Sodium bicarbonate
- CAS No.
- 144-55-8
- Chemical Name:
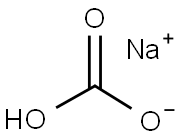
- Sodium bicarbonate
- Synonyms
- NAHCO3;SODIUM HYDROGEN CARBONATE;BAKING SODA;sodium bicarbonate solution;Sodium bicarbonate, GR,≥99.8%;BICARBONATE OF SODA;Sodium hydrocarbonate;TSQN;Sodium bicarbonate, AR,≥99.8%;Natrium Bicarbonate
- CBNumber:
- CB7492884
- Molecular Formula:
- CHNaO3
- Molecular Weight:
- 84.01
- MOL File:
- 144-55-8.mol
- Modify Date:
- 2025/4/1 13:12:09
| Melting point | >300 °C(lit.) |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 851°C |
| Density | 2.16 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| bulk density | 1000kg/m3 |
| refractive index | 1.500 |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | H2O: 1 M at 20 °C, clear, colorless |
| form | solution (7.5%) |
| color | White |
| Specific Gravity | 2.159 |
| PH Range | 7.8 - 8.2 |
| pka | (1) 6.37, (2) 10.25 (carbonic (at 25℃) |
| PH | 8.27(1 mM solution);8.22(10 mM solution);8.02(100 mM solution); |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Water Solubility | 9 g/100 mL (20 ºC) |
| Decomposition | 50 °C |
| Merck | 14,8583 |
| BRN | 4153970 |
| BCS Class | 1 |
| Stability | Stable. |
| LogP | -4.010 (est) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 144-55-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Sodium bicarbonate (144-55-8) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |  GHS07 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Warning | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H319-H303 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P264-P280i-P305+P351+P338-P337+P313 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 24/25 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 1 | |||||||||
| RTECS | VZ0950000 | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HS Code | 28363000 | |||||||||
| Hazardous Substances Data | 144-55-8(Hazardous Substances Data) | |||||||||
| Toxicity | LD50 orally in Rabbit: 4220 mg/kg | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Sodium bicarbonate price More Price(79)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | S8875 | Sodium bicarbonate ReagentPlus?, ≥99.5%, powder | 144-55-8 | 500G | ₹2316.55 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | S8875 | Sodium bicarbonate ReagentPlus?, ≥99.5%, powder | 144-55-8 | 1KG | ₹3453.18 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | S8875 | Sodium bicarbonate ReagentPlus?, ≥99.5%, powder | 144-55-8 | 2.5KG | ₹4048.55 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | S8875 | Sodium bicarbonate ReagentPlus?, ≥99.5%, powder | 144-55-8 | 5KG | ₹7815.65 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | S6014 | Sodium bicarbonate ACS reagent, ≥99.7% | 144-55-8 | 500G | ₹2435.63 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
Sodium bicarbonate Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Sodium bicarbonate, which is the compound commonly called baking soda, exists as a white,
odorless, crystalline solid. It occurs naturally as the mineral nahcolite, which derives its name
from its chemical formula by replacing the “3” in NaHCO3 with the ending “lite.” The world’s
main source of nahcolite is the Piceance Creek Basin in western Colorado, which is part of
the larger Green River formation. Sodium bicarbonate is extracted using solution mining by
pumping hot water through injection wells to dissolve the nahcolite from the Eocene beds
where it occurs 1,500 to 2,000 feet below the surface. The dissolved sodium bicarbonate is
pumped to the surface where it is treated to recover NaHCO3 from solution. Sodium bicarbonate
can also be produced from the trona deposits, which is a source of sodium carbonates
(see Sodium Carbonate).
Chemical Properties
Sodium bicarbonate, NaHC03, also known as sodium acid carbonate and baking soda, is a white water-soluble crystalline solid.It has an alkaline taste, loses carbon dioxide at 270°C (518 °F).and is used in food preparation. Sodium bicarbonate also finds use as a medicine,a butter preservative, in ceramics,and to prevent timber mold.
