Ketamine hydrochloride
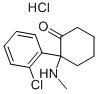
- CAS No.
- 1867-66-9
- Chemical Name:
- Ketamine hydrochloride
- Synonyms
- KETAMINE;ketalar;ketaset;Ketamine Hydrochloride (UB);2-(2-chlorophenyl)-2-(methylamino)cyclohexan-1-one hydrochloride;ci581;cl369;ketolar;ketavet;vetalar
- CBNumber:
- CB4141970
- Molecular Formula:
- C13H16ClNO.ClH
- Molecular Weight:
- 274.19
- MOL File:
- 1867-66-9.mol
- Modify Date:
- 2023/6/30 15:45:59
| Melting point | 252-254°C |
|---|---|
| Flash point | 9℃ |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | H2O: 200 mg/mL |
| form | solid |
| pka | 7.5(at 25℃) |
| color | white |
| Water Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in water |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 1867-66-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Ketamine hydrochloride (1867-66-9) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |    GHS02,GHS06,GHS08 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H225-H301+H311+H331-H370 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P210-P260-P280-P301+P310-P311 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | Xn,T,F | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 22-36/37/38-39/23/24/25-23/24/25-11 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 26-45-36/37-16-7 | |||||||||
| RIDADR | 3249 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 3 | |||||||||
| RTECS | GW1400000 | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 6.1(b) | |||||||||
| PackingGroup | III | |||||||||
| HS Code | 2923900100 | |||||||||
| Toxicity | LD50 in adult mice, rats (mg/kg): 224 ±4, 229 ±5 i.p. (Goldenthal) | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Ketamine hydrochloride Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Chemical Properties
Ketamine hydrochloride is Off-White Solid
Uses
Anesthetic (intravenous). Controlled substance (depressant).
Definition
ChEBI: The hydrochloride salt of ketamine.
Biological Functions
Ketamine is a cyclohexanone derivative whose pharmacological actions are quite different from those of the other IV anesthetics. The state of unconsciousness it produces is trancelike (i.e., eyes may remain open until deep anesthesia is obtained) and cataleptic; it has frequently been characterized as dissociative (i.e., the patient may appear awake and reactive but does not respond to sensory stimuli). The term dissociative anesthesia is used to describe these qualities of profound analgesia, amnesia, and superficial level of sleep.
General Description
Ketamine is formulated as an acidic solution, pH 3.5 to 5.5,available with or without 0.1 mg/mL benzethonium chloridepreservative. Ketamine is marketed as the racemic mixtureand some properties of the individual isomers have beenelucidated. Ketamine is a rapid-acting agent that can beused for induction, used as the sole agent for general anesthesiaor combined with other agents. Unlike the proposedmechanism of action for most anesthetics, ketamine doesnot act at the GABAA receptor. Ketamine acts as a noncompetitiveantagonist at the glutamate, NMDA receptor, anonspecific ion channel receptor. The NMDA receptor is locatedthroughout the brain and contains four well-studiedbinding sites. The primary binding site binds L-glutamate,NMDA, and aspartate. The allosteric site binds glycine,which facilitates primary ligand binding. There is also amagnesium binding site that blocks ion flow through thechannel and a phencyclidine (PCP) binding site that blocksthe ion channel when occupied. Ketamine is believed tobind to the PCP site in a stereoselective manner and blockthe ion flow in the channel. By blocking the flow ofcalcium ions into the cell, ketamine prevents the calcium concentration from building and triggering excitatorysynaptic transmissions in the brain and spinal cord.
Biological Activity
Non-competitive NMDA receptor antagonist (EC 50 values are 13.6 and 17.6 μ M for NR1/NR2A and NR1/NR2B subunit combinations respectively). Dissociative anesthetic.
Clinical Use
Like other dissociative anesthetics, ketamine isabused for its hallucinatory effects. Most of the illegallyused ketamine comes from stolen legitimate sources, particularlyfrom veterinary clinics or smuggled in fromMexico.
Ketamine is metabolized via N-demethylation to formthe main metabolite norketamine. Norketamine has aboutone third the potency of the parent compound. Minor metabolicpathways include hydroxylation of the cyclohexanonering; hydroxylation followed by glucuronide conjugation,and hydroxylation followed by dehydration to the cyclohexenonederivative.
Side effects
The most serious disadvantage to the use of ketamine is
its propensity to evoke excitatory and hallucinatory
phenomena as the patient emerges from anesthesia.
Patients in the recovery period may be agitated, scream
and cry, hallucinate, or experience vivid dreams. These
episodes may be controlled to some extent by maintaining
a quiet reassuring atmosphere in which the patient
can awaken or if necessary by administering tranquilizing
doses of diazepam.
Other reported side effects include vomiting, salivation,
lacrimation, shivering, skin rash, and an interaction
with thyroid preparations that may lead to hypertension
and tachycardia. Ketamine also may raise intracranial
pressure and elevate pulmonary vascular resistance, especially
in children with trauma or congenital heart disease.
Increases in intraocular pressure also may occur,
and vigilance is required if ketamine is used in ocular
surgery.
Safety Profile
Poison by intramuscular, intraperitoneal, and intravenous routes. Moderately toxic by ingestion. Human systemic effects by intravenous and possibly other routes: analgesia, coma, hallucinations and distorted perceptions, dyspnea. An experimental teratogen. An anesthetic. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of Cland NOx.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Adrenergic-neurone blockers: enhanced hypotensive
effect.
Antihypertensives: enhanced hypotensive effect.
Antidepressants: stop MAOIs 2 weeks before
surgery; increased risk of arrhythmias and
hypotension with tricyclics.
Antipsychotics: enhanced hypotensive effect.
Memantine: increased risk of CNS toxicity, avoid
concomitant use.
Muscle relaxants: enhances effects of atracurium.
Ketamine hydrochloride Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
1of3
chevron_rightPreparation Products
Related articles
- ?Pharmacokinetics and indications of Ketamine hydrochloride
- Ketamine hydrochloride produces dissociative anaesthesia (via non-competitive antagonism at the NMDA receptor) rather than cla....
- Feb 23,2022
1867-66-9(Ketamine hydrochloride)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




