Salicylic acid
- CAS No.
- 69-72-7
- Chemical Name:
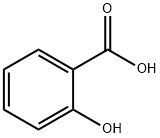
- Salicylic acid
- Synonyms
- 2-HYDROXYBENZOIC ACID;SALICYCLIC ACID;salicylic;171;380;Acido salicilico;Soluble SALICYLIC ACID, Liposomal SALICYLIC ACID, SALICYLIC ACID NanoEmulsion, NanoActive SALICYLIC ACID;SAX;Compound W;ACIDUM SALICYLICUM
- CBNumber:
- CB1680010
- Molecular Formula:
- C7H6O3
- Molecular Weight:
- 138.12
- MOL File:
- 69-72-7.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
- Modify Date:
- 2024/8/14 13:10:28
| Melting point | 158-161 °C(lit.) |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 211 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 1.44 |
| vapor density | 4.8 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 1 mm Hg ( 114 °C) |
| FEMA | 3985 | 2-HYDROXYBENZOIC ACID |
| refractive index | 1,565 |
| Flash point | 157 °C |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | ethanol: 1 M at 20 °C, clear, colorless |
| pka | 2.98(at 25℃) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White to off-white |
| PH Range | Non0 uorescence (2.5) to dark blue 0 uorescence (4.0) |
| PH | 3.21(1 mM solution);2.57(10 mM solution);2.02(100 mM solution); |
| Odor | at 100.00 %. faint phenolic nutty |
| Odor Type | nutty |
| Water Solubility | 1.8 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Sensitive | Light Sensitive |
| λmax | 210nm, 234nm, 303nm |
| Merck | 14,8332 |
| JECFA Number | 958 |
| Sublimation | 70 ºC |
| BRN | 774890 |
| Stability | Stable. Substances to be avoided include oxidizing agents, strong bases, iodine, fluorine. Combustible. Sensitive to light. |
| Major Application | Semiconductors, nanoparticles, photoresists, lubricating oils, UV absorbers, adhesive, leather, cleaner, hair dye, soaps, cosmetics, pain medication, analgesics, antibacterial agent, treatment of dandruff, hyperpigmented skin, tinea pedis, onychomycosis, osteoporosis, beriberi, fungicidal skin disease, autoimmune disease |
| InChIKey | YGSDEFSMJLZEOE-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| LogP | 2.01 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 69-72-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Benzoic acid, 2-hydroxy-(69-72-7) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Salicylic acid (69-72-7) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |    GHS05,GHS07,GHS08 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H302-H318-H361d | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P202-P264-P280-P301+P312-P305+P351+P338-P308+P313 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | Xn,F | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 22-41-36/37/38-36-20/21/22-11 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 26-39-37/39-36-36/37-16 | |||||||||
| RIDADR | UN 1648 3 / PGII | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 1 | |||||||||
| RTECS | VO0525000 | |||||||||
| Autoignition Temperature | 500 °C | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HS Code | 29182100 | |||||||||
| Toxicity | LD50 i.v. in mice: 500 mg/kg (Sota) | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Salicylic acid price More Price(41)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | W398500 | Salicylic acid ≥99%, FG | 69-72-7 | 1SAMPLE-K | ₹5141.88 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | W398500 | Salicylic acid ≥99%, FG | 69-72-7 | 1KG | ₹7220.28 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | W398500 | Salicylic acid ≥99%, FG | 69-72-7 | 10KG | ₹38905.05 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | W398500 | Salicylic acid ≥99%, FG | 69-72-7 | 25KG | ₹67039.23 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | S7401 | Salicylic acid suitable for plant cell culture | 69-72-7 | 500G | ₹5455.8 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
Salicylic acid Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Salicylic acid (from Latin salix, willow tree, from the bark of which the substance used to be obtained) is a mono hydroxy benzoic acid, a type of phenolic acid and a beta hydroxy acid. This colorless crystalline organic acid is widely used in organic synthesis and functions as a plant hormone. It is derived from the metabolism of salicin. In addition to being an important active metabolite of aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid), which acts in part as a prod rug to salicylic acid, it is probably best known for its use in anti-acne treatments. The salts and esters of salicylic acid are known as salicylates.
