Copper(II) sulfate
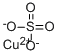
- CAS No.
- 7758-98-7
- Chemical Name:
- Copper(II) sulfate
- Synonyms
- CuSO4;COPPER SULFATE;COPPER SULPHATE;CUPRIC SULFATE;CUPRIC SULPHATE;Copper(Ⅱ) sulfate;COPPER SULPHATE (FEED GRADE);Sulfate de cuivre;Copper(II) sulfat;FEHLING SOLUTION B
- CBNumber:
- CB7751862
- Molecular Formula:
- CuO4S
- Molecular Weight:
- 159.61
- MOL File:
- 7758-98-7.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
- Modify Date:
- 2025/1/27 9:38:02
| Melting point | 200 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
|---|---|
| Density | 3.603 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| bulk density | 800kg/m3 |
| vapor pressure | 7.3 mm Hg ( 25 °C) |
| storage temp. | Store at +5°C to +30°C. |
| solubility | H2O: soluble |
| form | powder |
| color | Slightly greenish to gray |
| Specific Gravity | 3.603 |
| PH | 3.5-4.5 (50g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
| PH Range | 3.7 - 4.5 |
| Flame Color | Bluish-green |
| Odor | odorless |
| Water Solubility | 203 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| Merck | 14,2653 |
| Dielectric constant | 10.3(0.0℃) |
| Exposure limits |
ACGIH: TWA 1 mg/m3 NIOSH: IDLH 100 mg/m3; TWA 1 mg/m3 |
| Stability | hygroscopic |
| InChIKey | ARUVKPQLZAKDPS-UHFFFAOYSA-L |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7758-98-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Cupric sulfate(7758-98-7) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Cupric sulfate (7758-98-7) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |   GHS05,GHS09 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H318-H410 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P273-P280-P305+P351+P338-P391-P501 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | Xn,N,Xi | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 36/38-50/53-22-51/53-36/37/38 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 24/25-36-60-61-22-26 | |||||||||
| RIDADR | UN 3288 6.1/PG 3 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 2 | |||||||||
| RTECS | GL8800000 | |||||||||
| F | 3 | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HS Code | 2833 25 00 | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 6.1 | |||||||||
| PackingGroup | III | |||||||||
| Hazardous Substances Data | 7758-98-7(Hazardous Substances Data) | |||||||||
| Toxicity | LD50 orally in Rabbit: 481 mg/kg | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Copper(II) sulfate price More Price(36)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | PHR1477 | Copper Sulfate Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material | 7758-98-7 | 1G | ₹15966.88 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | C2284 | Copper(II) sulfate solution 4?% (w/v) (prepared from copper (II) sulfate pentahydrate) | 7758-98-7 | 25ML | ₹2219.13 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | C1297 | Copper(II) sulfate ReagentPlus?, ≥99% | 7758-98-7 | 100G | ₹6440.88 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 908940 | Copper(II) sulfate free-flowing, Redi-Dri?, ReagentPlus?, ≥99% | 7758-98-7 | 50G | ₹3972.78 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | C1297 | Copper(II) sulfate ReagentPlus?, ≥99% | 7758-98-7 | 500G | ₹18359.2 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
Copper(II) sulfate Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Chemical Properties
Cupric sulfate, a bluish crystalline powder, also known as hydrocyanite and copper sulfate, vitriol, chalcanthite, and bluestone, is an azure blue material used in the It is used in the leather industry. It is prepared by the reaction of sulfuric acid and copper. It is also obtained as a by-product from copper refineries.
Uses
Copper(II) sulfate may be employed for the following studies:
- As a catalyst for the acetylation of alcohols and phenols under solvent-free conditions.
- To compose the electrolyte for the electrodeposition of Cu-Zn-Sn precursors, required for the preparation of Cu2ZnSnS4 (CZTS) thin films.
- As a Lewis acid catalyst for the dehydration of alcohols.5
Definition
A compound prepared as the hydrate by the action of dilute sulfuric acid on copper( II) oxide or copper(II) carbonate. On crystallization, blue triclinic crystals of the pentahydrate (blue vitriol, CuSO4.5H2O) are formed. Industrially copper(II) sulfate is prepared by passing air through a hot mixture of dilute sulfuric acid and scrap copper. The solution formed is recycled until the concentration of the copper(II) sulfate is sufficient. Copper(II) sulfate is readily soluble in water. The monohydrate (CuSO4.H2O) is formed at 100°C and the anhydrous salt at 250°C. Anhydrous copper( II) sulfate is white; it is extremely hygroscopic and turns blue on absorption of water. It decomposes on heating to give copper(II) oxide and sulfur(VI) oxide.