Physical properties
White crystalline powder or granules; monoclinic crystals; density 2.20 g/cm3; decomposes around 50°C, begins to lose carbon dioxide; converts to sodium carbonate at 100°C; soluble in water, 10g/100 mL at 20°C; slowly decomposes to CO2 and Na2CO3 in aqueous solution at ambient temperature; decomposes to Na2CO3 in boiling water; aqueous solution slightly alkaline; pH of 0.1M solution at 25°C is about 8.3; insoluble in alcohol; decomposes in acids.
Uses
sodium bicarbonate (baking soda) is an inorganic salt used as a buffering agent and a pH adjuster, it also serves as a neutralizer. It is used in skin-smoothing powders.
Definition
Baking soda: A white solid formed either by passing an excess of carbon dioxide through sodium carbonate or hydroxide solution, or by precipitation when cold concentrated solutions of sodium chloride and ammonium hydrogencarbonate are mixed. Sodium hydrogencarbonate decomposes on heating to give sodium carbonate, carbon dioxide, and water. With dilute acids, it yields carbon dioxide. It is used as a constituent of baking powder, in effervescent beverages, and in fire extinguishers. Its aqueous solutions are alkaline as a result of salt hydrolysis. Sodium hydrogencarbonate forms monoclinic crystals.
Production Methods
Sodium bicarbonate is manufactured either by passing carbon dioxide into a cold saturated solution of sodium carbonate, or by the ammonia–soda (Solvay) process, in which first ammonia and then carbon dioxide is passed into a sodium chloride solution to precipitate sodium bicarbonate while the more soluble ammonium chloride remains in solution.
General Description
Odorless white crystalline powder or lumps. Slightly alkaline (bitter) taste. pH (of freshly prepared 0.1 molar aqueous solution): 8.3 at 77°F. pH (of saturated solution): 8-9. Non-toxic.
Air & Water Reactions
Stable in dry air, but slowly decomposes in moist air. Moderately water soluble. Decomposes slowly in water (accelerated by agitation) .
Reactivity Profile
Sodium bicarbonate reacts exothermically with acids to generate non-toxic carbon dioxide gas. Decomposes when heated. Incompatible with acids, acidic salts (dopamine hydrochloride, pentazocine lactate, many alkaloidal salts) aspirin and bismuth salicylate.
Fire Hazard
Literature sources indicate that Sodium bicarbonate is noncombustible.
Pharmaceutical Applications
Sodium bicarbonate is usually administered orally in order to regulate the serum pH. Imbalances of the plasma pH can be due to problems occurring in the kidneys such as renal tubular acidosis. Within the kidneys, blood is filtered before it passes through the tubular part of the nephrons where re-absorption or secretion of important salts and others takes place. In renal tubular acidosis, the kidneys either fail to filter or secrete acid ions (H+) from the plasma (secretion takes place in the distal tubule), or to recover bicarbonate ions (HCO3-) from the filtrate (passive re-absorption takes place in the proximal tubule, active re-absorption at the distal tubule), which is necessary to balance the pH. In the view of this mode of action, the pharmaceutically active component of sodium bicarbonate is the bicarbonate anion, but the cation Na+ is responsible for solubility and compatibility.
Biological Activity
Commonly used laboratory reagent
Safety Profile
Low toxicity by ingestion. An experimental teratogen. A nuisance dust. Human systemic effects: changes in potassium levels, increased urine volume, metabolic acidosis, nausea or vomiting, respiratory changes, sodium level changes. Mutation data reported.
Safety
Sodium bicarbonate is used in a number of pharmaceutical
formulations including injections and ophthalmic, otic, topical,
and oral preparations.
