Cyanamide
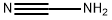
- CAS No.
- 420-04-2
- Chemical Name:
- Cyanamide
- Synonyms
- CARBODIIMIDE;HYDROGEN CYANAMIDE;H2NCN;CYANAMID;Cyanamide solution;Aminonitrile;cianamida hidrogenada;cianamida;Crystalline Cyanamide;1-(2-methoxyphenyl)-N-methylpropan-2-amine hydrochloride
- CBNumber:
- CB9256093
- Molecular Formula:
- CH2N2
- Molecular Weight:
- 42.04
- MOL File:
- 420-04-2.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
- Modify Date:
- 2024/5/23 8:52:57
| Melting point | 45-46 °C (lit.) |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 83 °C/0.5 mmHg (lit.) |
| Density | 1,282 g/cm3 |
| vapor pressure | 1Pa at 24.95℃ |
| refractive index | 1.405 |
| Flash point | >230 °F |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | ethanol: soluble10%, clear to hazy, colorless to faintly yellow |
| pka | 1.1(at 29℃) |
| form | Crystalline solid |
| Specific Gravity | 1.282 |
| Water Solubility | 775 g/L |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| Merck | 14,2684 |
| BRN | 1732569 |
| Exposure limits |
ACGIH: TWA 2 mg/m3 NIOSH: TWA 2 mg/m3 |
| Stability | Unstable - heat sensitive. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong reducing agents, bases, acids, iron and its salts, steel, brass, lead, moisture. Reacts with acids to produce very toxic gas. |
| InChIKey | XZMCDFZZKTWFGF-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| LogP | -0.72 at 20℃ |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 420-04-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Cyanamide(420-04-2) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Cyanamide (420-04-2) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |    GHS05,GHS06,GHS08 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H301+H311-H314-H317-H351-H361fd-H373-H412 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P260-P273-P280-P303+P361+P353-P304+P340+P310-P305+P351+P338 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | T | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 21-25-36/38-43 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 3-22-36/37-45-26 | |||||||||
| RIDADR | UN 2811 6.1/PG 3 | |||||||||
| OEB | B | |||||||||
| OEL | TWA: 2 mg/m3 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 2 | |||||||||
| RTECS | GS5950000 | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 8 | |||||||||
| PackingGroup | III | |||||||||
| HS Code | 29269090 | |||||||||
| Toxicity | LD50 i.p. in male mice: 200-300 mg/kg (Doull) | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Cyanamide price More Price(18)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | C87908 | Cyanamide solution 50?wt. % in H2O | 420-04-2 | 100G | ₹4135.15 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | C87908 | Cyanamide solution 50?wt. % in H2O | 420-04-2 | 250G | ₹8844.03 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | C87908 | Cyanamide solution 50?wt. % in H2O | 420-04-2 | 1KG | ₹20848.95 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 187364 | Cyanamide 99% | 420-04-2 | 5G | ₹1970.15 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich | 187364 | Cyanamide 99% | 420-04-2 | 25G | ₹4773.83 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
Cyanamide Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Cyanamide and its salts are used on various occasions, such as in chemistry, in anti-rust solutions or in drugs for treating alcoholism (Come).
Chemical Properties
Cyanamide is a combustible crystalline solid, but it is usually found as a 25% liquid solution.
Uses
In Europe, cyanamide is used as a fertilizer, weed killer,
and defoliant. In North America, these applications have
been practically discontinued. It is also used to produce
cationic starch and calcium cyanide, dicyandiamide, and
melamine. New uses include intermediates for pesticides;
detergents; medicines such as antihistamines, hypertension,
sedatives, and contraceptives; photography industry; additive
for fuels and lubricants; paper preservative; and cement
additive. Dormex is a common rest-breaking agent applied in
spring to stimulate uniform opening of buds.
Cyanamide has been tested as an effective and welltolerated
pharmacological adjunct to treat alcohol-dependent
patients. It is a potent aldehyde dehydrogenase inhibitor,
and alters cholinergic function in the frontal cortex and
hippocampus of rats exposed to ethanol.
