Carbofuran
- CAS No.
- 1563-66-2
- Chemical Name:
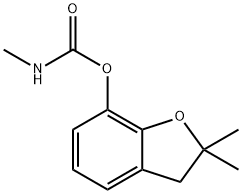
- Carbofuran
- Synonyms
- FURADAN;Nex;AGROFURAN;Furadan 3G;2,2-dimethyl-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl methylcarbamate;d1221;yalox;brifur;D 1221;oms864
- CBNumber:
- CB4322944
- Molecular Formula:
- C12H15NO3
- Molecular Weight:
- 221.25
- MOL File:
- 1563-66-2.mol
- Modify Date:
- 2024/3/14 15:18:26
| Melting point | 150-153 °C(lit.) |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 200°C |
| Density | 1.18 |
| vapor pressure | 2 x 10-5 mmHg at 33 °C (quoted, Verschueren, 1983) |
| refractive index | 1.5200 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 0-6°C |
| solubility | Methylene chloride (>200 g/L), 2-propanol (20–50 g/L) (Worthing and Hance, 1991) |
| pka | 12.28±0.46(Predicted) |
| form | Powder |
| color | White, brown |
| Water Solubility | Slightly soluble. 0.07 g/100 mL |
| Merck | 13,1813 |
| BRN | 1428746 |
| Henry's Law Constant | 3.88 (x 10-8 atm?m3/mol)at 30 °C (approximate - calculated from water solubility and vapor pressure) |
| Exposure limits | OSHA PEL: TWA 0.1 mg/m3; ACGIH TLV: TWA 0.1 mg/m3. |
| LogP | 2.320 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 1563-66-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Carbofurane(1563-66-2) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Carbofuran (1563-66-2) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |   GHS06,GHS09 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H300+H330-H410 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P260-P264-P270-P271-P273-P304+P340+P310 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | T+,N,T | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 26/28-50/53 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 36/37-45-60-61-1/2 | |||||||||
| RIDADR | UN 2811 6.1/PG 1 | |||||||||
| OEB | D | |||||||||
| OEL | TWA: 0.1 mg/m3 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 3 | |||||||||
| RTECS | FB9450000 | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 6.1(a) | |||||||||
| PackingGroup | I | |||||||||
| HS Code | 29329990 | |||||||||
| Toxicity | LD50 orally in mice: 2 mg/kg (Fahmy, 1970) | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Carbofuran price More Price(3)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 53859 | Carbofuran reference material | 1563-66-2 | 100MG | ₹13671.98 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 426008 | Carbofuran 98% | 1563-66-2 | 5G | ₹8097.1 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 32056 | Carbofuran PESTANAL?, analytical standard | 1563-66-2 | 250MG | ₹7176.98 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
Carbofuran Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Carbofuran is another systemic insecticidal/nematicidal carbamate available in granular and liquid formulations. Because use of carbofuran granules was associated with bird kills, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) prohibited the use of carbofuran granules in 1994.
Chemical Properties
Carbofuran is a broad-spectrum carbamate insecticide and nematicide. It is an odorless, white crystalline solid. On heating, it breaks down and can release toxic fumes, and irritating or poisonous gases. It is sparingly soluble in water, but very soluble in acetone, acetonitrile, benzene, and cyclohexone. The liquid formulations of carbofuran are classifi ed as RUPs because of their acute oral and inhalation toxicity to humans. Granular formulations are also classifi ed as an RUP. In fact, carbofuran was fi rst registered in the United States in 1969 and classifi ed as an RUP. Exposure to heat breaks down carbofuran, with the release of toxic fumes. Carbofuran is used for the control of soil-dwelling and foliar-feeding insects. It is also used for the control of aphids, thrips, and nematodes that attack vegetables, ornamental plants, crops of sunfl ower, potatoes, peanuts, soybeans, sugar cane, cotton, rice, and a variety of other crops
Uses
Carbofuran is used to control soil-dwelling insect pests and nematodes in a wide range of crops.
General Description
Carbofuran is an odorless white crystalline solid. Contact with skin may burn skin and eyes. When exposed to heat or flames Carbofuran may emit toxic oxides of nitrogen. Carbofuran is toxic by inhalation, skin contact, and/ or ingestion. Carbofuran is used as a pesticide.
Air & Water Reactions
Slightly soluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Carbofuran is a carbamate ester. Carbamates are chemically similar to, but more reactive than amides. Like amides they form polymers such as polyurethane resins. Carbamates are incompatible with strong acids and bases, and especially incompatible with strong reducing agents such as hydrides. Flammable gaseous hydrogen is produced by the combination of active metals or nitrides with carbamates. Strongly oxidizing acids, peroxides, and hydroperoxides are incompatible with carbamates. Carbofuran is unstable in an alkaline media. .