Sodium bicarbonate is metabolized to the sodium cation, which
is eliminated from the body by renal excretion, and the bicarbonate
anion, which becomes part of the body’s bicarbonate store. Any
carbon dioxide formed is eliminated via the lungs. Administration
of excessive amounts of sodium bicarbonate may thus disturb the
body’s electrolyte balance, leading to metabolic alkalosis or possibly
sodium overload with potentially serious consequences. The
amount of sodium present in antacids and effervescent formulations
has been sufficient to exacerbate chronic heart failure, especially in
elderly patients.
Orally ingested sodium bicarbonate neutralizes gastric acid with
the evolution of carbon dioxide and may cause stomach cramps and
flatulence.
When used as an excipient, sodium bicarbonate is generally
regarded as an essentially nontoxic and nonirritant material.
LD50 (mouse, oral): 3.36 g/kg
LD50 (rat, oral): 4.22 g/kg
Purification Methods
Crystallise it from hot water (6mL/g). The solid should not be heated above 40o due to the formation of carbonate.
Incompatibilities
Sodium bicarbonate reacts with acids, acidic salts, and many
alkaloidal salts, with the evolution of carbon dioxide. Sodium
bicarbonate can also intensify the darkening of salicylates.
In powder mixtures, atmospheric moisture or water of crystallization
from another ingredient is sufficient for sodium bicarbonate
to react with compounds such as boric acid or alum. In liquid
mixtures containing bismuth subnitrate, sodium bicarbonate reacts
with the acid formed by hydrolysis of the bismuth salt.
In solution, sodium bicarbonate has been reported to be
incompatible with many drug substances such as ciprofloxacin, amiodarone, nicardipine, and levofloxacin.
Regulatory Status
GRAS listed. Accepted for use as a food additive in Europe. Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (injections; ophthalmic preparations; oral capsules, solutions, and tablets). Included in parenteral (intravenous infusions and injections) and nonparenteral medicines (chewing gums; ear drops; eye lotions; oral capsules, chewable tablets, effervescent powders, effervescent tablets, granules, soluble tablets, orodispersible tablets, and tablets; suppositories and suspensions) licensed in the UK.
Sodium bicarbonate Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
1of2
chevron_rightPreparation Products
1of8
chevron_right| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GLR Innovations | +91 9891111994 | New Delhi, India | 4535 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Rishi Chemical Works Pvt Ltd | +91-3322290068 +91-3322290071 | Kolkata, India | 43 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Soham Chemical Industries | +91-7016081644 +91-7016081644 | Mumbai, India | 82 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Evans Fine Chem | +91-9821340302 +91-9821340302 | Maharashtra, India | 286 | 58 | Inquiry |
| UNILOSA INTERNATINAL PRIVATE LIMITED | +91-9999069917 +91-9999069917 | New Delhi, India | 152 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Cefa-Cilinas Biotics Pvt Ltd | +91-7875033155 +91-8080701561 | Maharashtra, India | 121 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Choice Chemicals | +91-9895031268 +91-9895031268 | Kerela, India | 118 | 58 | Inquiry |
| VITRAG CHEMICALS PVT LTD | +91-7490053194 +91-7490053194 | Gujarat, India | 47 | 58 | Inquiry |
| EAGLE CHEMICAL WORKS | +91-22263303652226330365 +91-2226330365 | Maharashtra, India | 61 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Pd Navkar Bio Chem Pvt Ltd | +91-8022157444 +91-8022157444 | Karnataka, India | 49 | 58 | Inquiry |
Related articles
- What are the medicinal functions and benefits of sodium bicarbonate?
- Sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3 or baking soda, abbreviated as SB), is a weak alkaline compound (pH 8.5) and belongs to the class o....
- Jan 3,2025
- Baking Powder And Vinegar Reaction
- Mixing Baking Powder and vinegar creates a chemical reaction
- Mar 7,2024
- The Manufacturing Process and Uses of Baking Soda
- Baking soda is a white, water-soluble crystalline solid with an alkaline taste, this article will introduce its manufacturing ....
- Mar 4,2024
144-55-8(Sodium bicarbonate)Related Search:
1of5
chevron_right