Production Methods
The basic process for the manufacture of cyanamide comprises four steps. The first three steps produce calcium cyanamide: lime is made from high grade limestone; (2) calcium carbide is manufactured from lime and coal or coke; calcium cyanamide is produced by passing gaseous nitrogen through a bed of calcium carbide with 1% calcium fluorspar, which is heated to 1000–1100°C to start the reaction—the heat source is then removed and the reaction continues because of its strong exothermic character; and cyanamide is manufactured from calcium cyanamide by continuous carbonation in an aqueous medium.
Definition
cyanamide: 1. An inorganic saltcontaining the ion CN22-. See calciumcyanamide. 2. A colourless crystallinesolid, H2NCN, made by the actionof carbon dioxide on hotsodamide. It is a weakly acidic compound(the parent acid of cyanamidesalts) that is soluble in water andethanol. It is hydrolysed to urea inacidic solutions.
Reactions
Cyanamide reacts (1) as a base with strong acids forming salts, (2) as an acid forming metallic salts, such as calcium cyanamide CaCN2. Cyanamide is formed (1) by reaction of cyanogen chloride CN·Cl plus ammonia (ammonium chloride also formed), (2) by reaction of thiourea plus lead hydroxide (lead sulfide also formed).
General Description
Colorless deliquescent crystals. Mp: 45°C; bp: 260°C. Density: 1.282 g cm-3. Quite soluble in water (77 g / 100 g solution at 15°C). Soluble in butanol, methyl ethyl ketone, ethyl acetate, alcohols, phenols, amines, ethers. Note: The term "Cyanamide" is also used to refer to the important compound calcium Cyanamide, which is a different chemical.
Reactivity Profile
Cyanamide is the amide of cyanic acid. Non-flammable but combustible (flash point: 140°C). Decomposes on warming above 49°C. Emits toxic fumes of CN- and NOx when heated to decomposition or on contact with acids or acid fumes (Hazardous Chemicals Desk Reference, p. 353 (1987)). Contact with moisture, acids or bases may cause a violent reaction at temperatures above about 40°C. Dry solid may polymerize at temperatures above 122°C. Rapid or explosive polymerization may occur during the evaporation of aqueous solutions. Reacts explosively with strong oxidizing agents and strong reducing agents. Attacks various metals (International Chemical Safety Card).
Hazard
Strong irritant to skin and mucous membranes; avoid inhalation or ingestion.
Health Hazard
Cyanamide is an irritant of the
eyes, mucous membranes, and skin; it is an
inhibitor of aldehyde dehydrogenase and can
cause an “antabuse” effect with ethanol
ingestion.
Cyanamide is severely irritating and
caustic to the eyes, skin, and respiratory tract.
Agricultural Uses
Herbicide, Plant growth regulator: A U.S. EPA restricted Use Pesticide (RUP). Not currently approved for use in EU countries (re-submitted). Used primarily as a plant growth regulator. Cyanamide may be melted to give a dimer, dicyandiamide or cyanoguanidine. At higher temperatures it gives the trimer, melamine, a raw material for melamine-formaldehyde resins.
Trade name
DORMEX®; SKW 83010®
Contact allergens
Cyanamide and its salts are used in various occasions such as in chemistry, in antirust solutions, or in a drug (Come?) for treating alcoholism (inhibition of alcohol deshydrogenase).
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion, inhalation, and intraperitoneal routes. Moderately toxic by skin contact. Experimental reproductive effects. Combustible when exposed to heat or flame. To fight fire, use CO2, dry chemical. Thermally unstable. Contact with moisture (water), acids, or alkalies may cause a violent reaction above 40'. Concentrated aqueous solutions may undergo explosive polymerization. Mixture with 1,2 phenylenediamine salts may cause explosive polymerization. When heated to decomposition or on contact with acid or acid fumes, it emits toxic fumes of CNand NOx. See also CYANIDE and AMIDES.
Potential Exposure
Cyanamide may be melted to give a dimer, dicyandiamide or cyanoguanidine. At higher tem- peratures it gives the trimer, melamine; a raw material for melamine-form aldehyde resins.
Shipping
UN3276 Nitriles, liquid, toxic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required, Potential Inhalation Hazard (Special Provision 5).