Chemical Properties
Salicylic acid has the formula C6H4(OH) COOH, where the OH group is ortho to the carboxyl group. It is also known as 2- hydroxybenzoic acid. It is poorly soluble in water (2 g / L at 20 °C). Aspirin (acetyl salicylic acid or ASA) can be prepared by the esterification of the phenolic hydroxyl group of salicylic acid with the acetyl group from acetic anhydride or acetyl chloride.
Physical properties
Salicylic acid. Appearance: white crystalline powder. Solubility: Absolutely soluble
in ethanol, soluble in ether and chloroform, slightly soluble in water and anhydrous
ether. Stability: Stable at room temperature, discomposes into phenol and carbon
dioxide after rapidly heated. It’s partially acidic.
Aspirin. Appearance: white crystal and decomposes at 136–140? °C. Melting
point: 136?°C.?Aspirin is the acetyl derivative of salicylic acid with weak acidity. Its
acidity coefficient is 3.5 at 25?°C. Stability: Aspirin decomposes rapidly in ammonium acetate, alkali metal of acetate, carbonate, citrate or hydroxide solutions.
There are two crystal forms of aspirin including crystal form I and II.
Occurrence
Unripe fruits and vegetables are natural sources of salicylic acid, particularly blackberries, blueberries, cantaloupes, dates, raisins, kiwi fruits, guavas, apricots, green pepper, olives, tomatoes, radish and chicory; also mushrooms. Some herbs and spices contain quite high amounts, although meat, poultry, fish, eggs and dairy products all have little to no salicylates. Of the legumes, seeds, nuts, and cereals, only almonds, water chestnuts and peanuts have significant amounts.
History
The Greek physician Hippocrates wrote in the 5th century BC about a bitter powder extracted from willow bark that could ease aches and pains and reduce fevers . This remedy was also mentioned in texts from ancient Sumer , Lebanon , and As syria .
The active extract of the bark, called salicin, after the Latin name for the white willow (Salix alba), was isolated and named by the German chemist Johann Andreas Buchner in 1826. Raffaele Piria, an Italian chemist was able to convert the substance into a sugar and a second component, which on oxidation becomes salicylic acid.
Salicylic acid was also isolated from the herb meadowsweet (Filipendula ulmaria, formerly classified as Spiraea ulmaria) by German researchers in 1839. While their extract was somewhat effective, it also caused digestive problems such as gastric irritation, bleeding, diarrhea, and even death when consumed in high doses.
Uses
Salicylic Acid is an Impurity of Acetylsalicylic Acid (A187780). Acetylsalicylic acid Impurity B.
Indications
Salicylic acid is a β-hydroxy acid that penetrates into the sebaceous gland
and has comedolytic and anti-inflammatory properties. It can be used as an
adjunctive therapy and is found in cleansers, toners, masks, and peels.
Salicylic acid is keratolytic and at concentrations between 3% and 6% causes softening
of the horny layers and shedding of scales. It produces this desquamation
by solubilizing the intercellular cement and enhances the shedding of corneocytes
by decreasing cell-to-cell cohesion. In concentrations >6%, it can be destructive to
tissue. Application of large amounts of the higher concentration of salicylic acid can
also result in systemic toxicity. Salicylic acid is used in the treatment of superficial
fungal infections, acne, psoriasis, seborrheic dermatitis, warts, and other scaling dermatoses.
When it is combined with sulfur, some believe that a synergistic keratolytic
effect is produced. Common preparations include a 3% and 6% ointment with
equal concentration of sulfur; 6% propylene glycol solution (Keralyt); 5% to 20%
with equal parts of lactic acid in flexible collodion for warts (Duofilm, Occlusal);
in a cream base at any concentration for keratolytic effects; as a 60% ointment for
plantar warts; and in a 40% plaster on velvet cloth for the treatment of calluses and
warts (40% salicylic acid plaster).
