n-Butane
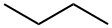
- CAS No.
- 106-97-8
- Chemical Name:
- n-Butane
- Synonyms
- BUTANE;r600;n-Butan;Batane;n-C4H10;BUTANES;1-Butane;A-17;Q GAS;Bu-Gas
- CBNumber:
- CB6152626
- Molecular Formula:
- C4H10
- Molecular Weight:
- 58.12
- MOL File:
- 106-97-8.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
- Modify Date:
- 2024/3/14 15:18:27
| Melting point | −138 °C(lit.) |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | −0.5 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 0.579 g/mL at 20 °C(lit.) |
| vapor density | 2.11 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 3.21, 1.26, and 0.66 mM at 4, 25, and 50 °C, respectively (Kresheck et al., 1965) |
| refractive index | 1.3326 |
| Flash point | 45 |
| form | gas |
| Odor | faint disagreeable odor |
| Odor Threshold | 1200ppm |
| Water Solubility | 73.24mg/L(25 ºC) |
| Merck | 1515 |
| BRN | 969129 |
| Henry's Law Constant | (atm?m3/mol): 0.356 at 5 °C, 0.454 at 10 °C, 0.568 at 15 °C, 0.695 at 20 °C, 0.835 at 25 °C (Ben-Naim et al., 1973) |
| Exposure limits | TLV-TWA 800 ppm (~1920 mg/m3) (ACGIH), 500 ppm (1200 mg/m3) (MSHA). |
| Dielectric constant | 1.4(-1℃) |
| Stability | Stable. Extremely flammable. Readily forms explosive mixtures with air. Note low flash point. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong acids, strong alkalies. |
| LogP | 2.890 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 106-97-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Butane (106-97-8) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |   GHS02,GHS04 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H220-H280 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P410+P403 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | F+,F,T | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 12-46-45 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 9-16-45-53 | |||||||||
| OEB | A | |||||||||
| OEL | TWA: 800 ppm (1900 mg/m3) | |||||||||
| RIDADR | UN 2037 2.1 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | - | |||||||||
| RTECS | EJ4200000 | |||||||||
| F | 4.5-31 | |||||||||
| Hazard Note | Extremely Flammable | |||||||||
| DOT Classification | 2.1 (Flammable gas) | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 2.1 | |||||||||
| HS Code | 2901100000 | |||||||||
| Toxicity | LC50 (inhalation) for mice 680 gm/m3/2-h, rats 658 gm/m3/4-h (quoted, RTECS, 1985). | |||||||||
| IDLA | 1,600 ppm (>10% LEL) | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
n-Butane Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Butane is a flammable, colorless gas that follows propane in the alkane series. Butane is also called n-butane, with the “n” designating it as normal butane, the straight chain isomer. Butane’s other isomer is isobutane. The chemical name of isobutane is 2-methylpropane. Isomers are different compounds that have the same molecular formula. Normal butane and isobutane are two different compounds, and the name butane is used collectively to denote both n-butane and isobutane; the names n-butane and isobutane are used to distinguish properties and chemical characteristics unique to each compound. Butane, along with propane, is a major component of liquefied petroleum gas . It exists as a liquid under moderate pressure or below 0℃ at atmospheric pressure, which makes it ideal for storage and transportation in liquid form.
Physical properties
Colorless, flammable gas with a faint, disagreeable, natural gas or gasoline-like odor. Odor threshold concentration in air is 1,200 ppmv (Nagata and Takeuchi, 1990). Detected in water at a concentration of 6.2 mg/L (Bingham et al., 2001).
History
Butane is extracted from natural gas and is also obtained during petroleum refining. Butane can be obtained from natural gas by compression, adsorption, or absorption. All three processes were used in the early days of the LPG industry, but compression and adsorption were generally phased out during the 20th century. Most butane now is obtained from absorption and separation from oil.
Uses
n-Butane can be obtained from natural gas and from refinery hydro cracker streams. Most of the n-butane goes into fuel additive uses. The major chemical use is as a feedstock for ethylene production by cracking . The other important chemical uses for butane are in oxidation to acetic acid and in the production of maleic anhydride. In the past, butane also was the main feedstock for the production of butadiene by dehydrogenation, but it has been replaced by coproduct butadiene obtained from ethylene production.