Purification Methods
Purify it by placing ca 15g in a Soxhlet thimble and extracting exhaustively (2-3hours) with two successive portions of Et2O (400mL, saturated with H2O by shaking before use) containing two drops of 1N acetic acid. Two successive portions of Et2O are used so that the NH2CN is not heated for too long. Each extract is dried over Na2SO4 (30g), then combined and evaporated under reduced pressure. The NH2CN may be stored unchanged at 0o in Et2O solution in the presence of a trace of AcOH. Extracts from several runs may be combined and evaporated together. The residue from evaporation of an Et2O solution is a colourless viscous oil which sets to a solid and can be recrystallised from a mixture of 2 parts of *C6H6 and 1 part of Et2O. Concentrating an aqueous solution of NH2CN at high temperatures causes EXPLOSIVE polymerisation. [Kurzer & Lawson Org Synth Coll Vol IV 645 1963, Pinck & Salissbury Inorg Synth III 39 1950, Soloway & Lipschitz J Org Chem 23 613 1958.] Hygroscopic.[Beilstein 3 IV 145.]
Incompatibilities
Cyanamide may polymerize at tempera- tures above 122℃ , or on evaporation of aqueous solutions. Reacts with acids, strong oxidants, strong reducing agents such as hydrides and water, causing explosion and toxic hazard. Attacks various metals. Decomposes when heated above 49℃ C, on contact with acids, bases, 1,2-phenylene diamine salts; and moisture; producing toxic fumes includ- ing nitrogen oxides and cyanides. Nitriles may polymerize in the presence of metals and some metal compounds. They are incompatible with acids; mixing nitriles with strong oxidizing acids can lead to extremely violent reac- tions. Nitriles are generally incompatible with other oxi- dizing agents such as peroxides and epoxides. The combination of bases and nitriles can produce hydrogen cyanide. Nitriles are hydrolyzed in both aqueous acid and base to give carboxylic acids (or salts of carboxylic acids). These reactions generate heat. Peroxides convert nitriles to amides. Nitriles can react vigorously with reducing agents. Acetonitrile and propionitrile are soluble in water, but nitriles higher than propionitrile have low aqueous solubility. They are also insoluble in aqueous acids .
Waste Disposal
Add excess alkaline calcium hypochlorite with agitation. Flush to sewer after 24 hours. Cyanamide can also be destroyed in an incinerator equipped with afterburner and scrubber.
Cyanamide Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
Preparation Products
1of4
chevron_right| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANJI BIOSCIENCES | +91-9000100077 +91-9000100077 | Hyderabad, India | 430 | 58 | Inquiry |
| JSK Chemicals | +919879767970 | Gujarat, India | 3756 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Canpex Chemicals Pvt Ltd | +91-2026351200 +91-2026351200 | Maharashtra, India | 1 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Otto Chemie Pvt. Ltd. | +91 9820041841 | Mumbai, India | 5873 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Alfa Aesar | 1 800 209 7001 | Maharashtra, India | 6913 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Triveni chemicals | 08048762458 | New Delhi, India | 6093 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Vision Pharma | 08048372762Ext 760 | Mumbai, India | 27 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Sunshine Fine Chemsol India Pvt. Ltd. | 08046055302 | Pune, India | 1 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Gargi Agro Services | 08048371705Ext 992 | Maharashtra, India | 4 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Amantech Chemicals Private Limited | 07842515829 | Mumbai, India | 62 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Supplier | Advantage |
|---|---|
| ANJI BIOSCIENCES | 58 |
| JSK Chemicals | 58 |
| Canpex Chemicals Pvt Ltd | 58 |
| Otto Chemie Pvt. Ltd. | 58 |
| Alfa Aesar | 58 |
| Triveni chemicals | 58 |
| Vision Pharma | 58 |
| Sunshine Fine Chemsol India Pvt. Ltd. | 58 |
| Gargi Agro Services | 58 |
| Amantech Chemicals Private Limited | 58 |
Related articles
- Cyanamide: A Versatile Compound in Modern Chemistry
- Cyanamide, a chemical compound with the formula NH?CN, stands as a pivotal substance in organic and agricultural chemistry.
- May 23,2024
- Safety of Cyanamide
- Cyanamide is a colorless, orthorhombic, hydrophilic, crystalline solid with amild odor. It is similar to but not as toxic as c....
- Jan 13,2022
- Applications of Cyanamide
- Cyanamide as chemical substance with unique and chemically promiscuous nitrogen-carbon-nitrogen connectivity, have been common....
- Nov 21,2019
420-04-2(Cyanamide)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