Definition
ChEBI: A monohydroxybenzoic acid that is benzoic acid with a hydroxy group at the ortho position. It is obtained from the bark of the white willow and wintergreen leaves.
Production Methods
Salicylic acid is biosynthesized from the amino acid phenylalanine. In Arabidopsis thaliana it can also be synthesized via a phenylalanine - independent pathway.
Sodium salicylate is commercially prepared by treating sodium phenolate ( the sodium salt of phenol ) with carbon dioxide at high pressure (100 atm ) and high temperature (390K) -a method known as the Kolbe-Schmitt reaction. Acidification of the product with sulfuric acid gives salicylic acid :
It can also be prepared by the hydrolysis of aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) or methyl salicylate (oil of winter green) with a strong acid or base.
Preparation
Prepared by heating sodium phenolate with carbon dioxide under pressure
General Description
Odorless white to light tan solid. Sinks and mixes slowly with water.
Air & Water Reactions
Sublimes and forms vapor or dust that may explode [USCG, 1999].
Hazard
Respiratory alkalosis, hyperkalemia, hyperthermia, dehydration, convulsions, shock, res- piratory paralysis, respiratory acidosis, lesions and death from respiratory collapse; fetotoxic.
Health Hazard
Inhalation of dust irritates nose and throat. Vomiting may occur spontaneously if large amounts are swallowed. Contact with eyes causes irritation, marked pain, and corneal injury which should heal. Prolonged or repeated skin contact may cause marked irritation or even a mild burn.
Mechanism of action
Salicylic acid has been shown to work through several different pathways. It produces its anti - inflammatory effects via suppressing the activity of cyclo oxygenase (COX), an enzyme which is responsible for the production of pro - inflammatory mediators such as the prostaglandins. Notably, it does this not by direct inhibition of COX, unlike most other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), but instead by suppression of the expression of the enzyme (via a yet-un elucidated mechanism) . Salicylic acid has also been shown to activate adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK), and it is thought that this action may play a role in the anticancer effects of the compound and its prod rugs aspirin and salsalate. In addition, the anti diabetic effects of salicylic acid are likely mediated by AMPK activation primarily through allosteric conformational change that increases levels of phosphorylation. Salicylic acid also uncouples oxidative phosphorylation which leads to increased ADP:ATP and AMP:ATP ratios in the cell. Consequently, salicylic acid may alter AMPK activity and subsequently exert its anti-diabetic properties through altered energy status of the cell. Even in AMPK knock - out mice, however, there is an anti-diabetic effect demonstrating that there is at least one additional, yet - unidentified action of the compound.
Pharmacology
Aspirin is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). The main pharmacological effect is to inhibit prostaglandin metabolism and thromboxane synthesis by
inhibiting prostaglandin metabolism-required cyclooxygenase, via irreversible acetylation of 530 serine residues in the hydroxyl of COX-1 polypeptide chain,
which results in COX-1 inactivation, blocks the conversion of arachidonic acid into
thromboxane A2 pathway and then inhibits the platelet aggregation.
Prostaglandin is a hormone produced locally in the body. It can pass the pain to
the brain, regulate body temperature in the hypothalamus and cause inflammation.
Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis can have antipyretic, analgesic, antiinflammatory and antirheumatic effects. The adverse effects of aspirin are mainly
gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, upper abdominal discomfort or
pain. It can also cause allergic reactions, cardiotoxicity, liver and kidney damage
and Wright’s syndrome. In addition, high doses of aspirin can cause salicylic acid
reactions such as headache, dizziness, tinnitus, hearing loss and other central nervous system symptoms.
Clinical Use
The clinical application of aspirin varies with the therapeutic dose. Low-dose aspirin (75–300?mg/day) has antiplatelet aggregation effect and can be used to prevent and treat the coronary and cerebrovascular thrombosis and other postoperative thrombosis. The middle dose of aspirin (0.5–3? g/day) has antipyretic analgesic effects, so it is commonly used in the treatment of fever, headache, toothache, neuralgia, muscle pain and menstrual pain. High doses of aspirin (more than 4?g/day) have anti-inflammatory and antirheumatic effects for the treatment of acute rheumatic fever and rheumatoid arthritis. In addition, aspirin is used for the treatment of skin and mucous membrane lymphadenopathy (Kawasaki disease) in paediatric.