Fire Hazard
May release nitrogen oxides. Containers may explode in heat of fire. Avoid alkalies. Stable under neutral or acid conditions.
Agricultural Uses
Insecticide, Acaricide, Nematicide: Carbofuran is a broad-spectrum carbamate pesticide that kills insects, mites, and nematodes on contact or after ingestion. It is used against soil and foliar pests of field, fruit, vegetable, and forest crops. Carbofuran, granule form, is banned in the U.S. A U.S. EPA restricted Use Pesticide (RUP). Not approved for use in EU countries. There are 40 global suppliers.. According to the Ecological Incident Investigation System, carbofuran has been responsible for more avian deaths than any other pesticide.
Trade name
A13-27164®; AU'ULTRAMICIN®; BAY 704143®; BAY 78537®; BRIFUR®; CARBODAN®; CARBOSIP 5G®; CRISFURAN®; CURETERR®; CHINUFUR®; D 1221®; DIAFURAN®; FMC 10242®; FURACARB®; FURADAN®; FURAN®; FURODAN®; KENFURAN®; KENOFURAN®; NEX®; NIA10242; NIAGARA 10242; NIAGARA NIA-10242; PILLARFURAN®; RAMPART®; YALTOX®
Contact allergens
It is a pesticide with insecticide properties, of the carbamate group. It was implicated as a sensitizer in two farmers
Safety Profile
to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of
Potential Exposure
A potential danger to those involved in the manufacture, formulation, and application of this insecticide, acaricide, and nematocide.
Environmental Fate
Carbofuran is soluble in water and is moderately persistent in soil. Its half-life is 30–120 days. It enters surface water as a result of runoff from treated fields and enters groundwater by leaching of treated crops. If released to soil, degradation occurs by chemical hydrolysis and biodegradation. The persistence of carbofuran in the soil increases as the clay and organic matter content of the soil increase, and as the pH and moisture content of soil decrease. Chemical hydrolysis occurs more rapidly in alkaline soil as compared to neutral or acidic soils. Carbofuran is likely to leach to groundwater in soils with low organic content. Volatilization from soil is not expected to be significant, although some evaporation from plants may occur. If released to water, carbofuran degrades by hydrolysis under alkaline conditions and by biodegradation. Aquatic volatilization, adsorption, and bioconcentration are not expected to be important.
Metabolic pathway
The fate of carbofuran has been investigated in soils, plants, mammals, birds, fish and insects. Metabolic pathways include hydrolysis, oxidation (ring and N-methyl hydroxylation) and conjugation. The metabolism of carbofuran has been extensively reviewed by Schlagbauer and Schlagbauer (1972) and Kuhr and Dorough (1976). Metabolism in economic animals was reviewed by Akhtar (1985). Consequently the many primary publications are not usually cited.
Metabolism
Carbofuran (1) is degraded by hydrolysis and oxidation in soil before ultimate mineralization . The rate of hydrolysis in soils is slightly higher under flooded than under nonflooded conditions. Products depend on the soil type and the prevalence of aerobic or anaerobic conditions, and it was also reported that carbofuran did not degrade under anaerobic conditions. The products, 3-hydroxycarbofuran (2) and 3-ketocarbofuran (3), have been isolated from soil extracts after incubation with carbofuran. The phenol (7) was identified as a major product in several studies. The products are further degraded and bound to soil organic matter. Enhanced degradation may follow repeated applications of carbofuran to soils, and bacterial cultures capable of rapidly degrading carbofuran have been obtained from treated soils.
storage
Carbofuran should be stored in a cool, dry, well-ventilated place, in their original containers only. It should not be kept stored or used near heat, open flame, or hot surfaces
Shipping
UN2757 Carbamate pesticides, solid, toxic, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials. UN 2811 Toxic solids, organic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name RequiredUN2811 Toxic solids, organic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required
Incompatibilities
Alkaline substances, acid, strong oxidizers, such as perchlorates, peroxides, chlorates, nitrates, permanganates.
Waste Disposal
Alkaline hydrolysis is the recommended mode of disposal. In accordance with 40CFR165, follow recommendations for the disposal of pesticides and pesticide containers. Must be disposed properly by following package label directions or by contacting your local or federal environmental control agency, or by contacting your regional EPA office.
Precautions
During use/handling of carbofuran, workers should wear coveralls or a long-sleeved uniform, head covering, and chemical protective gloves made of materials such as rubber, neoprene, or nitrile. Occupational workers should know that areas treated with carbofuran are hazardous. The runoff of carbofuran material and the fi re control releases irritating or poisonous gases. It is advisable that workers should enter storehouses or carbofuran-treated close spaces with caution
Carbofuran Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
1of5
chevron_rightPreparation Products
1563-66-2(Carbofuran)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




