number of these, but the dominant species for
the dye are Indigofera tinctoria grown mainly in India and tropical Asia and Indigofera suff ructiosa
from the tropical Americas. The name indigo comes from the Greek indikon and Latin
indicum meaning “dye from India.” There is evidence that indigo was used several thou sand
years b.c.e. Persian rugs containing indigo color exist from several thousand years b.c.e. Textile
artifacts from Egyptian tombs provide evidence of indigo’s use by royalty from as far back as
2500 b.c.e. The writings of Herodotus from approximately 450 b.c.e. mention indigo’s use in
the Mediterranean area.
Chemical Properties
dark violet powder
Occurrence
Indigo is a perennial shrub found in several regions of the world.
History
Indigotin. The blue dye of the ancient world was derived from indigo and woad. Which plant is the oldest is a matter of conjecture. That indigo was known at least four thousand years ago is evident from ancient Sanskrit writings. Cloth dyed with indigotin (CI Natural Blue; CI 75780) has been found in Egyptian tombs and in the graves of the Incas in South America. Indigo belongs to the legume family. The two most important species are Indigo tinctoria and I. suffruticosa, found in India and the Americas, respectively. The leaves of the indigo plant do not contain the dye as such, but in the form of its precursor, a glycoside known as indican.
Uses
In recent years researchers have used genetic engineering using Escherichia coli to convert tryptophan into indigo. The desire for natural organic products has also revived traditional production methods of indigo on a small scale. Indigo's dominant use is as a textile dye, but indigo-related compounds have limited use as indicators and in food coloring.the Food and Drug Administration's FD&C Blue #2 contains indigotine (also known as indigo carmine), which is a sulfonated sodium salt of indigo.
Production Methods
The first synthesis of indigo is attributed to Adolf von Baeyer (1835–1917), who began hisquest to synthesize indigo in 1865 but was not able to produce indigo until 1878. The syntheticproduction of indigo was first described by Baeyer and Viggo Drewson in 1882; Baeyeralso identified the structure of indigo in 1882.the Baeyer-Drewson synthesis of indigo startedwith 2-nitrobenzaldehyde and acetone proceeding through a series of steps in alkali solution.Baeyer’s work was not commercially viable, and it was not until 1897 that BASF (BadischeAnalin und Soda Fabrik) started to produce indigo commercially using a process developedby Karl von Heumann (1851–1894) that started with naphthalene. The synthetic productionof indigo spelled the end of traditional methods of indigo production. By the second decadeof the 20th century, nearly all indigo was produced synthetically.
Definition
indigo: A blue vat dye, C16H10N2O2.It occurs as the glucoside indican inthe leaves of plants of the genus Indigofera,from which it was formerlyextracted. It is now made synthetically.
Biological Functions
Indigo naturalis has a variety of pharmacological activities, such as anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antibacterial, antiviral, immunomodulatory and so on. It has very good clinical effect on psoriasis, leukemia and ulcerative colitis.
General Description
Dark blue powder with coppery luster. Occurs in isomeric forms (cis and trans). In solid state Indigo is in the trans form.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Health Hazard
ACUTE/CHRONIC HAZARDS: Indigo may cause irritation of the skin and mucous membranes.
Fire Hazard
Flash point data for Indigo are not available but Indigo is probably combustible.
Safety Profile
Mutation data reported. Whenheated to decomposition it emits toxic vapors of NOx.
Purification Methods
First reduce indigo in alkaline solution with sodium hydrosulfite, and filter. The filtrate is then oxidised by air, and the resulting precipitate is filtered off, dried at 65-70o, ground to a fine powder, and extracted with CHCl3 in a Soxhlet extractor. Evaporation of the CHCl3 extract gives the purified dye. [Brode et al. J Am Chem Soc 76 1034 1954; spectral characteristics are listed, Beilstein 24 II 233, 24 III/IV 1791.]
Indigo Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
1of4
chevron_rightPreparation Products
1of2
chevron_right| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Advent Dyestuffs And Chemicals Private Limited | +91-2261535031 +91-9825146920 | Maharashtra, India | 115 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Vikram And Company | +91-2226285989 +91-9821517722 | Maharashtra, India | 197 | 58 | Inquiry |
| CLEARSYNTH LABS LTD. | +91-22-45045900 | Hyderabad, India | 6351 | 58 | Inquiry |
| CHEMSWORTH | +91-261-2397244 | New Delhi, India | 6707 | 30 | Inquiry |
| Jaitra Dye Chem | 08048989974 | Maharashtra, India | 6 | 58 | Inquiry |
| TCI Chemicals (India) Pvt. Ltd. | 1800 425 7889 | New Delhi, India | 6778 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Henan Tianfu Chemical Co.,Ltd. | +86-0371-55170693 +86-19937530512 | China | 21669 | 55 | Inquiry |
| career henan chemical co | +86-0371-86658258 +8613203830695 | China | 29898 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Hebei Guanlang Biotechnology Co., Ltd. | +86-19930503282 | China | 8826 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Shaanxi Pioneer Biotech Co., Ltd . | +8613259417953 | China | 3000 | 58 | Inquiry |
Related articles
- Synthesis of Indigo Dye
- Indigo is a pigment extracted from the leaves of indigo-bearing plants and is the oldest natural source of blue dye in the wor....
- Aug 1,2024
- Indigo: physicochemical properties, production pathways and biological production
- Indigo is a dye derived from natural plants and can be produced through plant-based or microbial fermentation pathways, with g....
- Jan 15,2024
- Indigo: mechanism of action and applications in psoriasis treatment
- Indigo can treat psoriasis by regulating keratinocytes and inhibiting cell proliferation and differentiation. Combination ther....
- Aug 1,2023