Copper(II) sulfate is used as a wood preservative, a fungicide (in Bordeaux mixture), and in the dyeing and electroplating industries.
General Description
A white or off-white solid. Melting point 200°C with decomposition. Non-combustible.
Air & Water Reactions
Soluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Anhydrous Cupric sulfate serves as a weak oxidizing agent. Causes hydroxylamine to ignite. Gains water readily. The hydrated salt is vigorously reduced by hydroxylamine [Mellor 8:292(1946-1947)]. Both forms are incompatible with finely powdered metals. Both are incompatible with magnesium, corrode steel and iron, may react with alkalis, phosphates, acetylene gas, hydrazine, or nitromethane, and may react with beta-naphthol, propylene glycol, sulphathiazole and triethanolamine if the pH exceeds 7 . Both act as acidic salts, corrode metals and irritate tissues.
Hazard
Toxic; highly irritant.
Health Hazard
INGESTION: copper sulfate may induce severe gastroenteric distress (vomiting, gastroenteric pain, and local corrosion and hemorrhages), prostration, anuria, hematuria, anemia, increase in white blood cells, icterus, coma, respiratory difficulties, and circulatory failure.
Agricultural Uses
Fungicide, Algaecide, Bactericide, Herbicide, Molluscicide: Copper sulfate is a fungicide used to control bacterial and fungal diseases of fruit, vegetable, nut, and field crops. These diseases include mildew, leaf spots, blights, and apple scab. It is used as a protective fungicide (Bordeaux mixture) for leaf application and seed treatment. It is also used as an algaecide and herbicide, and to kill slugs and snails in irrigation and municipal water treatment systems. It has been used to control Dutch elm disease. It is available as a dust, wettable powder, or liquid concentrate. Used as a fungicide and algaecide, in veterinary medicine and others. Copper sulfate is also used todetect and to remove trace amounts of water from alcohols and organic compounds.
Industrial uses
Copper sulfate (CuSO4·5H2O) is widely used as an activator for sphalerite, pyrite,
pyrrhotite and other sulfides during processing of base metal ores. During flotation of
some silicate minerals, copper sulfate is used as depressant, e.g. zirconium.
In manufacturing copper sulfate, sulfuric acid and scrap copper metal are used. The
process is based on the oxidation of metal and dissolution with H2SO4 according to the
following reaction:
4Cu + O2 = 2Cu2O
Cu2O + H2SO4 = CuSO4 + H2O
2Cu2SO4 + 2H2SO4 + O2 = 4CuSO4 + 2H2O
Usually, in mineral processing applications, copper sulfate is delivered in crystal
form.
Trade name
AGRITOX®; BASICOP®; BCS COPPER FUNGICIDE®; BSC FLOWABLE®[C]; COPSIN®; CP BASIC SULFATE®; CUPROFIX®; FUNGI-SPERSE II[C]; SULTRACOB®; TNCS® 53; TRIANGLE®
Safety Profile
A human poison by ingestion. An experimental poison by ingestion, subcutaneous, parenteral, intravenous, and intraperitoneal routes. Human systemic effects by ingestion: gastritis, Qarrhea, nausea or vomiting, damage to kidney tubules, and hemolysis. Questionable carcinogen with experimental tumorigenic data. An experimental teratogen. Other experimental reproductive effects. Mutation data reported. Reacts violently with hydroxylamine, magnesium. See also COPPER COMPOUNDS and SULFATES. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of SOx
Potential Exposure
Copper sulfate is used as intermediate and wood preservative; also used in production of copper compounds; to detect and to remove trace amounts of water from alcohols and organic compounds; as a fungicide and algicide; in veterinary medicine and others.
storage
Workers should keep copper sulfate stored in a cool, dry area with suffi cient ventilation. It should be kept away from alkalis, magnesium, ammonia, acetylene, and sodium hypobromite.
Shipping
UN3288 Toxic solids, inorganic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required. UN3077 Environmentally hazardous substances, solid, n.o.s., Hazard class: 9; Labels: 9-Miscellaneous hazardous material, Technical Name Required.
