Copper(I) chloride
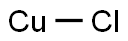
- CAS No.
- 7758-89-6
- Chemical Name:
- Copper(I) chloride
- Synonyms
- CuCl;COPPER CHLORIDE;CUPROUS CHLORIDE;COPPER(L) CHLORIDE;cooper chloride;Copper(Ⅰ)chloride;CUPROUS CHLORIDE, REAGENT (ACS)CUPROUS CHLORIDE, REAGENT (ACS)CUPROUS CHLORIDE, REAGENT (ACS)CUPROUS CHLORIDE, REAGENT (ACS);Cu-lyt;Cuproid;Nantokite
- CBNumber:
- CB7341838
- Molecular Formula:
- ClCu
- Molecular Weight:
- 99
- MOL File:
- 7758-89-6.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
- Modify Date:
- 2024/5/29 16:45:47
| Melting point | 430 °C (lit.) |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 1490 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 1.15 g/mL at 20 °C |
| vapor pressure | 1.3 mm Hg ( 546 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.93 |
| Flash point | 1490°C |
| storage temp. | Store at +5°C to +30°C. |
| solubility | 0.06 g/L (25°C) |
| form | beads |
| color | Slightly greenish-gray |
| Specific Gravity | 4.14 |
| PH | 5 (50g/l, H2O, 20℃)(slurry) |
| Water Solubility | 0.06 g/L (25 ºC) |
| Sensitive | Air & Moisture Sensitive |
| Crystal Structure | Hexagonal, Wurtzite (Zincite) Structure - Space Group P 63mc |
| Merck | 14,2660 |
| Solubility Product Constant (Ksp) | pKsp: 6.76 |
| Exposure limits |
ACGIH: TWA 1 mg/m3 NIOSH: IDLH 100 mg/m3; TWA 1 mg/m3 |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with oxidizing agents, potassium, water. Air, light and moisture sensitive. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7758-89-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Cuprous monochloride(7758-89-6) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Cuprous chloride (7758-89-6) |
| Hardness, Mohs | 2.3 |
|---|
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |    GHS05,GHS07,GHS09 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H302-H315-H318-H410 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P264-P273-P280-P301+P312-P302+P352-P305+P351+P338 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | Xn,N | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 22-50/53-51/53-36/37/38-41-37/38-38 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 26-61-60-22-39 | |||||||||
| RIDADR | UN 3082 9/PG 3 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 2 | |||||||||
| RTECS | GL6990000 | |||||||||
| F | 1-8-10 | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HS Code | 2827 39 85 | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 8 | |||||||||
| PackingGroup | III | |||||||||
| Toxicity | LD50 orally in Rabbit: 336 mg/kg | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Copper(I) chloride price More Price(29)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich | 651745 | Copper(I) chloride AnhydroBeads?, ≥99.99% trace metals basis | 7758-89-6 | 5G | ₹8876.5 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 651745 | Copper(I) chloride AnhydroBeads?, ≥99.99% trace metals basis | 7758-89-6 | 5G | ₹8876.5 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 651745 | Copper(I) chloride AnhydroBeads?, ≥99.99% trace metals basis | 7758-89-6 | 25G | ₹20091.2 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 229628 | Copper(I) chloride ≥99.995% trace metals basis | 7758-89-6 | 10G | ₹12502.88 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 61168 | Copper(I) chloride puriss. p.a., ACS reagent, ≥97.0% (RT) | 7758-89-6 | 25G | ₹2457.28 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
Copper(I) chloride Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Chemical Properties
white or pale grey powder
Physical properties
White cubic crystal which turns blue when heated at 178°C; density 4.14 g/cm3; the mineral nantokite (CuCl) has density 4.14 g/cm3, hardness 2.5 (Mohs), refractive index 1.930; melts at 430°C becoming a deep, green liquid; vaporizes around 1,400°C; vapor pressure 5 torr at 645°C and 400 torr at 1250°C; low solubility in water (decomposes partially); Ksp 1.72x10-7; insoluble in ethanol and acetone; soluble in concentrated HCl and ammonium hydroxide.The space lattice of CuCl belongs to the cubic system, and its zinc-blende structure has a lattice
constant of a=0.541 nm and Cu–Cl=0.235 nm below 407°C, and it belongs to the hexagonal
system and has a wurtzite structure at 407°C–422°C.
The reflection peaks at room temperature are positioned at λ: 58 and 65.4 mm. The transmission
peak is located at λ: 18.5 mm. The absorption spectrum near the absorption edge λ: 370.0 nm at liquid He temperature shows
many structures because of exciton absorption.
Uses
Copper(I) chloride (CuCl) or cuprous chloride is a white powder used as an absorbing agent for carbon dioxide gas in enclosed breathing areas such as space vehicles.
Uses
It is used for absorption of carbon monoxide in gas analysis. Cuprous chloride is used as a light modulator for λ: 0.43–2.5 mm.
Definition
ChEBI: An inorganic chloride of copper in which the metal is in the +1 oxidation state.