Side effects
Salicylic acid's side effects include erythema and scaling.
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion, intravenous, and intraperitoneal routes. Moderately toxic by subcutaneous route. An experimental teratogen. Human systemic effects by skin contact: ear tinnitus. Mutation data reported. A skin and severe eye irritant. Experimental reproductive effects. Incompatible with iron salts, spirit nitrous ether, lead acetate, iodine. Used in the manufacture of aspirin. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes.
Potential Exposure
Used as a topical keratolytic agent; in manufacture of aspirin, salicylates, resins, as a dyestuff intermediate; prevulcanization inhibitor; analytical reagent; fungicide, antiseptic, and food preservative.
Purification Methods
It has been purified by steam distillation, by recrystallisation from H2O (solubility is 0.22% at room temperature and 6.7% at 100o), absolute MeOH, or cyclohexane and by sublimation in a vacuum at 76o. The acid chloride (needles) has m 19-19.5o, b 92o/15mm, the amide has m 133o (yellow needles from H2O), the O-acetyl derivative has m 135o (rapid heating and the liquid resolidifies at 118o), and the O-benzoyl derivative has m 132o (aqueous EtOH). [IR: Hales et al. J Chem Soc 3145 1954, Bergmann et al. J Chem Soc 2351 1950]. [Beilstein 10 IV 125.]
Incompatibilities
iron salts; lead acetate; iodine. Forms an explosive mixture in air.
Salicylic acid Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
1of2
chevron_rightPreparation Products
1of8
chevron_right| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemicea Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd | +91-918482849343 +91-8482849343 | Mumbai, India | 461 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Anant Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd | +91-8550986868 +91-9485998001 | Haryana, India | 461 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Arnish Laborates Pvt Ltd | +91 7208475595 | Maharashtra, India | 187 | 58 | Inquiry |
| chakrachem Lifesciences | +91 9902744663 | Hyderabad, India | 451 | 58 | Inquiry |
| OPULENT PHARMA | +91-9106692785 +91-9106692785 | Gujarat, India | 479 | 58 | Inquiry |
| SNECOFRi Pvt Ltd | +91-9032850129 +91-9032850129 | Telangana, India | 404 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Royal Chemicals | +91-9221503305 +91-9221503305 | Maharashtra, India | 28 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Shreenath Chemicals | +91-8369634120 +91-8369634120 | Maharashtra, India | 48 | 58 | Inquiry |
| JSK Chemicals | +919879767970 | Gujarat, India | 3756 | 58 | Inquiry |
| KARPSCHEM LABORATORIES | +91-7249203006 +91-7249203006 | Maharashtra, India | 786 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Supplier | Advantage |
|---|---|
| Chemicea Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd | 58 |
| Anant Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd | 58 |
| Arnish Laborates Pvt Ltd | 58 |
| chakrachem Lifesciences | 58 |
| OPULENT PHARMA | 58 |
| SNECOFRi Pvt Ltd | 58 |
| Royal Chemicals | 58 |
| Shreenath Chemicals | 58 |
| JSK Chemicals | 58 |
| KARPSCHEM LABORATORIES | 58 |
Related articles
- How to Use Salicylic Acid?
- Salicylic acid (SA) is a simple phenolic compound synthesized in a wide range of prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms, includi....
- Aug 14,2024
- The Polar and Non-polar Characteristics in the Structure of Salicylic Acid
- Salicylic acid has two polar regions, a carboxyl group and a hydroxyl group, but also has a non-polar 6 carbon hydrocarbon, wh....
- Dec 27,2023
- Uses and benefits of Salicylic acid on the Skin
- Salicylic acid is a colorless, bitter-tasting solid, it is a precursor to and a metabolite of aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid). ....
- Jul 19,2022





