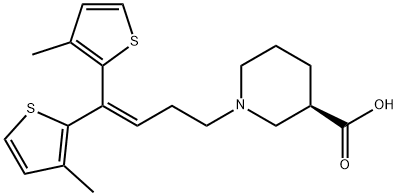
Tiagabine
- CAS No.
- 115103-54-3
- Chemical Name:
- Tiagabine
- Synonyms
- TGB;no328;Tiagabin;TIGABINE;TIAGABINE;NO-05-0328;nnc-05-0328;Tiagabine D4;NNC-05-0328:A-70569;Gabitril / NNC 05-328
- CBNumber:
- CB9761920
- Molecular Formula:
- C20H25NO2S2
- Molecular Weight:
- 375.55
- MOL File:
- 115103-54-3.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
- Modify Date:
- 2023/9/20 16:43:00
| Melting point | 192oC dec. |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 568.0±50.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.208±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | under inert gas (nitrogen or Argon) at 2-8°C |
| pka | 3.86±0.20(Predicted) |
| Water Solubility | ≥ 13.5mg/mL in Water |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 115103-54-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |  GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal word | Warning |
| Hazard statements | H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary statements | P261-P305+P351+P338 |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
| Risk Statements | 36/37/38 |
| Safety Statements | 26-37/39 |
Tiagabine Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Gabitril was launched in Denmark for use as an add-on therapy in patients refractory to other epilepsy therapies. The compound can be synthesized in five steps beginning with a bis-thiophenyl ketone derivative to produce the (R)-(-)- enantiomer. Its anti-epileptic activity resides in its potent and selective inhibition of GABA synaptosomal uptake. Tiagabine is selective for the GAT-1 GABA transporter in neurons and glia thus enhancing inhibitory GABAergic transmission. Because it has practically no effect on other uptake or receptor systems, it has a reduced potential for neurological side-effects. In particular, it does not have the benzodiazepine-like sedative effects. It is able to cross the blood brain barrier and is considered the most potent GABA uptake inhibitor known.
Chemical Properties
White to Off-White Crystalline Solid
Uses
A GABA uptake inhibitor
Definition
ChEBI: A piperidinemonocarboxylic acid that is (R)-nipecotic acid in which the hydrogen attached to the nitrogen has been replaced by a 1,1-bis(3-methyl-2-thienyl)but-1-en-4-yl group. A GABA reuptake inhibitor, it is used (generally as the hydroc loride salt) for the treatment of epilepsy.
Biological Functions
Tiagabine (Gabitril) blocks the reuptake of GABA into neurons and glia, thereby resulting in higher levels of GABA in the synaptic cleft. The ability to increase GABA concentrations is presumed to be involved in the effectiveness of tiagabine in the treatment of seizure disorders. It is primarily used in the treatment of partial complex seizures.Adverse effects of tiagabine administration include dizziness, somnolence, nervousness, nausea, and confusion.
General Description
A glance at tiagabine’s structure suggests anuptake inhibitor. Reportedly, it blocks GABA reuptake asa major mode of its anticonvulsant activity. Its use isagainst partial seizures. Inhibitors of GABA transporter-1(GAT-1 inhibitors) increase extracellular GABA concentrationin the hippocampus, striatum, and cortex, therebyprolonging the inhibitory action of GABA released synaptically.Nipecotic acid is a potent inhibitor of GABA reuptakeinto synaptosomal membranes, neurons, and glialcells. However, nipecotic acid fails to cross the blood-brainbarrier following systemic administration because of itshigh degree of ionization. Tiagabine, marketed as thesingle R(-)-enantiomer, a potent GAT-1 inhibitor structurallyrelated to nipecotic acid, has an improved ability tocross the blood-brain barrier, and it has recently receivedFood and Drug Administration (FDA) approval as anAED.It is well absorbed and readily metabolized byCYP3A4 to an inactive metabolite, 5-oxo-tiagabine (oxidationof the thiophen ring) or eliminated as glucuronide ofthe parent molecule.
Over 90% of tiagabine is metabolized by CYP3A4isozymes.The primary site of metabolic attack is the oxidationof the thiophen rings leading to 5-oxo-tiagabine thatlacks anticonvulsant activity and the glucuronidation via thecarboxylic function. Thus, the plasma concentrations oftiagabine would be greatly effected by any compound thatinduces or inhibits CYP3A4.
Mechanism of action
Tiagabine is a nipecotic acid derivative with an improved ability to cross the blood-brain barrier. It was rationally designed to be a GABA uptake inhibitor based on the fact that nipecotic acid (piperidine-3-carboxylic acid) inhibits GABA uptake by glial cells. Tiagabine binds to the GABA transporter GAT1, blocking the uptake of GABA into both neurons and glia, thus enhancing GABA-mediated inhibition. Tiagabine is presently approved for adjunct use in patients with epilepsy who are older than 12 years and have partial seizures not controlled by first-line drugs.
Pharmacokinetics
Tiagabine is well absorbed, with an oral bioavailability of 90 to 95%. It displays linear pharmacokinetics, with a plasma half-life of 5 to 8 hours, necessitating a multiple daily dosing regimen. It also is highly protein bound (96%). The major pathway of metabolism for tiagabine is oxidation by CYP3A4, followed by glucuronidation. Its pharmacokinetics are altered by the coadministration of enzyme-inducing AEDs, even though tiagabine does not appear to induce or inhibit hepatic microsomal metabolizing enzymes.
Side effects
Side effects are more common with tiagabine than with other adjunct drugs and most often involve the CNS. They include
somnolence, headache, dizziness, tremor, abnormal thinking, depression, and psychosis. Furthermore, recent reports have
implicated tiagabine in the development of nonconvulsive status epilepticus. There is an increased risk of seizure in
patients being treated for off-label psychiatric indications. Tiagabine may interfere with visual color perception.
Tiagabine does not affect the hepatic metabolism of other AEDs, but its half-life is decreased by enzyme-inducing AEDs, such
as CBZ, phenytoin, and barbiturates. Other CYP3A4-inducing drugs may act similarly. Valproate decreases the protein binding
of tiagabine. increasing its plasma concentration in these patients.
Hepatic disease causes decreased clearance of tiagabine, and a dose reduction may be required. Renal disease does not
affect elimination.
Tiagabine Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
1of2
chevron_rightPreparation Products
| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SMS Lifesciences India Ltd (MAHI Drugs Pvt Ltd) | +91-40-66288888 +91-8374455507 | Telangana, India | 23 | 58 | Inquiry |
| CLEARSYNTH LABS LTD. | +91-22-45045900 | Hyderabad, India | 6351 | 58 | Inquiry |
| SynZeal Research Pvt Ltd | +1 226-802-2078 | Gujarat, India | 6522 | 58 | Inquiry |
| CONIER CHEM AND PHARMA LIMITED | +8618523575427 | China | 49392 | 58 | Inquiry |
| career henan chemical co | +86-0371-86658258 +8613203830695 | China | 29825 | 58 | Inquiry |
| TargetMol Chemicals Inc. | +1-781-999-5354 +1-00000000000 | United States | 19892 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Hefei TNJ Chemical Industry Co.,Ltd. | +86-0551-65418684 +8618949823763 | China | 25363 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Hangzhou MolCore BioPharmatech Co.,Ltd. | +86-057181025280; +8617767106207 | China | 49739 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Wuhan Topule Biopharmaceutical Co., Ltd | +8618327326525 | China | 8474 | 58 | Inquiry |
| LEAPCHEM CO., LTD. | +86-852-30606658 | China | 43348 | 58 | Inquiry |