Preparation
Copper(I) chloride is prepared by reduction of copper(II) chloride in solution: 2CuCl2 + H2 2CuCl + 2HCl Alternatively, it can be prepared by boiling an acidic solution of copper(II) chloride with copper metal, which on dilution yields white CuCl: Cu + CuCl2 2CuCl Copper(I) chloride dissolved in concentrated HCl absorbs carbon monoxide under pressure forming an adduct, CuCl(CO). The complex decomposes on heating releasing CO. Copper(I) chloride is slightly soluble in water. However, in the presence of Cl- ion, it forms soluble complexes of discrete halogeno anions such as, CuCl2-, CuCl3 2-, and CuCl4 3-. Formation of complexes and organocopper derivatives as outlined below are not confined only to copper(I) chloride, but typify Cu+ in general. Reaction with ethylenediamine (en) in aqueous potassium chloride solution forms Cu(II)-ethylenediamine complex, while Cu+ ion is reduced to its metallic state: 2CuCl + 2en → [Cuen2]2+ + 2Cl- + Cu° It dissolves in acetonitrile, CH3CN forming tetrahedral complex ion [Cu(CH3CN)4]+ which can be precipitated with large anions such as ClO4 - or PF6- . Reactions with alkoxides of alkali metals produce yellow copper(I) alkoxides. For example, reaction with sodium ethoxide yield copper(I) ethoxide, a yellow compound that can be sublimed from the product mixture: CuCl + NaOC2H5 → CuOC2H5 + NaCl Copper(I) chloride forms complexes with ethylene and other alkenes in solutions that may have compositions such as [Cu(C2H4)(H2O)2]+ or [Cu(C2H4)(bipy)]+. (bipy = bipyridyl) Reactions with lithium or Grignard reagent yield alkyl or aryl copper(I) derivatives, respectively. Such organocopper compounds containing Cu-Cu bonds are formed only by Cu+ and not Cu2+ ions.
Production Methods
Cuprous chloride crystal is grown by direct deposition on the substrate from vapor (vapor phase
growth). Small, zinc-blende crystals without deformation can be obtained from solution.
Large single crystals are grown by the Czochralski method. The first grown crystal takes a
wurtzite structure, which changes to a zinc-blende structure below 407℃. It is inevitable to keep a
constant strain.
Cuprous chloride is soluble in water and ethyl alcohol is used for cutting and polishing.
General Description
The structure of copper(I) chloride is similar to zinc-blende crystal at room temperature; the structure is wurtzite at 407 °C and at higher temperatures it forms copper(I) chloride vapor as per mass spectroscopy.
Hazard
Copper(I) chloride is moderately toxic by ingestion and possibly other routes of entry into the body. The oral LD50 in mouse is reported to be 347 mg/kg; and subcutaneous LD50 in guinea pigs is 100 mg/kg.
Shipping
UN2802 Copper chloride, Hazard class: 8; Labels: 8-Corrosive material.
Purification Methods
Wash the solid with ethanol and diethyl ether, then dry it and store it in a vacuum desiccator [.sterl.f Acta Chem Scand 4 375 1950]. Alternatively, to an aqueous solution of CuCl2.2H2O is added, with stirring, an aqueous solution of anhydrous sodium sulfite. The colourless product is dried at 80o for 30minutes and stored under N2. Cu2Cl2 can be purified by zone-refining [Hall et al. J Chem Soc, Faraday Trans 1 79 343 1983]. [Glemser & Sauer in Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry (Ed. Brauer) Academic Press Vol II p 1005 1965.]
Incompatibilities
Contact with strong acids forms monovalent copper salts and toxic hydrogen chloride gas. Forms shock-sensitive and explosive compounds with potassium, sodium, sodium hypobromite, nitromethane, acetylene. Keep away from moisture and alkali metals. Attacks metals in the presence of moisture. Reacts with moist air to form cupric chloride dihydrate. May attack some metals, paints, and coatings. May be able to ignite combustible materials.
Copper(I) chloride Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
1of3
chevron_rightPreparation Products
1of8
chevron_right| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MEGHACHEM INDUSTRIES | +91 9825032614 | Ahmedabad, India | 11 | 58 | Inquiry |
| ADVENT CHEMBIO PRIVATE LIMITED | +91-9821524116 +91-9821524116 | Mumbai, India | 353 | 58 | Inquiry |
| JIVICHEM SYNTHESIS PVT LTD | +91-7028392790 +91-7028392790 | Maharashtra, India | 337 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Yogi Dye Chem Industries | +91-9821098577 +91-9821098577 | Mumbai, India | 124 | 58 | Inquiry |
| CHEMORGE JAIN | +91-9727716206 +91-9727716206 | Ahmedabad, India | 9 | 58 | Inquiry |
| JSK Chemicals | +919879767970 | Gujarat, India | 3756 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Otto Chemie Pvt Ltd | +91-2222070099 +91-2266382599 | Maharashtra, India | 429 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Kronox Lab Sciences Pvt Ltd | +91-9313231074 +91-9313231074 | Gujarat, India | 240 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Sajan Overseas Pvt Ltd | +91-9825074205 +91-9825074205 | Gujarat, India | 38 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Span Overseas | +91-9824048828 +91-9824032388 | Gujarat, India | 16 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Supplier | Advantage |
|---|---|
| MEGHACHEM INDUSTRIES | 58 |
| ADVENT CHEMBIO PRIVATE LIMITED | 58 |
| JIVICHEM SYNTHESIS PVT LTD | 58 |
| Yogi Dye Chem Industries | 58 |
| CHEMORGE JAIN | 58 |
| JSK Chemicals | 58 |
| Otto Chemie Pvt Ltd | 58 |
| Kronox Lab Sciences Pvt Ltd | 58 |
| Sajan Overseas Pvt Ltd | 58 |
| Span Overseas | 58 |
7758-89-6(Copper(I) chloride)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