Ethylene. The largest potential chemical market for n-butane is in steam cracking to ethylene and coproducts. n-Butane is a supplemental feedstock for olefin plants and has accounted for 1-4 percent of total ethylene production for most years since 1970. It can be used at up to 10-15 percent ofthe total feed in ethane/propane crackers with no major modifications . n-Butane can also be used as a supplemental feed at as high as 20-30 percent in heavy naphtha crackers. The consumption of C4S has fluctuated considerably from year to year since 1970, depending on the relative price ofbutane and other feedstocks. The yield of ethylene is only 36-40 percent, with the other products including methane, propylene, ethane, and butadiene, acetylene, and butylenes. About 2-3 billion Ib of butane are consumed annually to produce ethylene.
Definition
A gaseous hydrocarbon,C4H10; d. 0.58 g cm–3; m.p. –138°C;b.p. 0°C. Butane is obtained frompetroleum (from refinery gas orby cracking higher hydrocarbons).The fourth member of the alkaneseries, it has a straight chain ofcarbon atoms and is isomeric with2-methylpropane (CH3CH(CH3)CH3,formerly called isobutane). It can easilybe liquefied under pressure and issupplied in cylinders for use as a fuelgas. It is also a raw material for makingbuta-1,3-diene (for synthetic rubber).
General Description
N-BUTANE is a colorless gas with a faint petroleum-like odor. For transportation N-BUTANE may be stenched. N-BUTANE is shipped as a liquefied gas under its vapor pressure. Contact with the liquid can cause frostbite. N-BUTANE is easily ignited. Its vapors are heavier than air. Any leak can be either liquid or vapor. Under prolonged exposure to fire or intense heat the containers may rupture violently and rocket. N-BUTANE is used as a fuel, an aerosol propellant, in cigarette lighters, and to make other chemicals.
Air & Water Reactions
Highly flammable.
Reactivity Profile
N-BUTANE can explode when exposed to flame or when mixed with (nickel carbonyl + oxygen). N-BUTANE can also react with oxidizers. Strong acids and alkalis should be avoided. .
Hazard
Highly flammable, dangerous fire and explosion risk. Explosive limits in air 1.9–8.5%. Narcotic in high concentration. Central nervous sys- tem impairment.
Health Hazard
n-Butane is a nontoxic gas. Exposure toits atmosphere can result in asphyxia. Athigh concentrations it produces narcosis.Exposure to 1% concentration in air for10 minutes may cause drowsiness. Its odoris detectable at a concentration of 5000 ppm.
Fire Hazard
EXTREMELY FLAMMABLE. Will be easily ignited by heat, sparks or flames. Will form explosive mixtures with air. Vapors from liquefied gas are initially heavier than air and spread along ground. CAUTION: Hydrogen (UN1049), Deuterium (UN1957), Hydrogen, refrigerated liquid (UN1966) and Methane (UN1971) are lighter than air and will rise. Hydrogen and Deuterium fires are difficult to detect since they burn with an invisible flame. Use an alternate method of detection (thermal camera, broom handle, etc.) Vapors may travel to source of ignition and flash back. Cylinders exposed to fire may vent and release flammable gas through pressure relief devices. Containers may explode when heated. Ruptured cylinders may rocket.
Safety Profile
Mildly toxic by inhalation. Causes drowsiness. An asphyxlant. Very dangerous fire hazard when exposed to heat, flame, or oxidizers. Highly explosive when exposed to flame, or when mixed with [Ni(CO)4 + O2]. To fight fire, stop flow of gas. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and fumes.
Purification Methods
Dry by passing over anhydrous Mg(ClO4)2 and molecular sieves type 4A. Air is removed by prolonged and frequent degassing at -107o. [Beilstein 1 IV 236.]
n-Butane Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
Preparation Products
1of4
chevron_right| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bhuruka Gases Ltd | +91-7760976502 +91-8041818200 | Karnataka, India | 11 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Maharashtra Gas Co | +91-8097713800 +91-9833780675 | Maharashtra, India | 21 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Vadilal Chemicals Limited | +91-7948936937 +91-7203030735 | Gujarat, India | 39 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Saloni Refrigerants | 08047642314 | Mumbai, India | 2 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Henan Tianfu Chemical Co.,Ltd. | +86-0371-55170693 +86-19937530512 | China | 21669 | 55 | Inquiry |
| career henan chemical co | +86-0371-86658258 +8613203830695 | China | 29825 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Hefei TNJ Chemical Industry Co.,Ltd. | 0551-65418671 | China | 34571 | 58 | Inquiry |
| ANHUI WITOP BIOTECH CO., LTD | +8615255079626 | China | 23556 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Shaanxi Dideu Medichem Co. Ltd | +86-029-89586680 +86-18192503167 | China | 8930 | 58 | Inquiry |
| PT CHEM GROUP LIMITED | +86-85511178 +86-85511178 | China | 35426 | 58 | Inquiry |
106-97-8(n-Butane)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