Purification Methods
After adding 0.02g of KOH to a litre of nearly saturated aqueous solution of the sulfate, it is left for two weeks, then the precipitate is filtered on to a fibreglass filter with pore diameter of 5-15 microns. The filtrate is heated to 90o and allowed to evaporate until some CuSO4.5H2O crystallises out. The solution is then filtered hot and cooled rapidly to give crystals which are freed from mother liquor by filtering under suction [Geballe & Giauque J Am Chem Soc 74 3513 1952]. Alternatively crystallise the sulfate from water (0.6mL/g) between 100o and 0o. The pentahydrate is slowly efflorescent, losing 2H2O at 30o, two more H2O are lost at 110o and a white anhydrous powder (dessicant) is obtained on heating above 250o.
Incompatibilities
Aqueous solution is an acid. May form explosive materials on contact with acetylene and nitromethane. Incompatible with strong bases; hydroxylamine, magnesium; zirconium, sodium hypobromite, hydrazine.
Waste Disposal
Copper-containing soluble wastes can be concentrated through the use of ion exchange, reverse osmosis, or evaporators to the point where copper can be electrolytically removed and sent to a reclaiming firm. If recovery is not feasible, the copper can be precipitated through the use of caustics and the sludge deposited in a chemical waste landfill Add soda ash to waste CuSO4 solution; let stand 24 hours. Decant and neutralize solution before flushing to sewer. Landfill sludge.
Precautions
During handling and use of copper sulfate, students and occupational workers should wear safety glasses and should not breathe the material in powder form. Copper sulfate is an environmental pollutant and must be carefully incorporated when used in its varied applications. Workers should wear protective clothing, goggles, impermeable gloves, and rubber boots to avoid skin contact
Copper(II) sulfate Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
Preparation Products
1of8
chevron_right| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LABDHI CHEMICAL INDUSTRIES | +91-9322229293 +91-9322229293 | Mumbai, India | 21 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Vardhaman P Golechha | 9704422000 | Telangana, India | 292 | 58 | Inquiry |
| QUALIKEMS FINE CHEM PVT LTD | +911123618475 | New Delhi, India | 51 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Yogi Dye Chem Industries | +91-9821098577 +91-9821098577 | Mumbai, India | 124 | 58 | Inquiry |
| S.V ENTERPRISES | +919322701159 | Mumbai, India | 150 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Evans Fine Chem | +91-9821340302 +91-9821340302 | Maharashtra, India | 286 | 58 | Inquiry |
| UNILOSA INTERNATINAL PRIVATE LIMITED | +91-9999069917 +91-9999069917 | New Delhi, India | 152 | 58 | Inquiry |
| SAANVI CORP | +91-7208939370 +91-7208939370 | Maharashtra, India | 46 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Kronox Lab Sciences Pvt Ltd | +91-9313231074 +91-9313231074 | Gujarat, India | 240 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Dhara Industries | +91-9322395199 +91-9322395199 | Mumbai, India | 190 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Supplier | Advantage |
|---|---|
| LABDHI CHEMICAL INDUSTRIES | 58 |
| Vardhaman P Golechha | 58 |
| QUALIKEMS FINE CHEM PVT LTD | 58 |
| Yogi Dye Chem Industries | 58 |
| S.V ENTERPRISES | 58 |
| Evans Fine Chem | 58 |
| UNILOSA INTERNATINAL PRIVATE LIMITED | 58 |
| SAANVI CORP | 58 |
| Kronox Lab Sciences Pvt Ltd | 58 |
| Dhara Industries | 58 |
Related articles
- Chemical properties and color changes of copper sulfate
- In hydrated CuSO4, the water molecules surrounding the Central Metal (Cu) act as ligands, resulting in a d-d transition and, t....
- Mar 13,2024
- What is the charge of the metal ion in CuSO4?
- ?+2 Charge. The proper name for CuSO4 is copper(II) sulphate - the Roman numerals denote the oxidation state for any atom whic....
- Feb 18,2024
- Flame color of Copper sulfate and Principle of flame tests
- Copper(II) sulfate, also known as copper sulphate, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula CuSO4.
- Jan 25,2024
7758-98-7(Copper(II) sulfate)Related Search:
1of5
chevron_right




